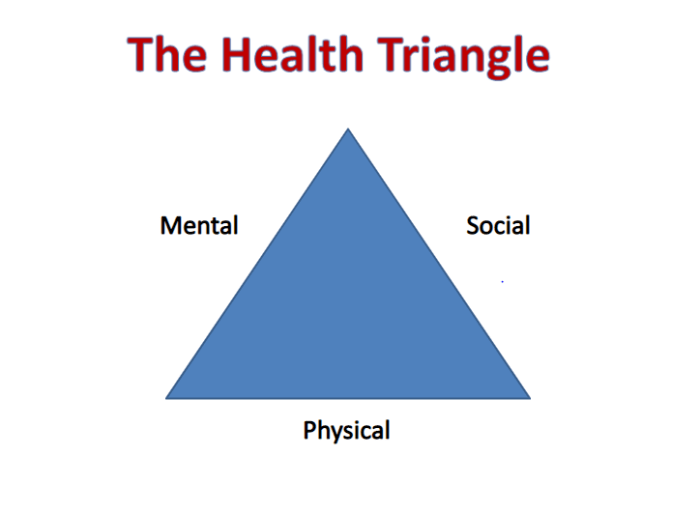
Health triangles represent a holistic framework for understanding and optimizing well-being. This model emphasizes the interconnectedness of three key components: physical, mental, and social health. Each aspect plays a vital role in achieving overall wellness, and maintaining a balanced equilibrium among them is crucial for a fulfilling life.
The health triangle provides a practical and relatable way to assess and manage different aspects of health. By understanding the individual components and their interplay, individuals can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to achieve optimal health outcomes.
What is a Health Triangle?

The health triangle is a model that represents the three essential components of overall well-being: physical health, mental health, and social health. It emphasizes that these three aspects are interconnected and influence each other, meaning that a balance in each area is crucial for optimal health and happiness.
The health triangle is a helpful model for understanding overall well-being, encompassing physical, mental, and social aspects. To achieve balance, it’s important to prioritize all three areas, and organizations like bloomington health partners can provide valuable resources and support.
By focusing on the health triangle, we can cultivate a holistic approach to our well-being, leading to a more fulfilling and balanced life.
Physical Health
Physical health encompasses the state of your body and its ability to function properly. This includes factors like nutrition, exercise, sleep, and avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Nutrition:Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein provides the necessary nutrients for energy, growth, and repair, supporting a strong immune system and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Exercise:Regular physical activity strengthens muscles, improves cardiovascular health, reduces stress, and promotes better sleep. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities at least twice a week.
- Sleep:Adequate sleep is essential for physical and mental restoration. Most adults require 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Getting enough sleep helps regulate hormones, boosts energy levels, and enhances cognitive function.
- Avoiding Unhealthy Habits:Habits like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can significantly harm physical health, increasing the risk of various diseases and premature death.
Importance of Balance

Imagine a three-legged stool. If one leg is shorter than the others, the stool will wobble and eventually fall. The health triangle is similar. Each side represents a crucial aspect of well-being, and maintaining balance between them is vital for overall health and happiness.
When one area of the health triangle is neglected, it can negatively impact the others, creating a domino effect. This can lead to a decline in overall well-being and make it harder to achieve your goals.
Examples of Imbalances
Here are some examples of how imbalances in one area of the health triangle can affect the others:
- Physical Health Imbalance:If you’re not getting enough sleep, you might experience decreased energy levels, making it harder to exercise or maintain a healthy diet. This can lead to weight gain, decreased mood, and difficulty focusing.
- Mental Health Imbalance:When you’re stressed or anxious, it can affect your physical health. You might experience headaches, muscle tension, or difficulty sleeping. This can lead to poor eating habits, decreased motivation, and difficulty maintaining relationships.
- Social Health Imbalance:Lack of social connections can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can negatively impact mental health. This can lead to decreased motivation, difficulty managing stress, and poor sleep habits.
Factors Affecting Health Triangle: Health Triangles
The health triangle is a dynamic model that is constantly influenced by various factors, both internal and external. Understanding these factors can help us identify potential challenges and opportunities for maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Internal Factors
Internal factors are those that originate within an individual and play a significant role in shaping their health triangle. These factors are often deeply ingrained and can have a lasting impact on overall well-being.
- Genetics: Our genes influence our susceptibility to certain diseases, our physical characteristics, and even our personality traits. For instance, individuals with a family history of heart disease may be more predisposed to cardiovascular issues. However, it’s important to note that genetics are not destiny.
Lifestyle choices can significantly mitigate the impact of genetic predispositions.
- Personality: Personality traits can influence our health behaviors and choices. For example, individuals who are highly conscientious are more likely to engage in healthy habits such as regular exercise and a balanced diet. On the other hand, individuals with a more impulsive personality may struggle with maintaining healthy habits.
- Coping Mechanisms: The way we deal with stress and challenges can have a profound impact on our physical and mental health. Effective coping mechanisms, such as exercise, meditation, or seeking social support, can help us manage stress and maintain balance. However, unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as substance abuse or avoidance, can negatively impact our health triangle.
External Factors
External factors are those that originate from the environment surrounding an individual. These factors can have a significant influence on our health choices and overall well-being.
- Environment: Our physical environment plays a crucial role in our health. Factors such as air and water quality, access to green spaces, and exposure to pollutants can all impact our health triangle. For example, living in a polluted area can increase the risk of respiratory problems, while access to parks and recreational facilities can promote physical activity and mental well-being.
- Relationships: Our relationships with family, friends, and colleagues can have a significant impact on our health. Supportive relationships can provide a sense of belonging, reduce stress, and promote healthy behaviors. Conversely, unhealthy relationships can lead to stress, isolation, and negative health outcomes.
- Social Support: Social support networks can provide emotional, practical, and informational assistance during times of need. This can be crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and coping with challenges. For example, having a supportive network can help individuals stay motivated to exercise, eat healthy, and manage stress.
Impact of Factors on Health Triangle
The factors discussed above can contribute to both positive and negative outcomes for our health triangle.
“A healthy lifestyle is not just about physical health, but also about mental and emotional well-being.”
- Positive Outcomes: When internal and external factors align to promote healthy choices and support well-being, individuals are more likely to experience positive outcomes in their health triangle. For example, having a supportive family, engaging in regular exercise, and having access to quality healthcare can contribute to a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
- Negative Outcomes: Conversely, when internal and external factors create challenges and obstacles, individuals may experience negative outcomes in their health triangle. For example, genetic predispositions, unhealthy coping mechanisms, and exposure to environmental pollutants can all contribute to health problems.
Strategies for Improving Health Triangle
Improving your health triangle is an ongoing process that requires commitment and effort. There are many different strategies you can use to improve each aspect of your health triangle, and it’s important to find what works best for you.
The key is to focus on making small, sustainable changes to your lifestyle.
Strategies for Improving the Health Triangle
| Physical Health | Mental Health | Social Health | Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engage in regular physical activity. | Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques. | Develop strong relationships with family and friends. | Join a gym, go for walks, take dance classes, or participate in team sports. |
| Eat a healthy diet. | Seek professional help if needed. | Engage in social activities that you enjoy. | Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. |
| Get enough sleep. | Develop healthy coping mechanisms for stress. | Learn effective communication skills. | Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. |
| Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. | Practice gratitude and positive self-talk. | Set boundaries and learn to say “no” when needed. | Seek support from trusted individuals. |
The Health Triangle in Different Life Stages

The health triangle, a model that encompasses physical, mental, and social well-being, is not static but evolves throughout a person’s life. Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities, influencing how individuals prioritize and manage their health.
Health Triangle in Childhood
Childhood is a crucial period for establishing healthy habits and building a strong foundation for future well-being. Physical health during this stage is characterized by rapid growth and development, necessitating adequate nutrition, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep. Children also develop their social skills and learn to navigate social situations, contributing to their social well-being.
The health triangle, with its focus on physical, mental, and social well-being, provides a holistic approach to health. This concept is central to the services offered by the midwest center for women’s health , where they offer a range of programs designed to empower women in all aspects of their health journey.
By understanding and nurturing each corner of the triangle, individuals can strive for a balanced and fulfilling life.
Mental health is equally important, as children learn to regulate their emotions, build self-esteem, and develop resilience.
- Physical Health:Children need balanced diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular physical activity. Adequate sleep is essential for growth and development.
- Mental Health:Parents and educators play a crucial role in fostering children’s emotional well-being. Encouraging positive self-talk, providing opportunities for social interaction, and teaching coping mechanisms for stress are essential.
- Social Health:Children develop social skills through interactions with peers, family, and community members. Building positive relationships and learning to communicate effectively are crucial for social well-being.
Health Triangle in Adolescence
Adolescence is a period of significant physical, emotional, and social changes. Adolescents experience rapid physical growth and hormonal changes, which can impact their body image and self-esteem. They also face increasing academic pressures, social expectations, and potential exposure to risky behaviors.
- Physical Health:Adolescents need adequate nutrition to support their growth spurt and energy levels. Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing stress.
- Mental Health:Adolescents are particularly vulnerable to mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, and eating disorders. Providing support, understanding, and access to mental health services is critical.
- Social Health:Adolescents develop their sense of identity and explore their place in society. Building strong relationships with peers and family members is important for their social well-being.
Health Triangle in Adulthood, Health triangles
Adulthood is a time of establishing careers, forming families, and taking on responsibilities. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle becomes increasingly important as individuals face the demands of work, family, and personal commitments.
Health triangles are a helpful model for understanding the interconnectedness of our physical, mental, and emotional well-being. A great example of this is the concept of “mile square health,” which emphasizes the importance of creating a healthy lifestyle that encompasses all three aspects of the triangle.
By focusing on all three areas, we can achieve a holistic approach to health and wellness.
- Physical Health:Adults need to prioritize regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep to manage stress and prevent chronic diseases.
- Mental Health:Adults often face stress from work, family, and financial pressures. Managing stress, maintaining a positive outlook, and seeking support when needed is crucial for mental well-being.
- Social Health:Adults benefit from strong social connections and meaningful relationships. Maintaining a healthy social life, participating in community activities, and nurturing relationships with family and friends is essential for social well-being.
Health Triangle in Senior Years
As individuals age, they may experience physical limitations, health challenges, and changes in their social roles. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle becomes even more important for preserving independence and quality of life.
- Physical Health:Seniors need to focus on maintaining physical activity, managing chronic conditions, and ensuring adequate nutrition. Regular check-ups and preventive screenings are essential.
- Mental Health:Seniors may experience age-related cognitive decline, social isolation, and grief. Maintaining cognitive function, staying socially engaged, and seeking support when needed are crucial for mental well-being.
- Social Health:Seniors may experience changes in their social networks as friends and family members pass away or move away. Maintaining social connections, participating in activities with others, and seeking support from community organizations can help seniors maintain social well-being.
The Health Triangle in Different Cultures

The concept of the health triangle, with its focus on physical, mental, and social well-being, is widely recognized. However, the way these dimensions are understood and prioritized can vary significantly across cultures. Cultural factors, including beliefs, values, and practices, shape perceptions of health and influence individual behaviors.
Cultural Perspectives on Health and Well-being
Different cultures have diverse perspectives on what constitutes health and well-being. Some cultures may emphasize physical health and longevity, while others may prioritize mental and emotional well-being. For instance, in some Asian cultures, a strong emphasis is placed on maintaining harmony and balance within the individual and with the environment, which can influence health practices.
The Health Triangle and Disease Prevention

A strong health triangle is not just about feeling good; it’s a powerful tool for preventing disease and living a longer, healthier life. By maintaining balance in all three areas – physical, mental, and social – you can build a robust foundation for your overall well-being, making you less susceptible to illness.
The Link Between Lifestyle Choices and Chronic Disease Risk
The choices we make in our daily lives have a profound impact on our health, both in the short and long term. These lifestyle choices, especially those related to diet, exercise, stress management, and social connections, significantly influence our risk of developing chronic diseases.
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and cancer, are the leading causes of death worldwide. They are often preventable or manageable through healthy lifestyle choices.
Summary

In conclusion, the health triangle offers a comprehensive and insightful perspective on well-being, highlighting the interconnectedness of physical, mental, and social health. By actively nurturing each component and striving for balance, individuals can cultivate a resilient and fulfilling life. Understanding the health triangle empowers us to make informed choices, prioritize well-being, and create a foundation for a healthy and thriving future.
Query Resolution
How can I assess my own health triangle?
Reflect on your current habits and behaviors in each area. Are you engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep? Are you managing stress effectively, cultivating positive relationships, and feeling emotionally balanced? Identifying strengths and weaknesses can help you develop targeted strategies for improvement.
What are some examples of imbalances in the health triangle?
An imbalance in one area can have a ripple effect on the others. For example, chronic stress can negatively impact physical health through increased cortisol levels, leading to weakened immunity and sleep disturbances. Social isolation can contribute to feelings of loneliness and depression, affecting mental health.
It’s important to recognize these interconnections and address imbalances proactively.
Can the health triangle be applied to different life stages?
Yes, the health triangle is a flexible framework that can be adapted to different life stages. The specific needs and priorities may change, but the core principles remain relevant. For example, adolescents may prioritize social health and peer relationships, while seniors might focus on managing chronic conditions and maintaining physical mobility.