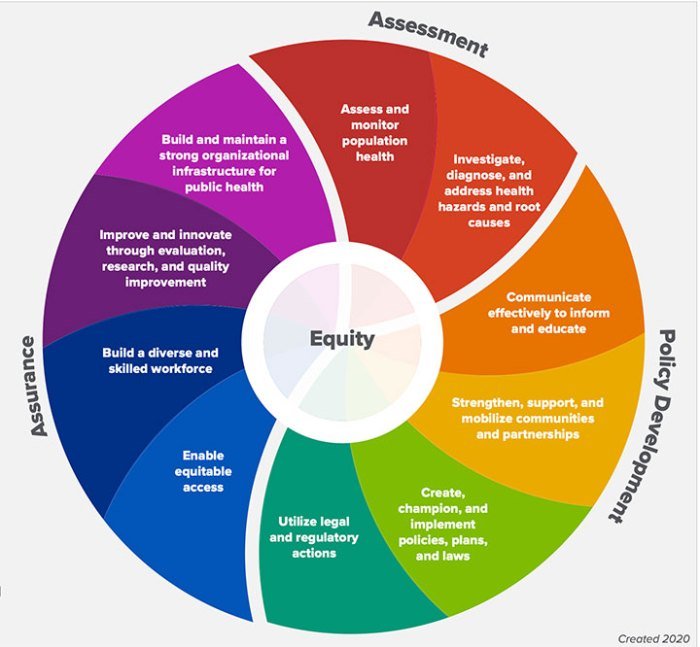
The 10 essential services of public health serve as the bedrock of a healthy society, encompassing a comprehensive approach to promoting well-being and preventing disease. These services address a wide range of public health concerns, from infectious disease control and environmental health to mental health and injury prevention.
By understanding and implementing these services, communities can work towards a future where health is not just a privilege but a fundamental right for all.
Each service plays a crucial role in safeguarding the health of individuals and communities. Public health surveillance helps identify and track health trends, allowing for targeted interventions. Health promotion and education empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health, while disease prevention and control strategies aim to reduce the incidence and spread of illness.
Environmental health ensures a safe and healthy environment for all, while maternal and child health services focus on providing essential care for mothers and children. Nutrition and food safety programs promote healthy eating habits and ensure access to safe and nutritious food.
Mental health services address the growing mental health needs of the population, and injury prevention and control programs work to reduce the incidence and severity of injuries. Finally, emergency preparedness and response ensure that communities are prepared to respond effectively to public health emergencies.
Public Health Surveillance
Public health surveillance is a crucial component of protecting and improving public health. It involves the ongoing systematic collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health data to monitor health events, identify trends, and guide public health actions.
Importance of Public Health Surveillance
Public health surveillance plays a vital role in identifying and tracking health trends, enabling timely and effective interventions to prevent and control disease outbreaks and other public health threats. It provides insights into the health status of a population, allowing public health professionals to:
- Identify emerging health threats: Surveillance systems can detect changes in disease patterns, such as increases in cases or geographic spread, alerting authorities to potential outbreaks or emerging diseases.
- Monitor disease trends: By tracking disease incidence and prevalence over time, surveillance can reveal patterns and trends, helping to understand the impact of interventions and identify areas for improvement.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of public health programs: Surveillance data can be used to assess the effectiveness of interventions, such as vaccination programs or public health campaigns, in reducing disease incidence and improving health outcomes.
- Allocate resources efficiently: By identifying areas with high disease burden or specific health needs, surveillance helps prioritize resource allocation and target interventions effectively.
Data Sources for Public Health Surveillance
Public health surveillance relies on a wide range of data sources, each providing valuable information about different aspects of health. These sources include:
- Vital statistics: Birth, death, and marriage records provide information on population demographics and mortality trends.
- Disease reporting: Healthcare providers are mandated to report cases of notifiable diseases, such as measles, tuberculosis, and HIV, to public health authorities.
- Laboratory data: Results from laboratory tests, such as blood cultures and antibiotic susceptibility testing, can be used to track the spread of infections and identify emerging antimicrobial resistance.
- Hospital discharge data: Information on hospital admissions and diagnoses provides insights into disease burden and health service utilization.
- Surveys: Regular surveys, such as the National Health Interview Survey, collect data on health status, health behaviors, and access to healthcare.
- Sentinel surveillance: This involves monitoring specific populations or locations to detect early signs of disease outbreaks or other health events.
- Syndromic surveillance: This uses data on symptoms or syndromes reported to healthcare providers or emergency departments to identify potential outbreaks or disease clusters.
Role of Surveillance in Disease Prevention and Control
Public health surveillance plays a crucial role in disease prevention and control by providing essential information to guide public health interventions. Surveillance data helps:
- Identify high-risk populations: Surveillance data can identify populations at increased risk of disease, allowing for targeted interventions and prevention strategies.
- Develop and implement effective control measures: Surveillance data informs the development and implementation of effective control measures, such as vaccination programs, quarantine measures, or public health campaigns.
- Monitor the effectiveness of interventions: Surveillance data allows for ongoing monitoring of the effectiveness of interventions and adjustments as needed.
- Allocate resources efficiently: Surveillance data helps prioritize resource allocation to address the most pressing health threats and ensure efficient use of public health resources.
Health Promotion and Education: 10 Essential Services Of Public Health
Health promotion and education are essential components of public health, working together to empower individuals and communities to make informed decisions about their well-being. They strive to create environments that support healthy choices and reduce health disparities.
Strategies for Promoting Healthy Behaviors and Lifestyles
Effective health promotion strategies aim to influence individual behavior and create supportive environments. These strategies encompass a range of approaches, including:
- Education and Information Dissemination:Providing accurate and accessible information about health risks and benefits of healthy behaviors through various channels, such as public service announcements, health campaigns, educational materials, and community workshops.
- Skill-Building and Behavioral Change Programs:Equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge to adopt and maintain healthy behaviors. This can include programs focusing on stress management, nutrition education, physical activity promotion, smoking cessation, and alcohol misuse prevention.
- Policy and Environmental Change:Advocating for policies and environmental changes that support healthy choices, such as smoke-free environments, increased access to healthy foods, and safe spaces for physical activity.
- Community Mobilization:Engaging community members in planning, implementing, and evaluating health promotion initiatives, ensuring they address local needs and priorities.
- Social Marketing:Utilizing marketing principles to promote healthy behaviors, using persuasive messaging, targeted communication channels, and community partnerships.
Importance of Health Education in Empowering Individuals
Health education empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being by:
- Increasing Health Literacy:Enhancing individuals’ ability to understand and use health information, enabling them to navigate the healthcare system effectively and make informed decisions about their health.
- Promoting Self-Efficacy:Building individuals’ confidence in their ability to make healthy choices and manage their health, fostering a sense of control over their well-being.
- Encouraging Healthy Behaviors:Providing individuals with the knowledge and skills to adopt and maintain healthy behaviors, leading to improved health outcomes and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
- Fostering Healthy Lifestyles:Promoting holistic well-being by addressing the interconnectedness of physical, mental, and social health, encouraging individuals to adopt a comprehensive approach to health.
Health Education Campaign Targeting a Specific Population Group
Imagine a health education campaign targeting adolescents to reduce the prevalence of unhealthy eating habits. This campaign would focus on:
- Target Audience:Adolescents aged 13-18 years, focusing on their specific needs and interests.
- Campaign Message:“Fuel Your Body, Fuel Your Future” – emphasizing the connection between healthy eating and optimal physical and mental performance, particularly relevant to adolescents’ active lifestyles.
- Communication Channels:Utilizing social media platforms popular among adolescents, engaging influencers, partnering with schools, and organizing interactive workshops and cooking demonstrations.
- Campaign Content:Providing practical information on balanced nutrition, portion control, healthy snack choices, and the benefits of cooking at home. Utilizing interactive tools, quizzes, and testimonials from peers to engage the target audience.
- Evaluation:Monitoring campaign reach, engagement, and impact on adolescents’ dietary behaviors through surveys, focus groups, and tracking social media engagement.
Disease Prevention and Control
Public health efforts aimed at preventing and controlling diseases are crucial for safeguarding the well-being of populations. By implementing comprehensive strategies, we can effectively reduce the incidence and spread of infectious diseases, minimize their impact on individuals and communities, and promote overall health.
Key Strategies for Preventing and Controlling Infectious Diseases
Disease prevention and control involve a multifaceted approach that encompasses various strategies to interrupt the chain of infection and reduce disease transmission. Here are some key strategies:
- Vaccination:Vaccination is a cornerstone of infectious disease prevention. By introducing weakened or inactive forms of pathogens into the body, vaccines stimulate the immune system to develop immunity against specific diseases. This helps to protect individuals and communities from contracting and spreading these diseases.
- Antimicrobial Stewardship:Antimicrobial stewardship programs aim to optimize the use of antibiotics and other antimicrobials to prevent the development of antimicrobial resistance. This involves promoting appropriate prescribing practices, educating healthcare providers and patients, and monitoring antimicrobial use patterns.
- Environmental Health Interventions:Addressing environmental factors that contribute to disease transmission is essential for prevention. This includes ensuring access to safe drinking water, promoting proper sanitation and hygiene practices, and controlling vectors such as mosquitoes that transmit diseases.
- Surveillance and Outbreak Response:Continuous surveillance systems monitor disease trends and identify outbreaks promptly. This allows for rapid response efforts, including case investigation, contact tracing, and implementation of control measures to prevent further spread.
- Public Health Education and Communication:Educating the public about infectious diseases, their modes of transmission, and preventive measures is crucial for promoting healthy behaviors. Public health campaigns and communication strategies can empower individuals to take proactive steps to protect themselves and others.
The Role of Immunization in Disease Prevention
Immunization is a highly effective public health intervention that has significantly reduced the incidence and impact of many infectious diseases. By introducing weakened or inactive forms of pathogens into the body, vaccines stimulate the immune system to develop immunity against specific diseases.
This protection not only benefits the individual but also contributes to herd immunity, where a large proportion of the population is immune, making it difficult for diseases to spread.
“Immunization is one of the most cost-effective public health interventions available, saving millions of lives every year.”
World Health Organization
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment in Controlling Disease Outbreaks
Early detection and treatment of infectious diseases are critical for controlling outbreaks and preventing further spread. Prompt identification of cases allows for timely isolation of infected individuals, contact tracing to identify and monitor potential contacts, and implementation of appropriate treatment and control measures.
This helps to minimize the impact of outbreaks, reduce morbidity and mortality, and prevent widespread transmission.
Environmental Health
The environment plays a crucial role in shaping public health. From the air we breathe to the water we drink, environmental factors have a significant impact on our overall well-being. Environmental health focuses on preventing disease and promoting health through the control of environmental factors.
Environmental Factors and Public Health
Environmental factors can have both positive and negative impacts on public health. Positive factors include access to clean air, safe water, and green spaces, which contribute to physical and mental well-being. However, negative environmental factors, such as air and water pollution, exposure to hazardous substances, and climate change, pose serious threats to public health.
Role of Public Health in Ensuring Safe Drinking Water and Air Quality
Public health plays a vital role in ensuring safe drinking water and air quality. This involves monitoring water sources, implementing water treatment processes, and setting air quality standards. Public health agencies also work to educate the public about the importance of safe water and air quality and to promote behaviors that reduce environmental pollution.
From promoting healthy lifestyles to preventing disease outbreaks, the 10 essential services of public health are crucial for ensuring a thriving community. A key component of this involves access to safe and effective exercise facilities, like those offered at old orchard lifetime fitness , which can empower individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
These services, alongside others like environmental health protection and health education, play a vital role in creating a healthier society for everyone.
Environmental Health Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
Environmental health hazards are factors in the environment that can cause harm to human health. Some common environmental health hazards include:
- Air pollution: Air pollution can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Mitigation strategies include reducing emissions from vehicles and industries, promoting clean energy sources, and encouraging public transportation.
- Water pollution: Water pollution can contaminate drinking water and harm aquatic life. Mitigation strategies include reducing industrial and agricultural runoff, treating wastewater, and protecting water sources from contamination.
- Exposure to hazardous substances: Exposure to hazardous substances, such as pesticides, lead, and asbestos, can cause various health problems. Mitigation strategies include regulating the use and disposal of hazardous substances, providing education and training on safe handling practices, and implementing workplace safety measures.
- Climate change: Climate change can exacerbate existing environmental health hazards, such as air pollution, heat waves, and extreme weather events. Mitigation strategies include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adapting to the effects of climate change, and promoting sustainable practices.
Maternal and Child Health
Maternal and child health is a crucial aspect of public health, focusing on the well-being of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the early years of a child’s life. This area encompasses a range of services and interventions aimed at ensuring healthy pregnancies, safe deliveries, and optimal child development.
Importance of Prenatal Care and Postpartum Support
Prenatal care is essential for the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Regular prenatal checkups allow healthcare providers to monitor the mother’s health, identify and manage potential risks, and provide education and support.
Prenatal care can help prevent complications during pregnancy and childbirth, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth.
Postpartum support is equally important, as it helps mothers adjust to motherhood, manage physical and emotional changes, and address any challenges they may face.
Public Health’s Role in Reducing Infant Mortality Rates
Public health plays a vital role in reducing infant mortality rates, which is defined as the number of deaths of infants under one year of age per 1,000 live births.
The leading causes of infant mortality include birth defects, premature birth, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Public health initiatives to reduce infant mortality rates include:
- Promoting breastfeeding
- Providing access to safe and affordable prenatal care
- Educating parents about safe sleep practices
- Implementing programs to reduce maternal smoking and substance abuse
Strategies for Promoting Healthy Child Development
Healthy child development encompasses physical, cognitive, social, and emotional growth. Public health strategies to promote healthy child development include:
- Providing early childhood education programs
- Encouraging regular physical activity and healthy eating habits
- Promoting safe and nurturing environments for children
- Providing access to mental health services for children and families
Nutrition and Food Safety
Nutrition and food safety are essential components of public health, playing a vital role in promoting well-being and preventing diseases. A balanced diet provides the body with the necessary nutrients for growth, development, and optimal functioning, while food safety measures ensure that food is safe to consume and free from harmful contaminants.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases. It involves consuming a variety of foods from all food groups in appropriate proportions to meet the body’s nutritional needs.
- Carbohydratesprovide energy for the body. They should be primarily from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, rather than refined grains and sugary drinks.
- Proteinsare essential for building and repairing tissues, as well as producing enzymes and hormones. Good sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu.
- Fatsare necessary for energy storage, hormone production, and cell function. Healthy fats come from sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
- Vitamins and Mineralsare vital for various bodily functions, including immune system support, bone health, and energy metabolism. They can be obtained from a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Public Health Role in Food Safety
Public health agencies play a crucial role in ensuring food safety and quality through various measures:
- Food Safety Regulations:Establishing and enforcing regulations for food production, processing, storage, and distribution to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Inspection and Monitoring:Conducting inspections of food establishments to ensure compliance with safety standards and identifying potential hazards.
- Outbreak Investigation:Investigating foodborne outbreaks to determine the source of contamination and implement corrective actions.
- Public Education and Awareness:Educating the public about food safety practices, such as proper handwashing, cooking temperatures, and food storage techniques.
Healthy Eating Habits for Different Age Groups, 10 essential services of public health
Dietary needs vary across different age groups. Public health professionals recommend age-appropriate dietary guidelines to promote optimal health and development:
- Infants and Toddlers (0-2 years):Breastfeeding is recommended for the first six months of life, followed by the introduction of solid foods alongside breast milk. It’s crucial to choose nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while avoiding sugary drinks, processed foods, and potential allergens.
- Children (2-5 years):Children at this age need a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods from all food groups. Encourage healthy snacking options, limit sugary drinks and processed foods, and involve children in meal preparation to promote healthy eating habits.
- School-Aged Children (6-13 years):This is a critical period for establishing healthy eating patterns. Encourage regular meals and snacks, promote physical activity, and limit unhealthy food choices. Encourage consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Adolescents (14-18 years):Adolescents require increased nutrient intake due to rapid growth and development. Focus on providing a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy products. Encourage healthy snacking options and discourage unhealthy food choices.
- Adults (19-64 years):Adults need to maintain a balanced diet to support overall health and prevent chronic diseases. Emphasize consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy products. Limit saturated and trans fats, added sugars, and sodium intake.
- Older Adults (65+ years):Older adults may experience changes in appetite and metabolism. Encourage consumption of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. Ensure adequate hydration and consider vitamin and mineral supplements if needed.
Mental Health
Mental health is an essential aspect of overall well-being, encompassing our emotional, psychological, and social health. It influences how we think, feel, and behave, impacting our ability to cope with life’s challenges, build relationships, and contribute to our communities. Just like physical health, mental health requires attention and care to thrive.
The Importance of Mental Health Services
Mental health services play a crucial role in promoting well-being by providing individuals with the support they need to manage mental health conditions and live fulfilling lives. These services offer a range of interventions, including:
- Diagnosis and Assessment:Mental health professionals conduct thorough evaluations to identify and diagnose mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or bipolar disorder. Accurate diagnosis is essential for tailoring appropriate treatment plans.
- Therapy and Counseling:Psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT), helps individuals develop coping mechanisms, manage symptoms, and improve their overall mental well-being.
- Medication Management:For some conditions, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve overall functioning. Mental health professionals work closely with individuals to monitor medication effectiveness and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Crisis Intervention:Mental health services provide immediate support during times of crisis, such as suicidal thoughts or severe emotional distress. Crisis intervention teams offer guidance, resources, and a safe space for individuals to process their experiences.
- Prevention and Early Intervention:Mental health services also focus on promoting mental well-being and preventing the development of mental health conditions through initiatives like stress management workshops, mindfulness programs, and early intervention programs for at-risk individuals.
Reducing Stigma Associated with Mental Health Conditions
Stigma surrounding mental health can be a significant barrier to seeking help. It often leads to shame, isolation, and reluctance to disclose mental health struggles. To reduce stigma, public health initiatives can:
- Promote Open Dialogue:Encouraging open conversations about mental health normalizes these experiences and helps dismantle the stigma associated with seeking help. Public awareness campaigns, educational programs, and community events can foster dialogue and create a more supportive environment.
- Share Personal Stories:Sharing personal experiences with mental health conditions can help break down stereotypes and show that mental health is a shared human experience. Public figures, celebrities, and everyday individuals can play a role in destigmatizing mental health by sharing their stories.
- Emphasize Mental Health as a Part of Overall Well-being:Integrating mental health into broader discussions about health and well-being helps to normalize mental health conditions and reduce the perception of them as separate or distinct from physical health.
- Challenge Misconceptions:Public health initiatives can address common misconceptions about mental health conditions, such as the belief that they are a sign of weakness or that individuals with mental health conditions are dangerous. Educating the public about the realities of mental health can dispel these myths and promote understanding.
Mental Health Awareness Campaign for a Specific Community
Designing a mental health awareness campaign requires understanding the specific needs and challenges of the target community. For example, a campaign aimed at college students might focus on:
- Stress Management Techniques:College students often face significant academic and social pressures, leading to increased stress levels. The campaign could provide information and resources on stress management techniques, such as mindfulness exercises, time management strategies, and healthy coping mechanisms.
- Mental Health Resources on Campus:The campaign could highlight the availability of mental health resources on campus, including counseling services, support groups, and mental health hotlines. This information could be disseminated through flyers, social media, and campus events.
- Peer Support Programs:Peer support programs can provide a safe and confidential space for students to connect with others who understand their experiences and offer support. The campaign could promote existing peer support programs or encourage the development of new ones.
- Open Dialogue and Destigmatization:The campaign could use social media and campus events to foster open dialogue about mental health and challenge stigma. Student testimonials, guest speakers, and interactive workshops could be incorporated to engage students in meaningful conversations.
Injury Prevention and Control
Injuries are a significant public health concern, leading to substantial morbidity, mortality, and economic burden globally. Public health plays a crucial role in addressing this issue by implementing effective injury prevention strategies.
Types of Injuries and Contributing Factors
Injuries encompass a wide range of events that can cause harm to individuals, ranging from minor cuts and bruises to severe disabilities and fatalities. The most common types of injuries include:
- Unintentional Injuries:These are the most prevalent type of injury, accounting for the majority of injury-related deaths and disabilities. Unintentional injuries include falls, motor vehicle crashes, poisonings, drownings, fires, and suffocation.
- Intentional Injuries:These injuries result from acts of violence, such as assault, homicide, and suicide.
- Work-Related Injuries:These injuries occur in the workplace and can result from falls, machinery accidents, and exposure to hazardous substances.
Several factors contribute to the occurrence of injuries, including:
- Environmental Factors:Physical hazards in the environment, such as unsafe roads, poorly maintained buildings, and lack of safety equipment, can increase the risk of injuries.
- Behavioral Factors:Risky behaviors, such as driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs, not wearing seatbelts, and engaging in unsafe activities, contribute significantly to injuries.
- Social Factors:Factors such as poverty, lack of education, and access to healthcare can increase the vulnerability of individuals to injuries.
- Biological Factors:Age, gender, and underlying health conditions can also influence the risk of injury.
Public Health Role in Injury Prevention
Public health plays a vital role in implementing effective injury prevention strategies. This involves:
- Surveillance and Data Collection:Public health agencies monitor injury trends, identify high-risk populations, and track the effectiveness of prevention programs.
- Policy Development and Implementation:Public health professionals work with policymakers to develop and implement regulations and laws aimed at reducing injuries. Examples include laws requiring seatbelt use, helmet use for cyclists and motorcyclists, and restrictions on alcohol sales to minors.
- Education and Outreach:Public health agencies conduct public awareness campaigns to educate the public about injury risks, prevention strategies, and the importance of safe behaviors.
- Community-Based Interventions:Public health programs work with communities to address local injury risks and develop tailored prevention strategies. This may include partnerships with schools, workplaces, and community organizations.
- Research and Evaluation:Public health agencies conduct research to evaluate the effectiveness of existing prevention programs and develop new interventions.
Examples of Successful Injury Prevention Programs
Numerous successful injury prevention programs have been implemented globally, demonstrating the effectiveness of public health interventions.
- Child Safety Seat Programs:These programs promote the use of child safety seats, which have significantly reduced the number of fatalities and injuries among children in motor vehicle crashes.
- Drunk Driving Prevention Programs:Campaigns targeting drunk driving have been successful in reducing alcohol-related traffic fatalities. These programs often involve public awareness campaigns, enforcement of drunk driving laws, and alternative transportation options.
- Helmet Use Laws:Laws requiring helmet use for cyclists and motorcyclists have been effective in reducing head injuries associated with these activities.
- Fall Prevention Programs:Programs aimed at preventing falls among older adults have been successful in reducing hospitalizations and other fall-related injuries. These programs often focus on home safety assessments, exercise programs, and medication reviews.
Emergency Preparedness and Response

Emergency preparedness is a crucial aspect of public health, as it involves proactive measures to anticipate, plan for, and respond to public health emergencies. This includes the development of strategies, policies, and plans to minimize the impact of these events on the population’s health and well-being.
The Importance of Emergency Preparedness in Public Health
Emergency preparedness in public health is essential for several reasons:* Protecting the Population:By anticipating potential emergencies and developing response plans, public health authorities can safeguard the health and well-being of the population during and after an event.
Minimizing Health Impacts
Proactive measures can reduce the severity and duration of health impacts, including injuries, illnesses, and deaths.
Ensuring Efficient Response
From disease prevention and health promotion to access to quality healthcare, the 10 essential services of public health ensure a healthy community. While we often think of public health in terms of traditional services, it also extends to promoting healthy habits, including those related to beauty and self-care.
The beauty master approach, which emphasizes natural beauty and healthy practices, aligns well with this aspect of public health, encouraging individuals to make informed choices about their well-being.
Preparedness plans streamline the response process, enabling coordinated efforts between different agencies and organizations to effectively address the emergency.
Building Resilience
Preparedness initiatives enhance the community’s resilience to future emergencies by fostering a culture of preparedness and empowering individuals to take protective actions.
The Role of Public Health in Coordinating Emergency Response Efforts
Public health plays a critical role in coordinating emergency response efforts, ensuring a coordinated and effective response to public health emergencies. This involves:* Leading and Coordinating:Public health authorities are responsible for leading and coordinating emergency response activities, bringing together various agencies and organizations to ensure a unified and efficient response.
Assessing and Monitoring
Public health professionals conduct assessments to determine the nature and extent of the emergency, monitor the situation, and track the effectiveness of response efforts.
Communicating Information
Public health plays a crucial role in communicating information about the emergency to the public, providing updates, and disseminating guidance on protective measures.
Providing Resources
Public health agencies provide essential resources to support emergency response efforts, such as medical supplies, vaccines, and trained personnel.
Developing a Community Emergency Response Plan
Developing a community emergency response plan is essential for ensuring an effective response to a public health emergency. The plan should Artikel the steps to be taken in the event of an emergency, including:* Identifying Potential Threats:Conduct a thorough assessment to identify potential public health emergencies that could affect the community, such as natural disasters, disease outbreaks, or technological incidents.
Establishing Communication Systems
Establish robust communication systems to ensure effective communication between emergency responders, community members, and other stakeholders.
Developing Evacuation Plans
Develop comprehensive evacuation plans, including designated evacuation routes, shelters, and procedures for evacuating vulnerable populations.
Training and Drills
Conduct regular training and drills to ensure that emergency responders and community members are familiar with their roles and responsibilities.
Public health is a multifaceted field that focuses on promoting health and well-being for entire communities. One of the 10 essential services of public health is to ensure access to quality health services, which can include promoting physical activity and healthy lifestyles.
To get a sense of how one popular fitness program, Orangetheory Fitness, stacks up in terms of effectiveness and user experience, you can check out reviews orangetheory fitness. Ultimately, the goal is to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and fitness, contributing to the overall health of the community.
Maintaining Emergency Supplies
Ensure the availability of essential emergency supplies, such as food, water, medicine, and medical equipment.
Health Policy and Advocacy
Public health professionals play a vital role in shaping health policy, advocating for health equity, and ensuring access to quality healthcare for all. They use their expertise to inform policy decisions, identify gaps in the system, and advocate for solutions that improve population health.
The Role of Public Health in Shaping Health Policy
Public health professionals contribute to health policy by conducting research, analyzing data, and providing evidence-based recommendations to policymakers. They work to ensure that policies are aligned with public health principles, promote health equity, and address the social determinants of health.
Advocating for Health Equity and Access to Care
Health equity is a fundamental principle of public health. It means that everyone has a fair and just opportunity to be as healthy as possible, regardless of their race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, gender, sexual orientation, or disability. Public health advocates work to eliminate health disparities and ensure that all individuals have access to quality healthcare, regardless of their circumstances.
Key Policy Issues Affecting Public Health
- Healthcare Access and Affordability:Public health advocates work to ensure that all individuals have access to affordable and comprehensive healthcare services. This includes advocating for policies that expand health insurance coverage, reduce out-of-pocket costs, and improve access to primary care and preventive services.
- Social Determinants of Health:Public health professionals recognize that factors such as poverty, education, housing, and environmental conditions significantly impact health outcomes. They advocate for policies that address these social determinants of health, such as investments in affordable housing, quality education, and job training programs.
- Environmental Health:Public health advocates work to protect the environment and ensure that communities have access to clean air, water, and food. This includes advocating for policies that reduce pollution, promote sustainable practices, and ensure safe food handling and distribution.
- Tobacco Control:Public health professionals advocate for policies that reduce tobacco use and its harmful effects. This includes supporting measures such as increased tobacco taxes, smoke-free environments, and cessation programs.
- Injury Prevention:Public health professionals advocate for policies that prevent injuries, such as traffic safety laws, gun safety regulations, and measures to reduce falls and other preventable injuries.
- Mental Health:Public health advocates work to reduce the stigma surrounding mental health and ensure that individuals have access to quality mental health services. This includes advocating for policies that expand access to mental health care, provide training for primary care providers to address mental health concerns, and promote mental health awareness.
- Substance Abuse:Public health professionals advocate for policies that prevent and treat substance abuse, including policies that reduce access to opioids, promote harm reduction strategies, and provide access to addiction treatment.
Wrap-Up
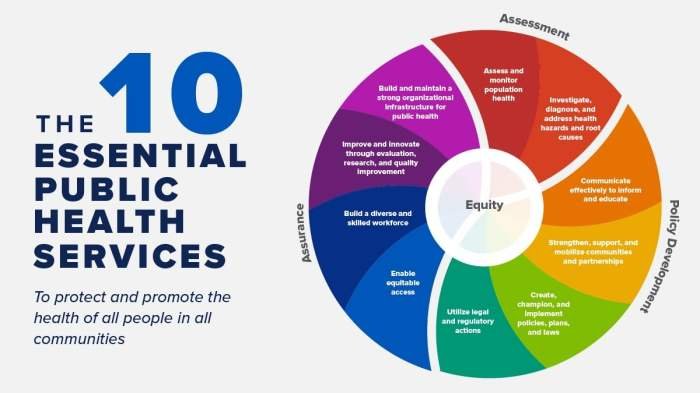
Together, the 10 essential services of public health represent a comprehensive and collaborative approach to building a healthier future. By working together, individuals, communities, and governments can create a world where everyone has the opportunity to live a long and healthy life.
Essential FAQs
What are the 10 essential services of public health?
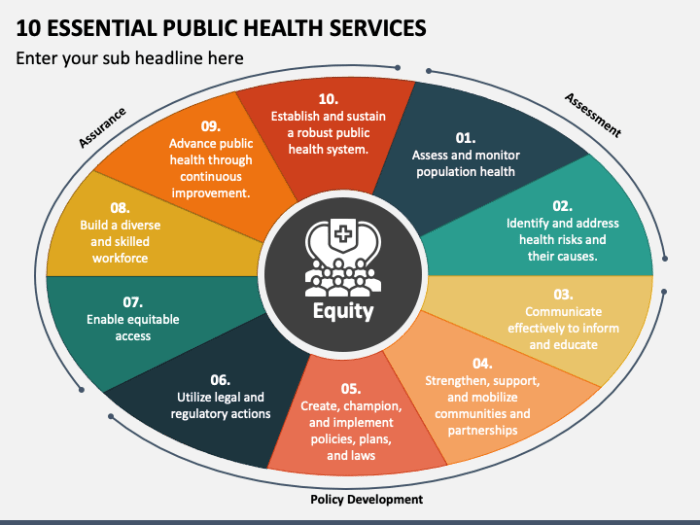
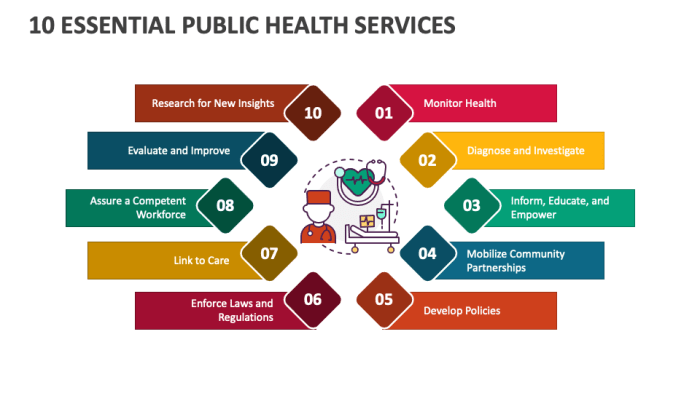
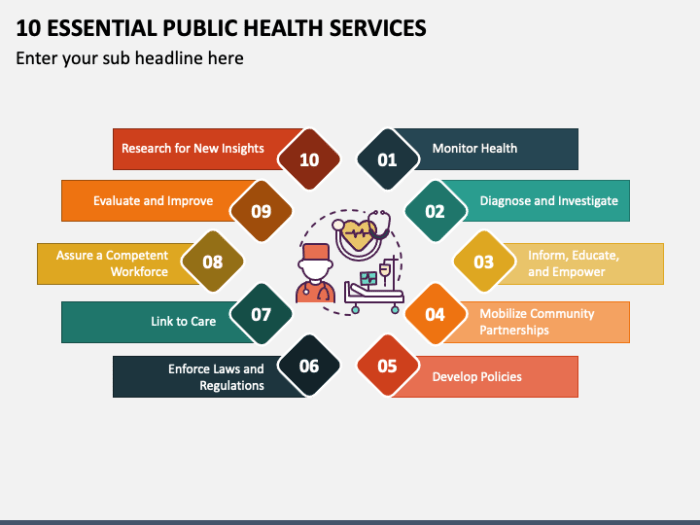
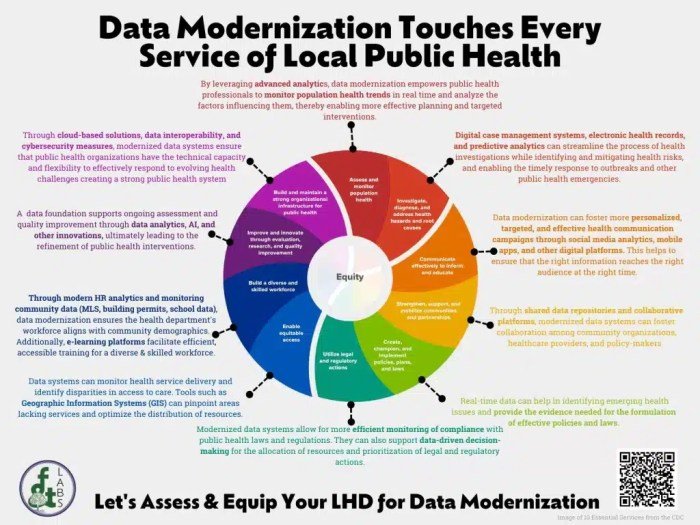
The 10 essential services of public health are: Public Health Surveillance, Health Promotion and Education, Disease Prevention and Control, Environmental Health, Maternal and Child Health, Nutrition and Food Safety, Mental Health, Injury Prevention and Control, Emergency Preparedness and Response, and Health Policy and Advocacy.
Why are the 10 essential services of public health important?
These services are essential for protecting and promoting the health of individuals and communities. They help to prevent disease, promote healthy behaviors, and ensure access to essential health services.
How can I get involved in public health?
There are many ways to get involved in public health. You can volunteer at a local health organization, advocate for health policy changes, or simply educate yourself about public health issues.