The public health nurse job is a critical component of public health, focusing on improving the health and well-being of entire communities. Public health nurses are often found working in various settings, including community health centers, schools, and public health departments, playing a vital role in addressing health disparities and promoting healthy lifestyles.
Their work extends beyond traditional hospital-based nursing, encompassing a broader spectrum of responsibilities that involve community outreach, health education, and disease prevention. Public health nurses are trained to assess the health needs of populations, develop programs to address those needs, and advocate for policies that improve community health.
Public Health Nurse Role and Responsibilities
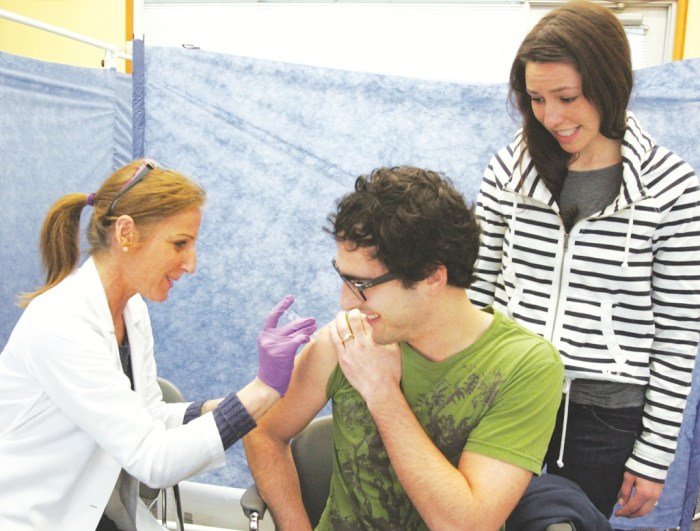
Public health nurses play a crucial role in promoting and protecting the health of individuals and communities. They are dedicated to improving the health outcomes of diverse populations by addressing health disparities and advocating for equitable access to healthcare services.
Core Duties and Responsibilities
Public health nurses are responsible for a wide range of duties that contribute to the overall well-being of the community. Their core responsibilities include:
- Health Education and Promotion:Public health nurses educate individuals and communities about health issues, risk factors, and preventive measures. They develop and implement health education programs, workshops, and campaigns to promote healthy behaviors and lifestyles.
- Disease Prevention and Control:Public health nurses play a vital role in preventing and controlling the spread of infectious diseases. They conduct surveillance, identify outbreaks, and implement interventions to protect the public health.
- Health Screening and Assessment:Public health nurses provide health screenings for various conditions, such as blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes. They also conduct health assessments to identify health risks and needs within the community.
- Case Management and Referral:Public health nurses provide case management services to individuals and families who need assistance navigating the healthcare system. They connect individuals with resources and services, such as medical care, social support, and mental health services.
- Community Health Planning and Policy Development:Public health nurses actively participate in community health planning and policy development. They collaborate with stakeholders to address health issues and advocate for policies that promote health equity.
- Research and Data Analysis:Public health nurses contribute to research and data analysis to identify health trends, evaluate interventions, and inform public health policies.
Populations Served
Public health nurses serve a diverse range of populations, including:
- Children and Families:Public health nurses provide prenatal care, well-child checkups, immunizations, and health education to children and families.
- Older Adults:Public health nurses assist older adults with managing chronic conditions, accessing healthcare services, and promoting healthy aging.
- Individuals with Chronic Diseases:Public health nurses provide education, support, and disease management services to individuals with chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and asthma.
- Individuals Experiencing Homelessness:Public health nurses provide outreach and health services to individuals experiencing homelessness, addressing their unique health needs and promoting access to healthcare.
- Immigrant and Refugee Populations:Public health nurses provide culturally sensitive health services and support to immigrant and refugee populations, addressing language barriers, cultural beliefs, and health disparities.
- Individuals with Mental Health Conditions:Public health nurses work to promote mental health and well-being, providing support and resources to individuals with mental health conditions.
Key Differences from Traditional Hospital-Based Nurses
Public health nurses differ from traditional hospital-based nurses in several key aspects:
- Focus on Population Health:Public health nurses focus on the health of entire populations rather than individual patients. They prioritize preventive measures and address health disparities within communities.
- Community-Based Practice:Public health nurses work in community settings, such as schools, clinics, and community centers, rather than hospital settings. They engage with individuals and communities to address health needs and promote well-being.
- Emphasis on Public Health Principles:Public health nurses are guided by public health principles, such as social justice, equity, and health promotion. They advocate for policies and programs that improve the health of all members of the community.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges, Public health nurse job
Public health nurses face a range of ethical considerations and challenges in their work:
- Confidentiality and Privacy:Public health nurses must maintain the confidentiality and privacy of their clients’ health information, while also balancing the need to protect the public health.
- Resource Allocation:Public health nurses often work with limited resources and must make difficult decisions about how to allocate those resources to meet the needs of the community.
- Advocacy and Social Justice:Public health nurses are advocates for social justice and health equity. They face challenges in addressing systemic barriers to health and promoting access to healthcare for all members of the community.
Education and Training Requirements
Becoming a public health nurse requires a solid educational foundation and specialized training. This section will explore the necessary qualifications, certifications, and continuing education opportunities to excel in this vital field.
Educational Qualifications
A Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) is the minimum educational requirement for most public health nurse positions. This degree provides a comprehensive understanding of nursing principles, clinical practice, and health promotion.
Licensure and Certification
Public health nurses must be licensed in the state where they practice. Licensure requirements vary by state but generally include:
- Graduation from an accredited nursing program
- Passing the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN)
- Meeting state-specific continuing education requirements
In addition to licensure, many public health nurses pursue specialized certifications to demonstrate advanced knowledge and skills in specific areas. Examples include:
- Certified Public Health Nurse (CPHN): This certification, offered by the National Board for Public Health Examiners (NBPHE), recognizes expertise in public health nursing practice.
- Certified Health Education Specialist (CHES): This certification, awarded by the National Commission for Health Education Credentialing (NCHEC), validates competency in health education principles and practices.
Relevant Coursework
Public health nursing programs typically include coursework in:
- Public Health:This foundational course provides an overview of public health principles, concepts, and systems.
- Epidemiology:This course focuses on the study of disease patterns, risk factors, and interventions to prevent and control health problems.
- Community Health:This course explores the social, environmental, and cultural factors that influence health within communities, and examines strategies for addressing health disparities.
- Health Promotion and Education:This course covers the principles and practices of health education, including program planning, implementation, and evaluation.
- Biostatistics:This course teaches the application of statistical methods to public health research and data analysis.
Continuing Education
Public health nurses are expected to maintain their knowledge and skills through ongoing professional development. This can be achieved through:
- Conferences and Workshops:Attending conferences and workshops offers opportunities to learn about new trends, research findings, and best practices in public health.
- Online Courses:Online courses provide flexible and convenient access to a wide range of public health topics.
- Journal Articles:Reading peer-reviewed journal articles keeps public health nurses informed about the latest research and evidence-based practices.
Key Areas of Focus in Public Health Nursing
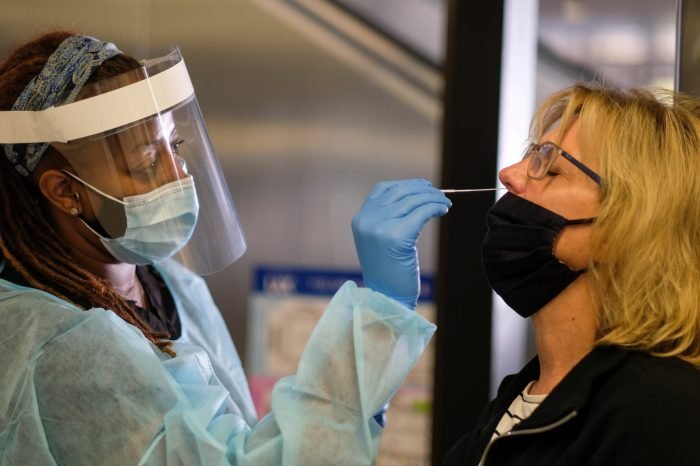
Public health nurses play a crucial role in improving the health and well-being of communities. They work in various settings, including clinics, schools, workplaces, and homes, to address a wide range of health issues. Their focus extends beyond individual patients to encompass the health of entire populations.Public health nursing is a specialized field that focuses on promoting health, preventing disease, and improving the health outcomes of populations.
Public health nurses work in various settings, including communities, schools, workplaces, and clinics, to address a wide range of health issues. They collaborate with other healthcare professionals, community leaders, and policymakers to achieve their goals.
Areas of Focus in Public Health Nursing
The following table highlights key areas of focus in public health nursing:
| Area of Focus | Description | Example Activities | Impact on Public Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community Health Assessment and Planning | This involves gathering data about the health status of a community, identifying health needs, and developing strategies to address those needs. | Conducting community health surveys, analyzing health data, developing community health plans, and collaborating with community stakeholders. | Improved community health outcomes, more efficient use of resources, and targeted interventions to address specific health needs. |
| Disease Prevention and Control | This focuses on preventing the spread of infectious and chronic diseases through various strategies, including vaccination, screening, and education. | Implementing vaccination programs, conducting screenings for diseases like cancer and diabetes, providing education on disease prevention, and promoting healthy behaviors. | Reduced incidence of preventable diseases, improved population health, and reduced healthcare costs. |
| Health Education and Promotion | This involves educating individuals and communities about health issues, promoting healthy behaviors, and empowering people to make informed decisions about their health. | Developing and delivering health education programs, promoting healthy lifestyles, providing counseling on health risks, and advocating for policies that support health. | Increased health knowledge and awareness, improved health behaviors, and reduced health disparities. |
| Maternal and Child Health | This focuses on improving the health of mothers and children, including prenatal care, childbirth education, and postpartum support. | Providing prenatal care, educating mothers about breastfeeding, promoting infant and child health, and advocating for policies that support maternal and child health. | Reduced maternal and infant mortality rates, improved child development, and healthier families. |
| Environmental Health | This involves protecting the environment and promoting public health by addressing environmental hazards, such as air and water pollution, and promoting safe food handling practices. | Monitoring environmental hazards, educating the public about environmental health risks, advocating for environmental policies, and collaborating with environmental agencies. | Improved air and water quality, reduced exposure to environmental toxins, and improved overall health and well-being. |
| Mental Health and Substance Abuse | This focuses on promoting mental health and preventing substance abuse through early intervention, counseling, and support services. | Providing mental health screenings, offering counseling services, educating the public about mental health issues, and advocating for policies that support mental health and substance abuse prevention. | Improved mental health outcomes, reduced substance abuse rates, and increased access to mental health services. |
| Emergency Preparedness and Response | This involves preparing for and responding to public health emergencies, such as natural disasters, pandemics, and outbreaks. | Developing emergency preparedness plans, training community members in emergency response, providing medical care during emergencies, and collaborating with emergency response agencies. | Improved community resilience, reduced morbidity and mortality during emergencies, and efficient response to public health threats. |
Skills and Competencies
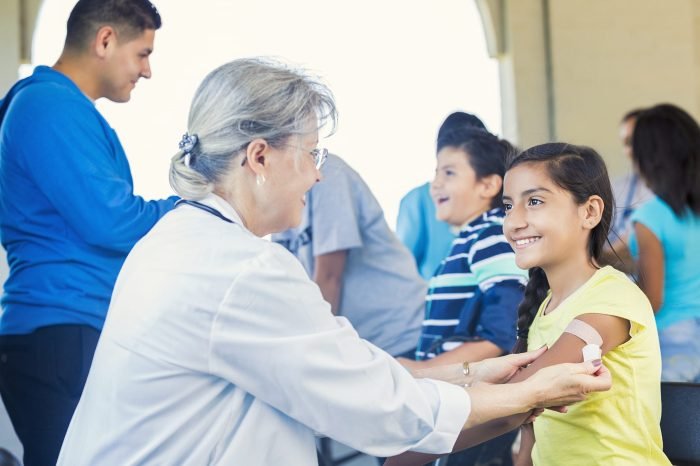

Public health nurses require a unique blend of skills and competencies to effectively address the health needs of communities. These skills can be categorized into two main groups: hard skills and soft skills. Hard skills are technical abilities that can be learned and measured, while soft skills are personal attributes that influence how effectively individuals interact with others and navigate complex situations.
Hard Skills
Hard skills are essential for public health nurses to perform their duties effectively. These skills allow them to collect, analyze, and interpret data, develop and implement health programs, and communicate effectively with diverse audiences.
- Epidemiology and data analysis: Public health nurses use epidemiological principles to understand the distribution and determinants of health and disease in populations. They analyze data to identify trends, risk factors, and areas where interventions are needed. This involves understanding statistical methods, interpreting data, and using data visualization tools to present findings clearly.
For example, a public health nurse might analyze data on childhood obesity rates to identify communities with higher rates and determine potential risk factors, such as access to healthy food options and physical activity opportunities.
- Program planning and evaluation: Public health nurses are responsible for developing and implementing health programs that address specific health issues in communities. This involves using evidence-based practices, setting realistic goals and objectives, and developing strategies to achieve those goals. They also evaluate the effectiveness of programs to ensure they are meeting their intended outcomes.
For instance, a public health nurse might plan and implement a program to promote breastfeeding among new mothers. This would involve collaborating with community partners, developing educational materials, and providing support services. The nurse would also evaluate the program’s impact by tracking breastfeeding rates and seeking feedback from participants.
- Communication and interpersonal skills: Public health nurses need to communicate effectively with diverse individuals and groups, including patients, community members, healthcare providers, and policymakers. This involves active listening, clear and concise communication, and adapting communication styles to different audiences. For example, a public health nurse might need to explain complex health information to a group of seniors in a way that is easy to understand.
They might also need to advocate for health policy changes with policymakers, using persuasive communication to explain the rationale for the proposed changes.
- Cultural competency: Public health nurses work with diverse populations and need to understand and respect different cultural beliefs, values, and practices. This involves recognizing how cultural factors can influence health behaviors and accessing resources. For example, a public health nurse working with a Hispanic community might need to understand the cultural significance of family and the role of traditional healers in health decision-making.
They would then adapt their approach to health education and outreach to be culturally sensitive and respectful.
- Health policy and advocacy: Public health nurses are involved in advocating for policies that promote health and well-being. This involves understanding health policy issues, advocating for policy changes, and working with policymakers to develop and implement policies that address health disparities. For example, a public health nurse might advocate for policies that increase access to affordable healthcare, promote healthy food choices, and reduce tobacco use.
They might also work with policymakers to develop programs that address specific health issues, such as mental health or substance abuse.
Soft Skills
Soft skills are equally important for public health nurses, as they enable them to build strong relationships, navigate complex situations, and achieve positive outcomes. These skills are essential for effective collaboration, communication, and problem-solving in public health settings.
Public health nurses play a crucial role in promoting health and well-being within communities. Their work often involves educating individuals about healthy lifestyle choices, which can encompass everything from proper nutrition to stress management. For example, a public health nurse might encourage individuals to prioritize self-care practices, such as visiting a beauty salon Fremont CA for a relaxing massage or facial.
Ultimately, public health nurses strive to empower individuals to make choices that support their overall health and well-being.
- Empathy and compassion: Public health nurses work with individuals and families facing health challenges. Empathy allows them to understand and connect with their clients’ experiences, while compassion motivates them to provide supportive and caring services. For instance, a public health nurse working with a family struggling with chronic illness might use empathy to understand their challenges and offer support and resources tailored to their needs.
Public health nurses play a vital role in promoting community well-being, often working with diverse populations to address health disparities. However, even with the best intentions, sometimes personal goals need to be re-evaluated, like when a gym membership no longer aligns with your schedule.
If you’re looking to cancel your Planet Fitness membership, you can find detailed instructions on how to do so online here. Once you’ve freed up your budget and time, you can focus on your public health nursing duties with renewed energy and commitment.
- Critical thinking and problem-solving: Public health nurses often face complex health issues and need to analyze situations, identify potential solutions, and implement effective strategies. Critical thinking skills allow them to evaluate information, identify patterns, and develop creative solutions. For example, a public health nurse might need to identify the root causes of a local health problem, such as high rates of childhood asthma, and develop a comprehensive plan to address the issue.
- Teamwork and collaboration: Public health nurses rarely work in isolation. They collaborate with healthcare providers, community organizations, policymakers, and other stakeholders to address health issues. Teamwork skills enable them to work effectively in teams, share information, and contribute to collective goals. For example, a public health nurse might collaborate with local schools to implement a program to promote healthy eating habits among students.
- Adaptability and resilience: Public health nursing involves working in dynamic and challenging environments. Public health nurses need to be adaptable to changing circumstances, able to adjust their approaches, and resilient in the face of setbacks. For instance, a public health nurse might need to adapt their program plans in response to unexpected events or community needs.
They might also need to remain resilient when facing obstacles or challenges in their work.
Career Paths and Opportunities: Public Health Nurse Job

Public health nurses have a wide range of career paths available to them, offering diverse opportunities to make a significant impact on the health and well-being of communities. These career paths span various settings, each presenting unique roles and responsibilities.
Community Health Centers
Community health centers are non-profit organizations that provide comprehensive health care services to underserved populations. Public health nurses working in these centers play a crucial role in providing preventive care, health education, and outreach programs. They may conduct health screenings, administer immunizations, and provide case management services.
Public Health Departments
Public health departments are government agencies responsible for protecting and improving the health of the community. Public health nurses in these departments work on a variety of initiatives, including disease surveillance, outbreak investigation, health education campaigns, and program development. They may also be involved in community health assessments, policy development, and advocacy.
Non-profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations dedicated to improving health outcomes often employ public health nurses. These organizations may focus on specific health issues, such as HIV/AIDS, chronic diseases, or mental health. Public health nurses in non-profit settings may provide direct patient care, conduct research, develop educational materials, or advocate for policy changes.
Schools and Universities
Public health nurses working in schools and universities provide health services to students, faculty, and staff. They may conduct health screenings, administer immunizations, provide counseling and education on health topics, and coordinate with parents and guardians. In universities, they may also participate in research projects and teach public health courses.
Government Agencies
Beyond public health departments, public health nurses can work for other government agencies, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO). These roles often involve conducting research, developing national health policies, and providing technical assistance to other countries.
Impact of Public Health Nursing on Community Health
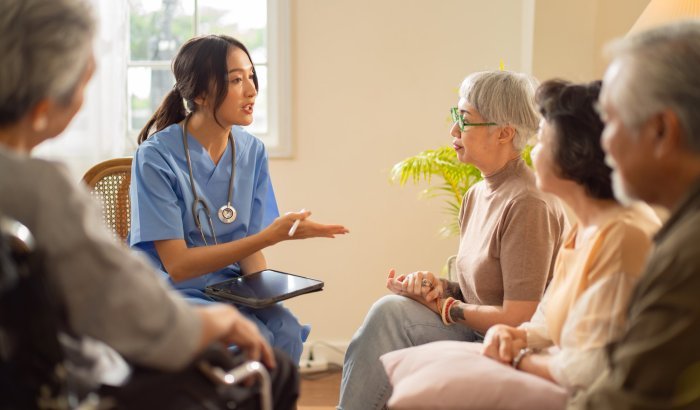

Public health nurses play a pivotal role in improving the health of communities by addressing health concerns, promoting wellness, and advocating for equitable access to healthcare. Their dedication to promoting health and well-being extends beyond individual care to encompass the broader community, fostering a healthier and more resilient society.
Examples of Successful Public Health Initiatives Led by Nurses
Public health nurses have spearheaded numerous successful initiatives that have significantly impacted community health. Their efforts have been instrumental in addressing critical health challenges and promoting positive health outcomes.
- Immunization Programs:Public health nurses have been instrumental in promoting widespread immunization programs, leading to a significant reduction in vaccine-preventable diseases. Their efforts involve educating the public about the benefits of vaccines, administering vaccines to children and adults, and monitoring vaccine coverage rates to ensure high immunization rates within communities.
- Maternal and Child Health Programs:Public health nurses have played a crucial role in improving maternal and child health outcomes. They provide prenatal care, conduct home visits to support new mothers, educate families about child development, and advocate for access to quality healthcare services for mothers and children.
Public health nurses play a vital role in ensuring the health and well-being of communities. One aspect of their work involves navigating the complex world of health insurance, including understanding different plan options. For those seeking more personalized coverage, exploring independent health plans might be a suitable avenue.
Public health nurses often serve as resources for individuals seeking guidance on these plans, ensuring they have access to quality healthcare that meets their specific needs.
- Chronic Disease Management:Public health nurses are actively involved in chronic disease management programs, aiming to prevent, manage, and control chronic illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. They provide education, support, and resources to individuals with chronic conditions, helping them manage their illnesses effectively and improve their quality of life.
Challenges Faced by Public Health Nurses in Addressing Health Disparities and Inequalities
Public health nurses encounter significant challenges in their efforts to address health disparities and inequalities. These disparities are often rooted in social determinants of health, such as poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and discrimination, which contribute to health inequities.
- Access to Healthcare:Many communities face challenges in accessing quality healthcare services, particularly those with limited resources or living in rural areas. Public health nurses often work to bridge this gap by providing essential healthcare services, advocating for increased access to healthcare, and connecting individuals with necessary resources.
- Social Determinants of Health:Public health nurses recognize the profound impact of social determinants of health on individuals’ well-being. They address these factors by promoting social justice, advocating for policies that address poverty and inequality, and working to create healthier environments for all communities.
- Health Disparities:Public health nurses are committed to addressing health disparities, which are differences in health outcomes among various population groups. They work to identify and understand the root causes of these disparities, advocate for policies that promote health equity, and develop culturally sensitive interventions that meet the unique needs of diverse communities.
Insights on the Future of Public Health Nursing and Its Role in Addressing Emerging Health Concerns
The future of public health nursing holds significant promise as the profession continues to evolve and adapt to emerging health challenges. Public health nurses are uniquely positioned to address complex health issues and promote health equity in the face of global health challenges and technological advancements.
- Emerging Health Concerns:Public health nurses are at the forefront of addressing emerging health concerns, such as infectious diseases, climate change, and mental health challenges. They play a critical role in educating communities, promoting preventive measures, and advocating for policies that address these issues.
- Technology and Innovation:Public health nurses are embracing technology and innovation to enhance their practice and reach broader populations. Telehealth, mobile health applications, and data analytics are transforming how they deliver care, monitor health trends, and connect with individuals in need.
- Health Equity and Social Justice:Public health nurses are increasingly focusing on health equity and social justice. They advocate for policies that promote health equity, address the social determinants of health, and ensure that everyone has access to quality healthcare.
Conclusive Thoughts
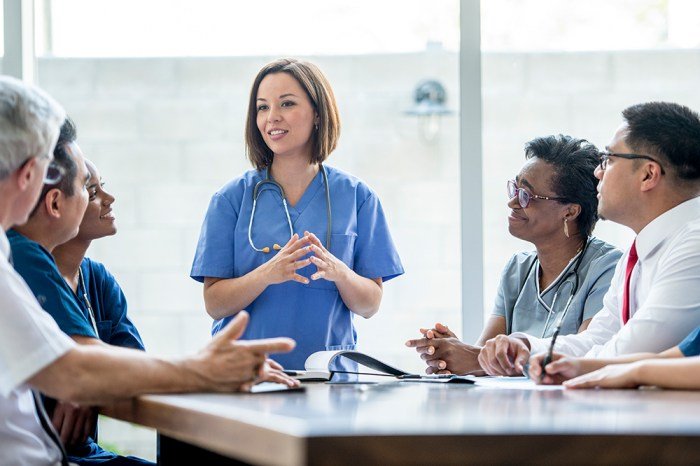

Public health nurses are instrumental in building healthier communities by bridging the gap between healthcare and the public. Their dedication to improving community health is evident in their diverse roles, from promoting healthy lifestyles to responding to public health emergencies.
As the field of public health continues to evolve, public health nurses will play an increasingly vital role in shaping a healthier future for all.
Questions Often Asked
What is the salary range for a public health nurse?
The salary for a public health nurse can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, and employer. However, the average salary for public health nurses in the United States is typically between $50,000 and $80,000 per year.
What are the benefits of working as a public health nurse?
Public health nursing offers a variety of benefits, including the opportunity to make a real difference in the lives of individuals and communities, a diverse and challenging work environment, and the chance to work with a team of dedicated professionals.
What are the challenges of working as a public health nurse?
Public health nurses often face challenges such as limited resources, high caseloads, and the need to work with diverse populations with varying health needs and cultural backgrounds.
How can I become a public health nurse?
To become a public health nurse, you will need to obtain a bachelor’s degree in nursing and a master’s degree in public health or a related field. You will also need to pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN) and obtain a public health nursing certification.