Health Flex Spending Accounts, often referred to as FSAs, are a valuable tool for individuals seeking to save money on eligible healthcare expenses. These accounts allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars for medical expenses, potentially reducing your overall tax burden and healthcare costs.
The concept of a Health FSA is straightforward. You contribute a portion of your pre-tax income to the account, which can then be used to pay for a wide range of medical expenses, including doctor’s visits, prescription drugs, and even over-the-counter medications.
The key advantage lies in the tax savings, as you are essentially using pre-tax dollars to pay for these expenses.
Introduction to Health Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)

A Health Flexible Spending Account (FSA) is a special account you can set up through your employer to pay for eligible medical expenses. It’s a way to save money on taxes and pay for healthcare costs using pre-tax dollars. An FSA is a valuable benefit that allows you to pay for eligible medical expenses with money that has not been taxed.
This can save you money on your taxes, as you are not taxed on the money you contribute to the FSA.
A Health Flex Spending Account (FSA) can be a great way to save money on eligible healthcare expenses. You can use your FSA to pay for a variety of services, including those offered by the Midwest Center for Women’s Health.
Remember to check with your FSA provider to ensure the specific services you need are covered.
Examples of Eligible Medical Expenses
The funds in your FSA can be used to pay for a variety of medical expenses, including:
- Doctor’s visits and hospital stays
- Prescription drugs
- Dental and vision care
- Over-the-counter medications (with a prescription)
- Medical equipment, such as crutches or wheelchairs
- Mental health services
- Long-term care
- Certain health insurance premiums
How Health FSAs Work: Health Flex Spending Account
Health FSAs, also known as Flexible Spending Accounts, are employer-sponsored accounts that allow you to set aside pre-tax money to pay for eligible medical expenses. This means you can save money on taxes and pay for your medical expenses with money you’ve already set aside.
Setting Up a Health FSA
Setting up a Health FSA is a straightforward process that usually involves a few simple steps.
- Enroll during your company’s open enrollment period.This is typically the time when employees can make changes to their benefits, including adding or removing FSAs.
- Choose your contribution amount.You can choose to contribute a specific amount of money each pay period or a lump sum at the beginning of the year.
- Complete the necessary paperwork.This might include an enrollment form and a direct deposit authorization form.
Contribution Limits and Eligibility Requirements
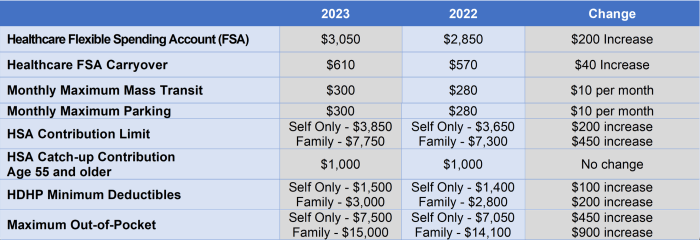
The amount you can contribute to your Health FSA each year is limited by the IRS. For 2023, the maximum contribution limit is $3,050. You may also be eligible for a higher limit if you have a qualifying health condition.
To be eligible for a Health FSA, you must be employed by a company that offers this benefit. The specific eligibility requirements can vary by employer, so it’s essential to check with your HR department for more information.
A Health Flex Spending Account (FSA) can be a great way to save money on healthcare expenses, but it’s important to understand how they work. Individuals with a strong interest in healthcare administration might find it beneficial to pursue a doctor of health administration degree.
This type of program can equip you with the knowledge and skills to manage healthcare programs and organizations, including those that utilize FSAs. By understanding the intricacies of FSAs and other healthcare programs, you can help ensure individuals and families have access to affordable healthcare.
Tax Advantages of Using a Health FSA, Health flex spending account
The primary benefit of using a Health FSA is the tax savings. Since your contributions are pre-tax, you won’t have to pay income tax on the money you use for eligible medical expenses. This can result in significant tax savings, especially for individuals who have high medical expenses.
Example:If you contribute $1,000 to your Health FSA and use it to pay for $1,000 in medical expenses, you’ll save the amount of income tax you would have paid on that $1,000. This savings can be substantial, especially if you’re in a high tax bracket.
The “Use It or Lose It” Rule
One important thing to remember about Health FSAs is the “use it or lose it” rule. This means that any money you contribute to your FSA that you don’t use by the end of the plan year will be forfeited.
To avoid losing money, it’s essential to estimate your medical expenses carefully and contribute the appropriate amount. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, some employers offer a grace period or a rollover option that allows you to carry over a portion of your unused FSA funds to the next year.
Common Uses of Health FSAs
Health FSAs are designed to help you pay for eligible medical expenses that aren’t covered by your health insurance. They can be a valuable tool for saving money on out-of-pocket healthcare costs.
Common Medical Expenses Covered by Health FSAs
Here’s a table outlining some common medical expenses covered by Health FSAs, along with eligibility criteria and additional notes:
| Expense Category | Example | Eligibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prescription Drugs | Antibiotics, insulin, allergy medication | Prescribed by a licensed medical professional | May be subject to formulary restrictions. |
| Over-the-Counter Medications | Pain relievers, cold and flu remedies, first aid supplies | Must be prescribed by a doctor | Check with your FSA administrator for a list of eligible OTC medications. |
| Dental and Vision Care | Dental cleanings, eyeglasses, contact lenses | Covered under your dental and vision plans | May have limitations on coverage amounts. |
| Mental Health Services | Therapy sessions, counseling, psychiatric evaluations | Provided by a licensed mental health professional | Check with your FSA administrator for coverage details. |
| Medical Equipment | Wheelchairs, walkers, crutches, diabetic supplies | Prescribed by a doctor for a medical condition | May require documentation of medical necessity. |
| Doctor’s Visits | Checkups, specialist appointments, emergency room visits | Covered under your health insurance plan | May have deductibles or co-pays. |
| Physical Therapy | Rehabilitation for injuries or conditions | Prescribed by a doctor | May have limitations on the number of sessions covered. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Health FSAs

Health Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) can be a valuable tool for managing healthcare costs, but like any financial product, they have both advantages and disadvantages. It’s important to weigh these factors carefully before deciding if an FSA is right for you.
Advantages of Health FSAs
The primary advantage of using a Health FSA is the potential for tax savings. This is because contributions to a Health FSA are made with pre-tax dollars. This means that you’ll pay less in taxes throughout the year, and you’ll have more money available to cover healthcare expenses.
- Tax Savings:One of the biggest benefits of an FSA is that contributions are made with pre-tax dollars. This means you’ll pay less in taxes throughout the year, leaving you with more money to cover healthcare expenses.
- Pre-Tax Deductions:By contributing to an FSA, you’re effectively lowering your taxable income. This can result in a lower tax bill, especially if you’re in a higher tax bracket.
- Potential for Lower Healthcare Costs:Using an FSA can help you save money on healthcare costs. You can use FSA funds to pay for eligible expenses, such as deductibles, copayments, and prescription drugs, without having to pay out of pocket.
Disadvantages of Health FSAs
While Health FSAs offer several advantages, they also come with some potential drawbacks. It’s important to understand these limitations before deciding if an FSA is the right choice for you.
- “Use it or Lose it” Rule:One of the biggest drawbacks of Health FSAs is the “use it or lose it” rule. This means that any money remaining in your FSA at the end of the year is forfeited. You cannot roll it over to the next year or withdraw it for other purposes.
Health Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) are a great way to save money on eligible medical expenses. While many think of doctor visits and prescriptions, you might be surprised to learn that some beauty treatments can also qualify. For example, if you’re looking for a way to tone and strengthen your muscles, you could consider using your FSA to pay for classes at a beauty barre.
These classes can help improve posture, balance, and overall fitness, which are all beneficial for your health. Just be sure to check with your FSA provider to confirm which beauty treatments are eligible before you make any purchases.
- Potential for Unused Funds:If you don’t use all of the money in your FSA during the year, you will lose it. This can be a significant financial loss, especially if you have a healthy year and don’t incur many healthcare expenses.
- Administrative Complexities:FSAs can involve some administrative complexities. You need to keep track of your spending, submit receipts for reimbursement, and follow the rules of your plan.
Choosing the Right Health FSA

Deciding whether a Health FSA is the right choice for you involves considering several factors. You need to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the potential drawbacks to make an informed decision.
Expected Medical Expenses
Your expected medical expenses play a crucial role in determining if a Health FSA is a good fit. If you anticipate incurring significant medical costs, a Health FSA can be beneficial. This is because you can use pre-tax dollars to pay for these expenses, resulting in tax savings.
For example, if you have a chronic condition that requires ongoing medication or treatments, a Health FSA can help you save on taxes. However, if you generally have low medical expenses, a Health FSA might not be as advantageous. To estimate your expected medical expenses, consider:
- Prescription medications
- Dental and vision care
- Over-the-counter medications
- Doctor’s visits
- Other eligible medical expenses
Tax Bracket
Your tax bracket significantly impacts the potential tax savings you can realize with a Health FSA. The higher your tax bracket, the greater the tax savings you can potentially achieve. For instance, if you are in the 25% tax bracket, for every $100 you contribute to a Health FSA, you save $25 in taxes.
However, if you are in a lower tax bracket, such as 12%, your tax savings would be less, at $12 for every $100 contributed.To determine your tax bracket, you can consult IRS tax tables or use online tax calculators.
Preferred Level of Risk
Health FSAs involve a certain level of risk. This is because you are essentially pre-paying for medical expenses. If you don’t use all the funds in your account by the end of the plan year, you may lose them. Therefore, if you are risk-averse, you might want to reconsider a Health FSA.
However, if you are comfortable with the potential risk and are confident you will utilize the funds, a Health FSA can be a valuable tool for saving money on medical expenses.
Managing Your Health FSA

Managing your Health FSA effectively is crucial to maximizing its benefits and ensuring you get the most out of your contributions. It involves understanding the claims process, maintaining accurate records, and avoiding common pitfalls.
Submitting Claims for Reimbursement
Submitting claims for reimbursement is a straightforward process. Typically, you’ll need to gather the following information:
- Date of Service:The date the medical expense was incurred.
- Provider Name:The name of the doctor, hospital, or other healthcare provider.
- Provider Address:The address of the healthcare provider.
- Procedure or Service:A brief description of the medical service or procedure.
- Amount Paid:The amount you paid for the medical expense.
- Receipt or Invoice:A copy of the original receipt or invoice for the expense.
Most FSA administrators offer convenient online portals or mobile apps for submitting claims, allowing you to upload required documents electronically. Some administrators also accept claims via mail or fax. It’s important to review your FSA plan documents for specific instructions and deadlines for claim submission.
Keeping Accurate Records of Medical Expenses
Keeping accurate records of your medical expenses is essential for tracking your FSA balance and ensuring you receive proper reimbursements. Here are some tips:
- Organize Receipts:Maintain a separate folder or file for all medical receipts, including those for prescriptions, over-the-counter medications, and doctor’s visits.
- Use a Spreadsheet:A spreadsheet can help you track your expenses, including the date, provider, service, and amount paid. This can make it easier to submit claims and reconcile your FSA balance.
- Keep Digital Records:Scan or take photos of receipts and store them digitally in a secure location. This can help prevent lost or damaged receipts.
Maximizing the Benefits of Your Health FSA
Here are some tips to help you maximize the benefits of your Health FSA:
- Plan Ahead:Estimate your annual medical expenses and contribute the maximum amount allowed to your FSA. This can help you save money on healthcare costs.
- Use Your FSA for Eligible Expenses:Familiarize yourself with the list of eligible expenses under your FSA plan. This includes expenses like doctor’s visits, prescription drugs, dental care, and vision care.
- Consider a “Use It or Lose It” Provision:Some FSA plans have a “use it or lose it” provision, meaning you may lose any unused funds at the end of the plan year. If this applies to your plan, try to spend your FSA funds before the end of the plan year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using your Health FSA:
- Not Using Your FSA:Many people don’t fully utilize their FSA benefits, leaving funds unused. Make sure you’re taking advantage of your FSA to cover eligible expenses.
- Missing Deadlines:Be aware of claim submission deadlines and ensure your claims are submitted on time. Late claims may not be reimbursed.
- Overspending:Don’t contribute more to your FSA than you anticipate spending. You may end up with unused funds that you lose at the end of the plan year.
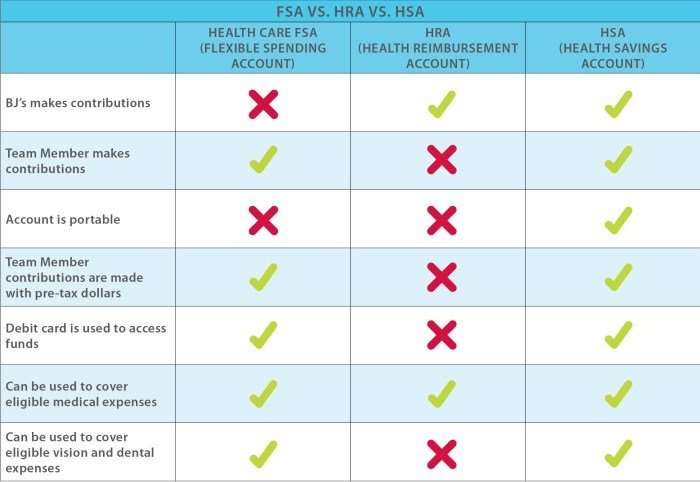
Health FSA vs. Other Healthcare Savings Options
When considering how to save for healthcare expenses, you have several options beyond a Health FSA. Understanding the differences between these options is crucial for making the best choice for your needs. This section compares and contrasts Health FSAs with other popular healthcare savings options.
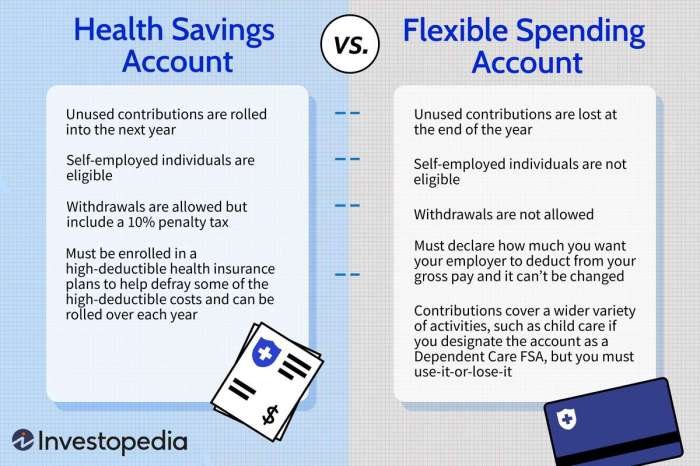
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts available to those enrolled in high-deductible health plans (HDHPs). They offer a triple tax advantage: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
- Contributions: HSA contributions are made by the individual, often with employer matching, and are limited annually. These contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income.
- Ownership: You own your HSA and can take it with you if you change jobs or retire.
- Rollover: Unused funds roll over year to year, allowing you to accumulate savings for future healthcare expenses.
- Investment Options: Some HSAs offer investment options, allowing your funds to grow potentially faster.
Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) for Dependent Care
Dependent care FSAs are designed to help pay for the care of children or other dependents who cannot care for themselves. These accounts are similar to Health FSAs in that contributions are pre-tax, but they are specifically for dependent care expenses.
- Contributions: You contribute pre-tax dollars to the account, reducing your taxable income.
- Usage: Funds can be used for eligible dependent care expenses, such as daycare, after-school programs, and adult care.
- Use-it-or-Lose-it Rule: A common feature of FSAs, unused funds at the end of the year are typically forfeited.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance Plans
Employer-sponsored health insurance plans are a common way for employees to access healthcare coverage. These plans are typically offered with different options and features, including deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
- Premiums: Premiums are typically paid through payroll deductions, with employers often contributing a portion of the cost.
- Coverage: These plans offer a wide range of healthcare services, including preventive care, hospital stays, and prescription drugs.
- Limited Savings: Unlike HSAs and FSAs, employer-sponsored plans do not provide tax-advantaged savings options for future healthcare expenses.
Choosing the Best Option for You
The best healthcare savings option depends on your individual circumstances and needs. Consider factors such as your health status, expected medical expenses, and tax bracket.
- Health Status: If you anticipate high medical expenses, an HSA or Health FSA might be a good choice to help you save for those costs.
- Tax Bracket: The tax benefits of HSAs and FSAs are more significant for those in higher tax brackets.
- Investment Needs: If you want to grow your healthcare savings, an HSA with investment options may be appealing.
- Dependent Care: If you need assistance with dependent care, a dependent care FSA can help cover those expenses.
Closure
Health Flex Spending Accounts offer a compelling opportunity to save money on healthcare expenses and potentially reduce your tax liability. By understanding the rules and regulations, carefully planning your contributions, and utilizing the account effectively, you can maximize the benefits of this valuable healthcare savings tool.
Remember to consider your individual needs and financial situation when deciding if a Health FSA is the right choice for you.
Questions Often Asked
Can I use my Health FSA for cosmetic procedures?
Generally, cosmetic procedures are not covered by Health FSAs. However, there may be exceptions for procedures deemed medically necessary.
What happens to my FSA funds if I leave my job?
The rules regarding unused FSA funds vary depending on your employer’s plan. Some plans allow you to roll over a small amount of funds, while others may require you to forfeit any unused funds. It’s essential to review your plan’s terms and conditions.
Can I use my Health FSA for my dependents’ medical expenses?
Yes, you can typically use your Health FSA to pay for eligible medical expenses for your dependents, such as your spouse and children.