Health education health education is a vital component of promoting individual and community well-being. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, leading to healthier lifestyles and reduced health disparities. By providing knowledge, skills, and resources, health education fosters a culture of health awareness and preventative measures.
This comprehensive approach encompasses a wide range of topics, from nutrition and physical activity to mental health and disease prevention. Health education is implemented in various settings, including schools, workplaces, community centers, and healthcare facilities, tailoring its message to the specific needs and interests of each target audience.
The Importance of Health Education: Health Education Health Education
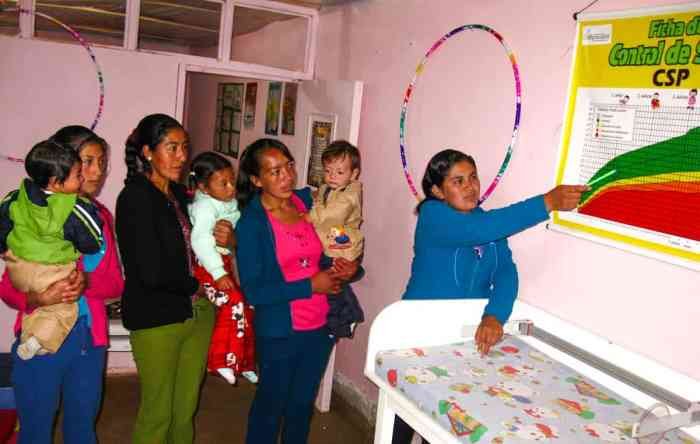

Health education is a crucial aspect of promoting individual and community well-being. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, leading to healthier lifestyles and improved health outcomes.
The Role of Health Education in Promoting Individual and Community Well-being
Health education plays a vital role in promoting individual and community well-being by equipping individuals with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes necessary to make informed decisions about their health. It provides individuals with the tools to:
- Understand the risks and benefits of different health behaviors.
- Develop healthy habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking.
- Recognize the signs and symptoms of common health conditions.
- Access and utilize healthcare services effectively.
- Advocate for their own health and the health of their communities.
By promoting healthy behaviors and preventing disease, health education contributes to a healthier population, reducing healthcare costs and improving overall quality of life.
Empowering Individuals to Make Informed Decisions About Their Health
Health education empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health by providing them with the necessary information and resources.
- For example, health education campaigns on the dangers of smoking have led to a significant decrease in smoking rates in many countries.
- Similarly, health education programs on the importance of regular exercise and a balanced diet have contributed to an increase in physical activity and healthier eating habits.
Health education also encourages individuals to be active participants in their own health care, leading to better adherence to treatment plans and improved health outcomes.
Health education empowers individuals to make informed choices about their well-being. A key aspect of this is understanding the importance of physical activity, which can be facilitated through joining a fitness center like club fitness maplewood. These facilities provide a structured environment with qualified instructors and diverse equipment, helping individuals achieve their fitness goals and improve their overall health.
Impact of Health Education on Reducing Health Disparities and Promoting Equity
Health disparities, or differences in health outcomes between different population groups, are often rooted in social, economic, and environmental factors. Health education can play a significant role in reducing these disparities by:
- Providing culturally sensitive and accessible health information to underserved populations.
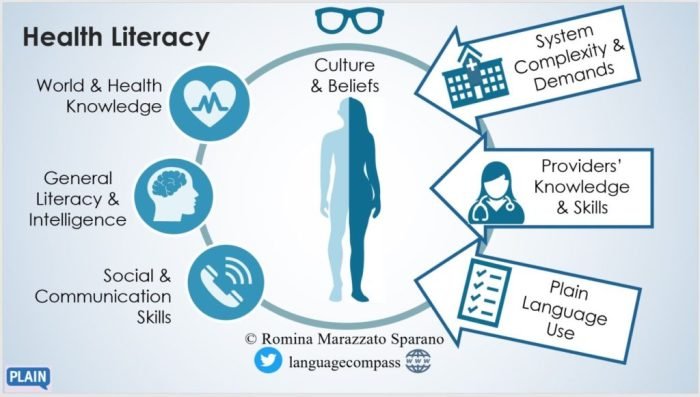
- Addressing health literacy issues and promoting health equity.
- Empowering individuals to advocate for their health and access the resources they need.
By promoting health equity, health education helps to create a healthier and more just society for all.
Key Components of Health Education
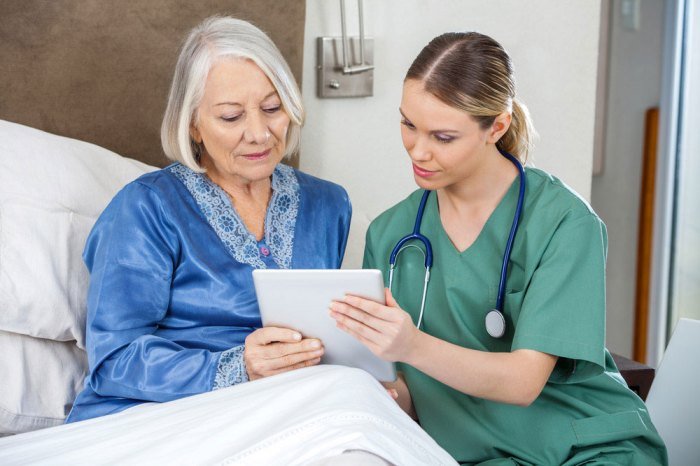

Health education involves more than just disseminating information; it’s about fostering positive behavioral changes that lead to improved well-being. Effective health education programs are grounded in specific principles and employ a range of methods and strategies.
Core Principles of Effective Health Education
Effective health education programs are guided by several core principles:
- Focus on Behavior Change:Health education aims to influence behaviors that impact health, such as promoting physical activity, healthy eating, or reducing tobacco use.
- Evidence-Based Practices:Programs should be based on scientific evidence and best practices to ensure effectiveness.
- Tailored to the Audience:Health education should be adapted to the specific needs, interests, and cultural backgrounds of the target audience.
- Interactive and Engaging:Programs should involve active participation and encourage learners to engage with the material.
- Culturally Sensitive:Health education should be respectful of diverse cultures and avoid perpetuating stereotypes.
- Empowerment and Self-Efficacy:Programs should empower individuals to take control of their health and build self-confidence in making healthy choices.
Health Education Methods and Strategies
A variety of methods and strategies are employed in health education:
- Classroom Instruction:Traditional lectures, discussions, and group activities are commonly used in school settings.
- Community Outreach:Health fairs, workshops, and public presentations reach a wider audience.
- Mass Media Campaigns:Public service announcements, television commercials, and social media campaigns can raise awareness and promote healthy behaviors.
- Health Communication:Using various communication channels, such as brochures, posters, and websites, to disseminate health information.
- Peer Education:Training individuals to educate their peers about health topics.
- Counseling and Support Groups:Providing individual or group support to help people make healthy changes.
- Policy Advocacy:Advocating for policies that promote health, such as smoke-free environments or increased funding for health education.
Role of Technology and Digital Media
Technology and digital media play an increasingly significant role in health education:
- Online Health Information:Websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms provide access to a wealth of health information.
- Interactive Health Tools:Apps and websites offer tools for tracking fitness, managing chronic conditions, and accessing personalized health advice.
- Telehealth:Video conferencing and other technologies allow for remote consultations and health education sessions.
- Gamification:Using game-like elements to make health education more engaging and motivating.
Health Education Curriculum Development

Developing a comprehensive health education curriculum is essential for promoting healthy behaviors and improving overall well-being. This involves carefully considering the target audience, identifying key learning objectives, and selecting appropriate teaching methods and assessment strategies.
Curriculum Design for Adolescents
A health education curriculum for adolescents should address topics relevant to their developmental stage and the challenges they face.
Key Learning Objectives
- Understand the physical, emotional, and social changes associated with adolescence.
- Develop critical thinking skills related to health information and decision-making.
- Identify and manage stress and anxiety effectively.
- Learn about healthy relationships and communication skills.
- Gain knowledge about substance use and abuse prevention.
- Develop healthy eating habits and physical activity routines.
- Understand the importance of sexual health and responsible choices.
Assessment Strategies
- Pre- and post-tests to measure knowledge gain.
- Role-playing activities to assess communication and decision-making skills.
- Group projects to encourage collaboration and problem-solving.
- Journaling and reflective writing to promote self-awareness and critical thinking.
- Peer evaluations to foster feedback and accountability.
Resources and Materials
- Interactive websites and online resources tailored to adolescent interests.
- Guest speakers from healthcare professionals and community organizations.
- Videos, documentaries, and films addressing relevant health issues.
- Interactive games and simulations to engage learners.
- Health-related books, articles, and pamphlets.
Curriculum Design for Seniors
A health education curriculum for seniors should focus on maintaining health and well-being as they age.
Key Learning Objectives
- Understand the normal aging process and common health concerns.
- Develop strategies for managing chronic conditions and promoting healthy aging.
- Learn about available resources and support services for seniors.
- Improve physical activity levels and maintain functional independence.
- Enhance social connections and reduce isolation.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms for stress and emotional well-being.
- Understand the importance of preventative health measures and screenings.
Assessment Strategies
- Surveys and questionnaires to assess health knowledge and behaviors.
- Group discussions and sharing of personal experiences.
- Practical demonstrations and skill-building activities.
- Case studies and scenarios to apply health knowledge to real-life situations.
- Follow-up assessments to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement.
Resources and Materials
- Senior-friendly websites and online resources with accessible content.
- Health fairs and community events targeted at seniors.
- Brochures and pamphlets on age-related health topics.
- Videos and presentations by healthcare professionals.
- Support groups and peer mentoring programs for seniors.
Health Education in Different Settings

Health education is a crucial aspect of promoting well-being and preventing diseases. Its effectiveness depends heavily on the context in which it is delivered. This section explores the diverse approaches and challenges of implementing health education in various settings, highlighting the unique characteristics and opportunities of each environment.
Health Education in Schools
Schools play a vital role in shaping health behaviors and attitudes from a young age. School-based health education programs are designed to equip students with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to make informed decisions about their health. These programs typically cover topics such as nutrition, physical activity, substance abuse prevention, mental health, and sexual health.
- Strengths:School-based programs offer a structured environment for delivering health education, reaching a large number of students at a formative stage in their lives. Teachers, counselors, and other school personnel can provide consistent support and guidance. The school setting also allows for integrating health education into various subjects, reinforcing key concepts across the curriculum.
- Challenges:One challenge is the limited time available for health education, often competing with other academic priorities. Curriculum development and implementation require collaboration between educators, health professionals, and community stakeholders. Addressing sensitive topics, such as sexual health and substance abuse, can be challenging due to societal norms and parental concerns.
Health Education in Workplaces
Workplaces are increasingly recognizing the importance of promoting employee health and well-being. Workplace health education programs aim to improve employee health outcomes, reduce absenteeism, and boost productivity. These programs often focus on topics such as stress management, nutrition, physical activity, smoking cessation, and workplace safety.
- Strengths:Workplaces offer a captive audience, allowing for targeted interventions based on specific occupational hazards or employee demographics. Employers can incentivize participation through benefits or recognition programs. Workplace health education programs can foster a culture of health and well-being, encouraging employees to adopt healthy habits.
- Challenges:Implementing workplace health education programs can be challenging due to time constraints, competing priorities, and employee resistance to change. Addressing sensitive topics, such as mental health and substance abuse, may require careful consideration of privacy and confidentiality. The effectiveness of programs depends on the commitment and support of management and employees.
Health Education in Community Centers
Community centers provide a valuable platform for reaching diverse populations with health education messages. These programs often address health disparities and focus on topics such as chronic disease prevention, healthy aging, and access to healthcare.
- Strengths:Community centers offer a welcoming and accessible environment, reaching individuals who may not have access to other health services. They can build relationships with community members and tailor programs to address local health needs. Community centers often partner with local organizations and healthcare providers, leveraging existing resources and expertise.
- Challenges:Community centers often face limited funding and resources, requiring creative approaches to program development and implementation. Reaching underserved populations can be challenging due to transportation barriers, language differences, and cultural sensitivity. Building trust and engagement with community members requires sustained effort and collaboration.
Successful Health Education Initiatives
Numerous successful health education initiatives have been implemented in various settings, demonstrating the effectiveness of targeted interventions.
- School-based programs:The “Let’s Move” initiative, launched by former First Lady Michelle Obama, aimed to address childhood obesity through school-based programs promoting physical activity and healthy eating habits. The program has resulted in increased physical activity and improved nutrition choices among students.
- Workplace programs:The American Heart Association’s “Worksite Wellness” program provides resources and support for employers to implement workplace health programs, including health screenings, employee education, and health risk assessments. The program has been shown to reduce healthcare costs and improve employee health outcomes.
Health education is all about making informed choices for a healthier life. A key aspect of this is understanding where our food comes from and how to make healthy choices. One great way to do this is by learning about harvesting health food , which connects us to the source of our nutrition and helps us appreciate the importance of fresh, wholesome ingredients.
This knowledge can empower us to make better decisions about our food choices, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
- Community-based programs:The YMCA’s “Healthy Living” program offers community-based programs addressing health disparities, including chronic disease prevention, healthy aging, and access to healthcare. The program has been successful in improving health outcomes and promoting health equity among underserved populations.
Health Education and Behavior Change

Health education plays a crucial role in promoting positive health behaviors and improving overall well-being. It is essential to understand the theories and models that underpin behavior change to effectively design and implement health education interventions.
Theories and Models of Behavior Change
Theories and models of behavior change provide a framework for understanding the factors that influence individuals’ health behaviors. They help health educators identify target behaviors, develop appropriate interventions, and evaluate their effectiveness. Some prominent theories and models include:
- Health Belief Model:This model suggests that individuals’ beliefs about the severity of a health threat, their susceptibility to it, and the benefits and costs of taking action influence their behavior. For example, an individual who believes smoking is harmful and that they are likely to develop lung cancer if they continue smoking is more likely to quit.
- Theory of Planned Behavior:This theory emphasizes the role of attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control in shaping intentions and ultimately behavior. For instance, if an individual holds positive attitudes toward physical activity, believes that their social group supports it, and feels confident in their ability to engage in it, they are more likely to be physically active.
- Social Cognitive Theory:This theory emphasizes the reciprocal interaction between individuals, their behaviors, and their environment. It highlights the importance of observational learning, self-efficacy, and reinforcement in promoting behavior change. For example, seeing role models engage in healthy behaviors can increase an individual’s self-efficacy and motivate them to adopt those behaviors.
- Transtheoretical Model (Stages of Change):This model proposes that individuals progress through a series of stages when changing a behavior: precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance, and termination. Health education interventions can be tailored to each stage to support individuals’ efforts to change their behavior.
Examples of Effective Health Education Interventions
Numerous health education interventions have been successful in promoting positive health behaviors. Examples include:
- Smoking Cessation Programs:Programs that combine counseling, nicotine replacement therapy, and behavioral support have been effective in helping smokers quit. For example, the “Quitline” program, which provides telephone counseling and support to smokers, has been shown to increase quit rates significantly.
- Physical Activity Promotion Programs:Interventions that provide information about the benefits of physical activity, promote access to facilities and resources, and offer social support have been effective in increasing physical activity levels. For instance, community-based programs that offer free fitness classes and walking groups have been shown to improve physical activity participation.
- Nutrition Education Programs:Programs that teach individuals about healthy eating habits, provide cooking demonstrations, and promote access to affordable and nutritious foods have been effective in improving dietary choices. For example, school-based programs that teach children about healthy eating and provide them with opportunities to make healthy choices have been shown to improve dietary habits.
Role of Social and Environmental Factors
Social and environmental factors play a significant role in shaping health behaviors. These factors can either support or hinder individuals’ efforts to adopt healthy behaviors. Examples include:
- Social Norms:If an individual’s social group engages in unhealthy behaviors, they are more likely to do the same. For example, if a teenager’s friends smoke, they are more likely to start smoking themselves.
- Access to Resources:The availability of affordable and accessible healthcare, healthy food options, and safe places to exercise can influence health behaviors. For example, individuals living in food deserts may have limited access to fresh fruits and vegetables, making it difficult to maintain a healthy diet.
Health education plays a crucial role in promoting well-being, and it’s fascinating to see how even pop culture can contribute. For example, you can find some stunning beauty and beast wallpaper that might inspire a healthier lifestyle. These wallpapers can be a subtle reminder to prioritize self-care, and that’s a valuable message to integrate into everyday life.
- Policy and Environmental Factors:Policies that regulate smoking, promote physical activity, and improve access to healthy food can have a significant impact on health behaviors. For example, smoke-free policies in public places have been shown to reduce smoking rates.
Emerging Trends in Health Education

The field of health education is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing societal norms, and a growing understanding of human health. Emerging trends are shaping how health information is delivered, how individuals engage with health messages, and how health outcomes are achieved.
The Impact of Technology on Health Education, Health education health education
Technology has revolutionized health education, offering new ways to reach wider audiences, personalize learning experiences, and track progress.
- Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications:Mobile apps provide convenient access to health information, personalized fitness trackers, medication reminders, and interactive health education programs. Examples include apps that offer nutrition guidance, mental health support, and disease management tools.
- Social Media Platforms:Social media platforms have become powerful tools for health communication, allowing for the dissemination of health information, community engagement, and the sharing of personal health experiences. Health organizations utilize these platforms to raise awareness about health issues, promote healthy behaviors, and connect with individuals.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):VR and AR technologies are emerging as innovative tools for immersive health education experiences. VR simulations can provide realistic scenarios for training healthcare professionals, while AR applications can overlay digital information onto the real world, enhancing patient education and understanding of medical procedures.
Closure
In conclusion, health education plays a crucial role in shaping healthier societies. By equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to make informed choices about their health, it empowers them to take control of their well-being and contribute to a healthier future.
Through continuous innovation and adaptation, health education continues to evolve, embracing emerging technologies and social trends to reach broader audiences and create a lasting impact on health outcomes.
FAQ
What are the benefits of health education?
Health education offers numerous benefits, including improved health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, increased health literacy, and empowered individuals who actively participate in their health journey.
How can I get involved in health education?
There are many ways to get involved in health education, such as volunteering at community health organizations, participating in health education programs, or advocating for health policies that promote well-being.