Health grades set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a system that aims to quantify and evaluate the quality of healthcare. This system provides a framework for understanding the complex landscape of healthcare, offering valuable insights for patients, providers, and the industry as a whole.
Health grades are numerical ratings assigned to healthcare providers, hospitals, and other medical facilities based on a variety of factors, including patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes, and adherence to best practices. These ratings serve as a tool for patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare, while also providing providers with a benchmark for quality improvement.
Introduction to Health Grades
Health grades are a valuable tool for navigating the complex healthcare landscape. They provide a standardized way to evaluate and compare the quality of care offered by hospitals and healthcare providers. This information empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health and helps healthcare providers identify areas for improvement.
Purpose and Value of Health Grades
Health grades serve a crucial purpose by enhancing transparency and accountability in the healthcare system. They benefit patients, healthcare providers, and the industry as a whole.
Patients
- Informed Decision-Making:Health grades provide patients with a clear and objective assessment of hospital and provider performance, allowing them to make informed decisions about where to seek care.
- Improved Patient Safety:By highlighting hospitals with strong safety records, health grades encourage patients to choose facilities that prioritize patient safety.
- Enhanced Quality of Care:Health grades motivate healthcare providers to strive for excellence, leading to improvements in the quality of care delivered.
Healthcare Providers
- Benchmarking and Improvement:Health grades provide healthcare providers with valuable insights into their performance compared to peers, allowing them to identify areas for improvement.
- Increased Patient Trust:Hospitals and providers with high health grades benefit from increased patient trust and confidence.
- Attracting and Retaining Staff:High-performing hospitals and providers are more attractive to skilled professionals, contributing to a better workforce.
Healthcare Industry
- Accountability and Transparency:Health grades promote accountability and transparency in the healthcare industry, encouraging providers to prioritize quality and safety.
- Market Differentiation:Health grades help patients differentiate between hospitals and providers, driving competition and innovation in the healthcare market.
- Policy and Regulation:Health grades data can inform healthcare policy decisions and regulatory oversight, leading to improvements in the healthcare system.
Factors Considered in Assigning Health Grades
Health grades are assigned based on a comprehensive evaluation of various factors, including:
- Patient Safety:This includes measures such as infection rates, readmission rates, and adverse events.
- Clinical Outcomes:These measures assess the effectiveness of care provided, such as survival rates and complication rates.
- Patient Experience:This includes patient satisfaction surveys and measures of communication and responsiveness.
- Efficiency and Cost:This considers factors such as hospital length of stay and overall cost of care.
Types of Health Grades

Health grades are numerical representations of a healthcare provider’s performance, encompassing various aspects like patient outcomes, efficiency, and quality of care. They serve as valuable tools for patients, payers, and healthcare providers themselves, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering continuous improvement in healthcare delivery.
Hospital Grades
Hospital grades evaluate the performance of hospitals based on various metrics, including patient safety, effectiveness of care, and patient experience.
- Patient Safety:This category assesses the rate of preventable hospital-acquired infections, complications from procedures, and readmissions within a specific timeframe.
- Effectiveness of Care:This evaluates the effectiveness of treatments, including adherence to best practices and the success rate of specific procedures.
- Patient Experience:This category assesses patient satisfaction with communication, responsiveness, cleanliness, and overall experience during their hospital stay.
Examples of hospital grades include those provided by organizations like Leapfrog Group and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). These grades are often presented on a letter scale, with “A” representing the highest performance and “F” the lowest.
Physician Grades, Health grades
Physician grades evaluate the performance of individual physicians based on factors such as patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes, and adherence to best practices.
- Patient Satisfaction:This category measures patient satisfaction with the physician’s communication, bedside manner, and overall experience during their visits.
- Clinical Outcomes:This assesses the physician’s success rate in treating specific conditions and achieving desired outcomes for patients.
- Adherence to Best Practices:This evaluates the physician’s adherence to evidence-based guidelines and protocols for treating specific conditions.
Physician grades are often calculated using data from patient surveys, medical records, and other sources. Examples include those provided by organizations like Healthgrades and Vitals.
Nursing Home Grades
Nursing home grades evaluate the quality of care provided by nursing homes based on factors such as patient safety, quality of care, and staffing levels.
- Patient Safety:This category assesses the rate of preventable adverse events, including falls, pressure ulcers, and infections.
- Quality of Care:This evaluates the quality of nursing care provided, including medication management, wound care, and rehabilitation services.
- Staffing Levels:This assesses the adequacy of staffing levels, including the number of nurses and certified nursing assistants (CNAs) available to provide care.
Nursing home grades are often calculated using data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). These grades are presented on a five-star rating system, with five stars representing the highest quality of care and one star the lowest.
Methodology for Calculating Health Grades
Different organizations employ various methodologies for calculating health grades.
Commonly used methods include:
- Risk-adjusted analysis:This method adjusts for differences in patient populations, accounting for factors like age, health status, and socioeconomic factors.
- Statistical modeling:This method uses statistical models to predict the likelihood of certain outcomes based on various factors, including patient characteristics and provider practices.
- Patient surveys:This method collects data directly from patients about their experiences with healthcare providers.
It’s important to note that different organizations may use different methodologies and weight factors differently, leading to variations in health grades across different sources.
Impact of Health Grades on Healthcare

Health grades, a numerical representation of healthcare provider performance, have become increasingly influential in shaping patient choices and influencing healthcare delivery. They aim to provide patients with valuable information to make informed decisions about their healthcare, while also incentivizing providers to improve their quality of care.
Influence on Patient Choice and Healthcare Utilization
Health grades can significantly impact patient choices by providing them with a readily accessible and easily understandable metric to compare different healthcare providers. This information empowers patients to select providers with higher ratings, potentially leading to increased utilization of those providers.
For instance, a patient seeking a specific type of surgery might be more likely to choose a surgeon with a consistently high health grade compared to one with lower ratings.
- Patients may be more likely to travel further distances to access a provider with a higher health grade, even if a provider closer to their location has lower ratings.
- Patients may be more inclined to choose a provider with a higher health grade, even if they have to wait longer for an appointment.
This shift in patient behavior can have both positive and negative implications. On the one hand, it can encourage providers to prioritize quality care to maintain high ratings, ultimately benefiting patients. However, it can also lead to increased demand for high-rated providers, potentially resulting in longer wait times and limited access for patients seeking care from less-rated providers.
Health grades can be a helpful tool for understanding the quality of healthcare facilities, but it’s important to remember that they are just one piece of the puzzle. Organizations like health action international play a crucial role in advocating for access to safe and effective healthcare globally.
By understanding the work of these organizations, we can gain a broader perspective on the factors that influence health grades and the overall health of individuals and communities.
Effects on Healthcare Provider Performance and Quality Improvement Initiatives
Health grades can incentivize healthcare providers to focus on improving their performance and implementing quality improvement initiatives to achieve higher ratings. The potential for improved rankings can motivate providers to adopt evidence-based practices, implement standardized protocols, and invest in staff training.
This competitive pressure can lead to a general improvement in the quality of care across the healthcare system.
- Hospitals with lower health grades may be more likely to invest in new technologies and equipment to improve patient outcomes.
- Providers with lower health grades may be more likely to participate in quality improvement programs to improve their ratings.
However, the pursuit of higher health grades can also lead to unintended consequences. Providers may focus on metrics that are easily measured and reported, potentially neglecting other aspects of care that are less quantifiable. This can create a “gaming” effect where providers prioritize improving their scores on specific metrics rather than delivering holistic and patient-centered care.
Health grades can provide a valuable snapshot of a person’s overall well-being, encompassing factors like nutrition, exercise, and stress management. While these elements contribute to a healthy body, they also play a significant role in achieving a radiant appearance. Beauty , after all, is often a reflection of inner health, and by prioritizing your health grades, you can unlock a natural glow that radiates from within.
Potential Biases and Limitations
While health grades can provide valuable information, it’s important to acknowledge their limitations and potential biases.
- Health grades are often based on limited data, which may not accurately reflect the full spectrum of a provider’s performance.
- The methodologies used to calculate health grades can vary widely, making it difficult to compare ratings across different systems.
- Health grades may be influenced by factors beyond a provider’s control, such as the socioeconomic status of their patient population.
Furthermore, health grades may inadvertently create a hierarchy among providers, potentially leading to a stigma associated with lower ratings. This can discourage patients from seeking care from providers with lower grades, even if they are capable of providing excellent care.
Evaluating Health Grades
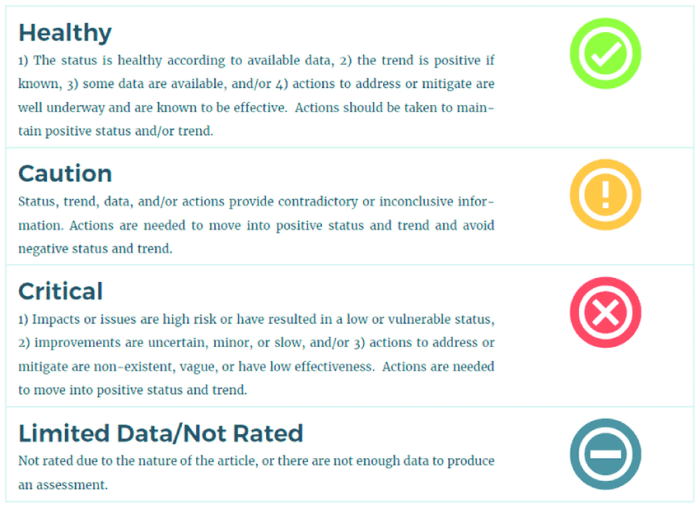
Health grades are valuable tools for patients and healthcare providers, but it’s crucial to approach them with a critical eye. Understanding how to interpret and evaluate health grades effectively is essential for making informed decisions about healthcare.
Interpreting and Evaluating Health Grades
The interpretation and evaluation of health grades involve considering various factors that influence their accuracy and relevance.
- Data Sources:The reliability of health grades hinges on the quality and comprehensiveness of the data used. Consider the source of the data, the methods used for data collection, and the potential for biases or inaccuracies. For example, data from patient surveys may be subject to recall bias, while data from administrative records may not capture all relevant information.
- Methodology:Understanding the methodology used to calculate health grades is essential for assessing their validity. Different organizations may use different methodologies, which can lead to variations in the results. It’s important to understand the specific metrics used, the weighting of different factors, and the statistical methods employed.
- Contextual Factors:Health grades should be interpreted within the context of the specific patient population and the healthcare setting. For example, a hospital with a high proportion of complex cases may have lower health grades than a hospital with a more homogeneous patient population.
It’s important to consider factors such as patient demographics, socioeconomic status, and access to resources when evaluating health grades.
Checklist for Assessing the Reliability and Validity of Health Grade Data
To ensure that health grade data is reliable and valid, consider the following checklist:
- Transparency:The organization providing the health grades should be transparent about its data sources, methodology, and any limitations of the data. This includes disclosing any potential conflicts of interest.
- Accountability:There should be mechanisms in place for holding the organization accountable for the accuracy and validity of the health grade data. This may involve independent audits or peer review processes.
- Relevance:The health grade measures should be relevant to the specific healthcare services being evaluated. For example, a hospital’s performance on heart surgery should not be assessed using the same metrics as a primary care clinic’s performance on diabetes management.
- Timeliness:The data used to calculate health grades should be up-to-date and reflect the most recent performance information. Out-of-date data can lead to inaccurate and misleading results.
- Comparability:Health grades should be comparable across different healthcare providers and settings. This allows patients to make informed comparisons between different options.
Role of Transparency and Accountability in Health Grade Systems
Transparency and accountability are crucial for building trust in health grade systems.
Transparency ensures that patients and providers have access to the information they need to make informed decisions.
Accountability provides a mechanism for addressing any concerns about the accuracy or validity of the data.
By promoting transparency and accountability, health grade systems can play a valuable role in improving the quality and safety of healthcare.
The Future of Health Grades
The future of health grades is poised for significant transformation, driven by advancements in data analytics, technology, and a growing emphasis on patient-centric care. These developments will lead to more comprehensive, accurate, and personalized health grade systems, empowering patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Health grades are a valuable tool for assessing the quality of food and products. While they often focus on nutritional content and safety, there’s a growing awareness of the impact of skincare on overall health. This is where brands like beauty joseon come in, offering products that prioritize both beauty and well-being.
By considering the health benefits of ingredients and production methods, these brands contribute to a holistic approach to health grades, ensuring that what we put on our skin is just as important as what we put in our bodies.
Emerging Trends and Advancements in Health Grade Methodologies
The evolution of health grade methodologies is driven by a continuous quest for greater accuracy, comprehensiveness, and transparency.
- Integration of Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs):PROs, such as patient satisfaction surveys and symptom tracking data, provide valuable insights into the patient experience, supplementing traditional clinical data. This integration enhances the accuracy of health grades by reflecting a more holistic view of healthcare quality.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):AI and ML algorithms are revolutionizing health grade methodologies by analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns, and predicting outcomes. These technologies can improve the accuracy of health grades by factoring in complex variables and identifying subtle trends that might be missed by traditional methods.
- Focus on Value-Based Care:The shift towards value-based care emphasizes the importance of outcomes over volume. Health grade methodologies are evolving to reflect this shift, incorporating metrics that measure the effectiveness and efficiency of care delivery, such as cost-effectiveness and patient outcomes.
The Impact of Technology and Data Analytics on Future Health Grade Systems
The integration of technology and data analytics is transforming health grade systems into powerful tools for healthcare improvement.
- Real-time Data Monitoring:Real-time data analytics enables continuous monitoring of healthcare quality, allowing for immediate identification and correction of issues. This proactive approach can significantly improve patient safety and outcomes.
- Personalized Health Grades:By leveraging patient-specific data, health grade systems can provide personalized recommendations and insights, tailoring care plans to individual needs and preferences. This empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
- Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment:Advanced analytics can predict potential health risks based on patient data, allowing for early intervention and preventive care strategies. This proactive approach can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
The Role of Health Grades in Shaping the Future of Healthcare
Health grades are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare, fostering transparency, accountability, and patient empowerment.
- Driving Quality Improvement:Health grades provide a powerful incentive for healthcare providers to continuously improve their performance, striving for higher rankings and better patient outcomes. This competition for quality fosters a culture of excellence in healthcare.
- Enhancing Patient Engagement:Transparent and accessible health grade information empowers patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare, choosing providers based on quality, experience, and patient satisfaction. This increased patient engagement fosters a more collaborative and personalized healthcare experience.
- Facilitating Healthcare Innovation:Health grades can incentivize the development and adoption of innovative healthcare technologies and practices by rewarding providers who demonstrate excellence in using these advancements to improve patient outcomes. This fosters a culture of innovation in healthcare, leading to better care and outcomes for patients.
Closing Summary
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, health grades play a crucial role in fostering transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement. By understanding the complexities and nuances of this system, we can empower ourselves as consumers and contribute to a future where healthcare is not only accessible but also of the highest quality.
FAQs: Health Grades
What are the benefits of using health grades?
Health grades provide patients with valuable information to make informed decisions about their healthcare. They also incentivize healthcare providers to improve their quality of care and patient experience.
How are health grades calculated?
Health grades are typically calculated using a combination of data sources, including patient surveys, medical records, and performance metrics. The specific methodologies vary depending on the organization assigning the grades.
Are health grades always accurate?
While health grades provide a useful tool, it’s important to remember that they are not always a perfect reflection of a healthcare provider’s quality. There are inherent limitations in any rating system, and it’s essential to consider other factors when making healthcare decisions.