Health and tongue set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The tongue, more than just a muscle for tasting and speaking, plays a vital role in your overall health.
It’s a silent messenger, reflecting internal imbalances and potential health concerns. From the intricate anatomy of its papillae to the subtle changes in its appearance, the tongue reveals a fascinating tale about your well-being.
This exploration delves into the world of the tongue, examining its structure, functions, and its connection to various aspects of health. We’ll uncover the secrets hidden within this seemingly simple organ, unraveling the mysteries of tongue health and the vital role it plays in maintaining a healthy life.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Tongue
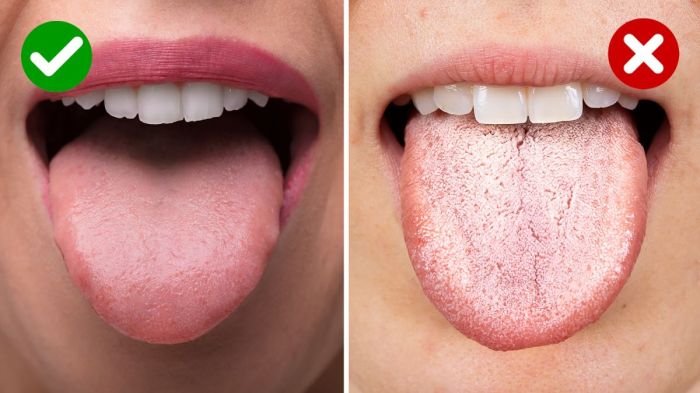
The tongue is a muscular organ located in the mouth, playing a crucial role in various functions, including taste perception, speech, and swallowing. Understanding its anatomy and physiology provides insight into its remarkable capabilities.
A healthy tongue is essential for proper taste and speech, and it’s a good indicator of overall well-being. If you’re looking to keep your tongue healthy, regular exercise is key! To make sure you have enough time to hit the gym, you might want to check what time does the planet fitness close.
After all, a strong body can support a healthy tongue and a healthy tongue can help you enjoy all the flavors of a balanced diet.
Structure of the Tongue
The tongue comprises a complex arrangement of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. The intrinsic muscles, located within the tongue, allow for intricate movements, while the extrinsic muscles, originating outside the tongue, control its position and shape.
- Intrinsic Muscles:These muscles are responsible for the fine movements of the tongue, such as shaping it for speech and manipulating food during chewing. Some of the intrinsic muscles include the superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal, transverse, and vertical muscles.
- Extrinsic Muscles:These muscles control the tongue’s position and overall movement. Examples include the genioglossus, hyoglossus, styloglossus, and palatoglossus muscles.
- Nerves:The tongue receives innervation from multiple cranial nerves. The hypoglossal nerve controls the tongue’s motor function, while the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves are involved in taste sensation.
- Blood Vessels:The tongue is richly supplied with blood vessels, ensuring its proper function. The lingual artery provides oxygenated blood, while the lingual vein drains deoxygenated blood.
Types of Papillae on the Tongue
The tongue’s surface is covered in numerous small projections called papillae, which enhance its ability to perceive taste. Different types of papillae are specialized for different functions.
- Filiform Papillae:These are the most numerous papillae, covering the entire tongue’s surface. They are cone-shaped and lack taste buds, primarily responsible for providing a rough texture that aids in manipulating food.
- Fungiform Papillae:These mushroom-shaped papillae are scattered among the filiform papillae and contain taste buds. They are responsible for detecting sweet and salty tastes.
- Circumvallate Papillae:These large, circular papillae are located at the back of the tongue, forming a V-shaped pattern. They contain numerous taste buds and are primarily responsible for detecting bitter tastes.
- Foliate Papillae:These vertical folds are located on the sides of the tongue. They contain taste buds and are primarily responsible for detecting sour tastes.
Connection Between the Tongue and Taste Perception
Taste perception is a complex process involving the interaction of taste buds, nerves, and the brain. When food enters the mouth, its molecules dissolve in saliva, interacting with taste receptors on the taste buds. These receptors send signals to the brain via cranial nerves, triggering the perception of different tastes.
- Sweet:Detected by the tip of the tongue.
- Salty:Detected by the sides of the tongue.
- Sour:Detected by the sides of the tongue.
- Bitter:Detected by the back of the tongue.
- Umami:Detected by the entire tongue, but particularly the center.
Role of the Tongue in Speech and Swallowing, Health and tongue
The tongue plays a vital role in speech production and swallowing.
- Speech:The tongue’s ability to move and shape itself allows for the production of various sounds. By manipulating its position and shape, it controls the airflow through the mouth, resulting in different sounds.
- Swallowing:The tongue plays a critical role in swallowing, pushing food toward the back of the mouth and into the esophagus. It also helps to seal off the nasal cavity, preventing food from entering the nasal passages.
Tongue Health and Conditions
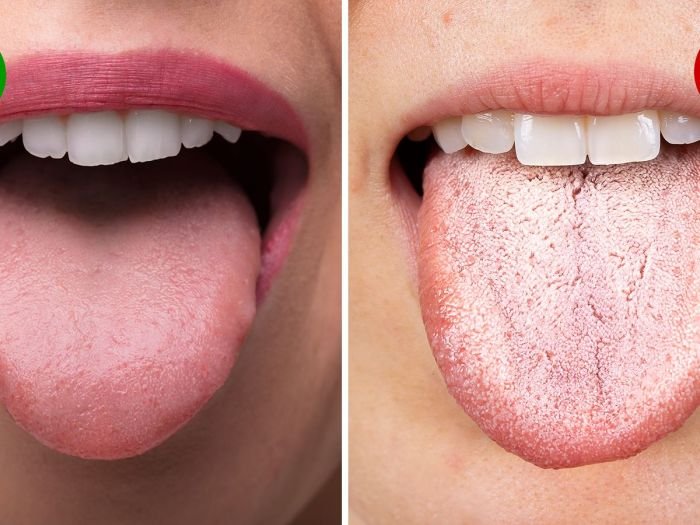
The tongue, a vital organ for taste, speech, and swallowing, is susceptible to various conditions that can affect its health and functionality. These conditions can range from minor irritations to serious infections, highlighting the importance of maintaining proper tongue hygiene and seeking medical attention when necessary.
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush, also known as candidiasis, is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of the Candida albicans fungus. This fungus is naturally present in the mouth in small amounts, but certain factors can lead to its overgrowth.The most common symptoms of oral thrush include:
- White patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, or roof of the mouth that can be scraped off, revealing a red, sore area underneath.
- Pain or soreness in the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- A cottony feeling in the mouth.
- Loss of taste.
Oral thrush can be caused by:
- Weakened immune system due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or cancer treatment.
- Use of antibiotics, which can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the mouth.
- Dry mouth.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Use of dentures or other oral appliances.
- Certain medical conditions, such as pregnancy or diabetes.
Treatment for oral thrush typically involves antifungal medications, which can be applied topically or taken orally. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health.
Geographic Tongue
Geographic tongue is a harmless condition characterized by smooth, red patches on the tongue that resemble a map. These patches are caused by inflammation of the papillae, the small bumps on the tongue that give it its rough texture.The exact cause of geographic tongue is unknown, but it is thought to be related to:
- Genetics.
- Stress.
- Hormonal changes.
- Certain foods or medications.
Geographic tongue is usually painless, but some people may experience a burning sensation or sensitivity to spicy foods. The patches can change shape and location over time, and they often disappear on their own.There is no specific treatment for geographic tongue, but some people find relief from using mouthwashes or topical medications to reduce inflammation.
Hairy Tongue
Hairy tongue is a condition that occurs when the papillae on the tongue become elongated and coated with a layer of dead cells, bacteria, and food debris. This can give the tongue a hairy or furry appearance.Hairy tongue is usually caused by:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Smoking.
- Use of certain medications, such as antibiotics.
- Dehydration.
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes.
Hairy tongue is typically harmless and does not cause pain or discomfort. However, it can affect the sense of taste and make the tongue appear discolored.Treatment for hairy tongue involves improving oral hygiene practices, such as brushing the tongue with a toothbrush or tongue scraper.
In some cases, a dentist or physician may recommend using a mouthwash or other oral medications to reduce the buildup of bacteria and debris.
Risks of Neglecting Tongue Health
Neglecting tongue health can lead to various complications, including:
- Increased risk of infections: Poor oral hygiene can create an environment where bacteria and fungi can thrive, leading to infections like oral thrush or gum disease.
- Difficulty swallowing: Conditions like oral thrush can cause pain and inflammation in the mouth, making swallowing difficult.
- Bad breath: Bacterial buildup on the tongue can contribute to bad breath.
- Social stigma: Conditions like hairy tongue can affect a person’s self-esteem and social interactions.
Maintaining Healthy Tongue Hygiene
Maintaining good tongue hygiene is crucial for preventing tongue conditions and promoting overall oral health. Here are some tips:
- Brush your tongue: Brush your tongue gently with a toothbrush or tongue scraper after brushing your teeth.
- Use mouthwash: Rinse your mouth with an antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth moist and prevent dryness.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can irritate the tongue and increase the risk of oral cancer.
- See your dentist regularly: Regular dental checkups can help identify and treat any tongue conditions early on.
The Tongue as an Indicator of Health
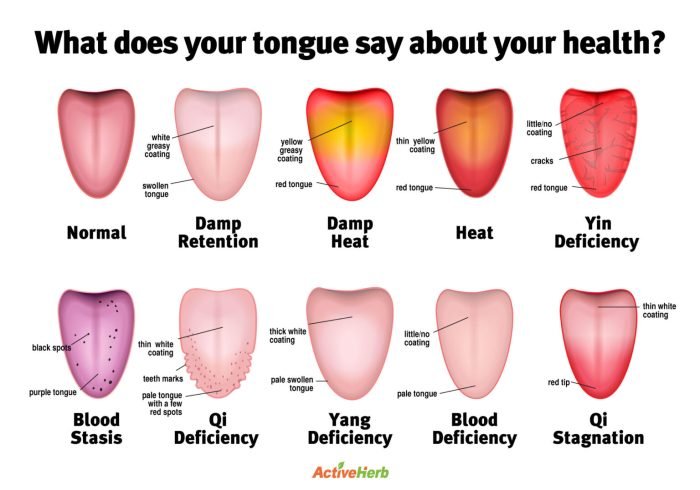
Your tongue is more than just a muscle that helps you speak and chew. It’s a window into your overall health, and changes in its appearance can signal underlying medical conditions.
Your tongue is a muscle that plays a vital role in your overall health, from chewing and swallowing to speech and taste. If you’re looking to strengthen your body and mind, consider checking out crunch fitness bensonhurst , which offers a wide range of fitness classes and equipment.
A healthy body often leads to a healthy tongue, and vice versa, so don’t forget to include tongue exercises in your fitness routine.
Tongue Appearance and Health Conditions
The appearance of your tongue can reveal valuable insights into your health.
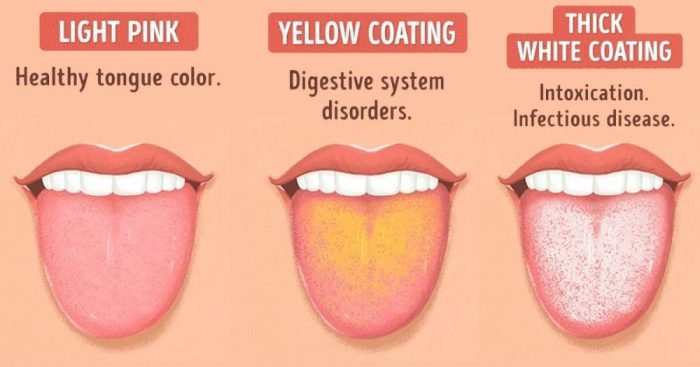
- A coated tongue:A white or yellow coating on the tongue can indicate poor oral hygiene, dehydration, or digestive issues.
- Red and swollen tongue:This can be a sign of vitamin deficiencies, such as B12 or iron deficiency, or an allergic reaction.
- Smooth tongue:A smooth, shiny tongue can indicate a lack of papillae, the tiny bumps on the tongue’s surface. This can be caused by nutritional deficiencies, infections, or certain medications.
- Cracked tongue:This can be a sign of dehydration, nutritional deficiencies, or certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or Sjogren’s syndrome.
- Sore tongue:A sore or painful tongue can be caused by a variety of factors, including oral thrush, canker sores, or irritation from sharp teeth or braces.
- Geographic tongue:This condition is characterized by patches of smooth, red areas on the tongue that resemble a map. It is often harmless but can be associated with other conditions, such as psoriasis or vitiligo.
Examples of Tongue Changes Associated with Specific Diseases or Deficiencies
Here are some examples of how specific tongue changes can be associated with particular diseases or deficiencies:
- Iron deficiency:A pale tongue can be a sign of iron deficiency anemia.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency:A smooth, shiny tongue can be a sign of vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as pernicious anemia.
- Oral thrush:This fungal infection can cause a white, cottage cheese-like coating on the tongue.
- Syphilis:In its secondary stage, syphilis can cause a white, painless patch on the tongue.
- Scarlet fever:A strawberry tongue, characterized by a red, swollen tongue with white bumps, is a classic symptom of scarlet fever.
Tongue Appearance and Potential Health Implications
The following table summarizes the potential health implications of different tongue appearances:
| Tongue Appearance | Potential Health Implications |
|---|---|
| White or yellow coating | Poor oral hygiene, dehydration, digestive issues |
| Red and swollen | Vitamin deficiencies, allergic reaction |
| Smooth, shiny | Nutritional deficiencies, infections, certain medications |
| Cracked | Dehydration, nutritional deficiencies, diabetes, Sjogren’s syndrome |
| Sore or painful | Oral thrush, canker sores, irritation from sharp teeth or braces |
| Geographic tongue | Harmless, but can be associated with psoriasis or vitiligo |
| Pale | Iron deficiency anemia |
| White, cottage cheese-like coating | Oral thrush |
| White, painless patch | Syphilis (secondary stage) |
| Red, swollen with white bumps (strawberry tongue) | Scarlet fever |
Importance of Consulting a Medical Professional
If you notice any unusual changes in your tongue, it’s important to consult a medical professional. They can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
The Tongue and Diet

The tongue plays a crucial role in food consumption and digestion, acting as the primary organ for taste perception and facilitating chewing and swallowing. Its intricate structure and sensory capabilities contribute to the enjoyment of food and the overall process of breaking down nutrients.
Taste Preferences
Taste preferences are a complex interplay of genetics, culture, and personal experiences. Genetics influences our inherent sensitivity to different tastes, such as bitterness or sweetness. Culture shapes our food choices and preferences through exposure to specific cuisines and culinary traditions.
Personal experiences, such as early childhood exposure to certain flavors, can also significantly impact our taste preferences.
Foods Beneficial for Tongue Health
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for maintaining a healthy tongue. Here’s a list of foods that contribute to optimal tongue health:
- Fruits and Vegetables:Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables support overall oral health, including the tongue. Examples include apples, oranges, carrots, and spinach.
- Dairy Products:Calcium and vitamin D in dairy products are essential for strong teeth and healthy gums, indirectly promoting tongue health.
- Lean Protein:Sources like fish, poultry, and beans provide essential amino acids for tissue repair and growth, benefiting the tongue’s structure and function.
- Whole Grains:Rich in fiber, whole grains aid digestion and promote a healthy gut microbiome, which can indirectly impact oral health.
- Water:Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health, including maintaining a moist and healthy tongue. Adequate water intake also helps prevent dry mouth, which can contribute to tongue discomfort.
Creating a Balanced Diet for Oral Health
A balanced diet that supports overall oral health includes:
- Limiting sugary foods and drinks:Excessive sugar consumption can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease, which can indirectly affect tongue health.
- Reducing acidic foods and beverages:Acidic foods can erode tooth enamel, potentially leading to sensitivity and discomfort in the tongue.
- Incorporating foods rich in calcium and vitamin D:These nutrients are crucial for strong teeth and healthy gums, contributing to overall oral health.
- Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains:This provides essential nutrients for a healthy tongue and overall well-being.
- Staying hydrated:Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining a moist and healthy tongue, as well as for overall oral health.
The Tongue and Oral Hygiene: Health And Tongue
A clean tongue is essential for maintaining good oral hygiene and overall health. While brushing your teeth is crucial, neglecting your tongue can lead to bad breath, a buildup of bacteria, and even affect your sense of taste.
Tongue Brushing Techniques
Proper tongue brushing removes bacteria, food debris, and dead cells that accumulate on its surface. This helps prevent bad breath, improve taste perception, and maintain a healthy oral environment.
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush:Choose a toothbrush with soft bristles, specifically designed for tongue cleaning. Hard bristles can irritate the tongue’s delicate surface.
- Extend Your Tongue:Gently extend your tongue out of your mouth.
- Brush from Back to Front:Start brushing at the back of your tongue, moving the toothbrush forward towards the tip. Use gentle, back-and-forth strokes, ensuring you cover the entire surface.
- Rinse and Repeat:Rinse your mouth thoroughly with water after each brush. Repeat the process two to three times a day.
Tongue Scraping
Tongue scraping is a highly effective method for removing bacteria, debris, and coatings from the tongue’s surface. This practice can significantly improve oral hygiene and reduce bad breath.
A healthy tongue is essential for proper digestion and speech, and it can be a good indicator of overall health. If you’re looking for ways to improve your overall well-being, you might consider checking out lifetime fitness montvale , a facility that offers a variety of fitness classes and programs.
Regular exercise can help improve circulation and promote healthy cell growth, which can indirectly benefit your tongue and overall health.
- Use a Dedicated Tongue Scraper:Tongue scrapers are specifically designed for this purpose and come in various materials, such as stainless steel or plastic.
- Position the Scraper:Place the scraper at the back of your tongue and gently push it forward, applying moderate pressure.
- Rinse and Repeat:Rinse the scraper after each stroke and repeat the process several times until the tongue appears clean.
- Frequency:It’s recommended to scrape your tongue once or twice a day, ideally after brushing your teeth.
Common Tongue Cleaning Mistakes
Even with good intentions, many people make mistakes when cleaning their tongues, which can reduce the effectiveness of the process and potentially cause discomfort.
- Using Too Much Pressure:Excessive pressure can irritate the tongue and even cause damage. Gentle strokes are key.
- Ignoring the Back of the Tongue:The back of the tongue harbors a significant amount of bacteria. Ensure you thoroughly clean this area.
- Brushing Too Hard:Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing too aggressively can irritate the tongue and cause pain.
- Not Cleaning Regularly:Consistent cleaning is essential to prevent the buildup of bacteria and debris. Aim to clean your tongue at least once a day.
Recommended Oral Hygiene Products
Maintaining good oral hygiene involves using the right products and tools. Here are some recommended products for tongue health:
- Soft-Bristled Toothbrush:Choose a toothbrush with soft bristles designed for both teeth and tongue cleaning.
- Tongue Scraper:A dedicated tongue scraper is highly recommended for effective cleaning.
- Antibacterial Mouthwash:An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and freshen breath.
- Fluoride Toothpaste:Fluoride toothpaste strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent cavities.
Final Conclusion

By understanding the nuances of tongue health, we empower ourselves to take proactive steps towards a healthier life. Remember, the tongue is a window to your overall well-being. Pay attention to its appearance, practice proper oral hygiene, and consult a healthcare professional if you notice any unusual changes.
With a little care and awareness, you can ensure your tongue remains a healthy and reliable companion for years to come.
Helpful Answers
What are some signs of a healthy tongue?
A healthy tongue is typically pink, smooth, and moist. It should have a thin white coating and no signs of redness, swelling, or sores.
How often should I clean my tongue?
It’s recommended to clean your tongue daily, preferably after brushing your teeth. You can use a tongue scraper or a toothbrush with a tongue cleaner.
Can a tongue scraper actually improve my breath?
Yes, a tongue scraper can help remove bacteria and food particles that can contribute to bad breath.
What are some foods that are good for tongue health?
Foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, such as fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens, are beneficial for tongue health.