County Health Rankings offer a comprehensive snapshot of health outcomes across the United States, providing valuable insights into the factors that influence community well-being. By examining health outcomes, health factors, and policy interventions, these rankings shed light on the intricate relationship between health and various aspects of life.
These rankings go beyond simply listing counties from best to worst. They delve into the underlying causes of health disparities, highlighting areas where communities can focus their efforts to improve health outcomes. The rankings encompass a wide range of factors, including health behaviors, access to healthcare, social and economic conditions, and the physical environment.
This comprehensive approach allows for a nuanced understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing different communities.
Understanding County Health Rankings

The County Health Rankings are an annual assessment of the health of nearly every county in the United States. They aim to provide a comprehensive view of the health status of communities across the nation and identify areas for improvement.
Methodology
The County Health Rankings use a data-driven approach to assess county health. They employ a methodology that combines health outcomes and health factors, providing a holistic view of county health.
Health Outcomes
Health outcomes measure the length and quality of life in a county. The rankings use two key indicators:
- Years of Potential Life Lost (YPLL): This measure reflects the number of years lost due to premature death. A higher YPLL indicates a shorter average lifespan in the county.
- Poor or Fair Health Status: This indicator represents the proportion of residents who report their health as poor or fair. A higher percentage indicates a greater prevalence of poor health.
Health Factors
Health factors are the conditions that influence health outcomes. They are categorized into five domains:
- Health Behaviors: These include factors like smoking, physical activity, diet, and alcohol consumption.
- Clinical Care: This domain focuses on access to quality healthcare services, including preventive screenings and chronic disease management.
- Social and Economic Factors: This category encompasses factors like poverty, education, employment, and housing that influence health outcomes.
- Physical Environment: This domain examines the physical surroundings of a county, including air and water quality, access to safe and affordable housing, and recreational opportunities.
- Community and Policy: This domain considers factors like access to healthy foods, safe transportation, and community support systems that contribute to overall health.
Policies
Policies play a significant role in shaping the health of a community. The County Health Rankings examine policies related to:
- Tobacco Control: Policies that restrict smoking in public places and increase tobacco taxes can help reduce smoking rates and improve health outcomes.
- Access to Healthy Foods: Policies that promote healthy food choices, such as zoning regulations that encourage grocery stores in underserved areas, can improve dietary habits.
- Physical Activity: Policies that encourage physical activity, such as creating bike lanes and pedestrian-friendly environments, can promote a healthier lifestyle.
Health Outcomes
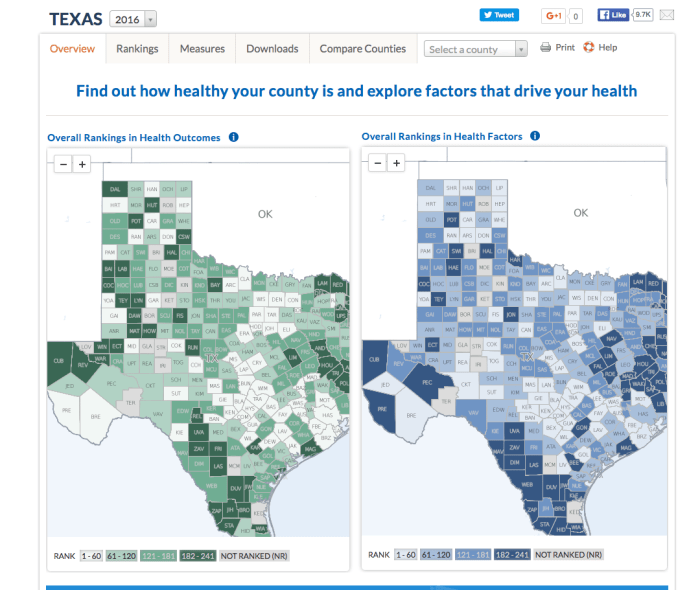
The County Health Rankings measure the health of the population in each county across the United States. They use a set of health outcomes and health factors to paint a picture of how healthy people are and the conditions that influence their health.
Health outcomes are the results of people’s health status, including how long they live and how healthy they feel. These outcomes are influenced by a variety of factors, including their access to healthcare, their environment, and their behaviors.
Trends in Health Outcomes
The County Health Rankings track trends in health outcomes over time, providing valuable insights into the progress made in improving health and the areas where more work is needed.
- Life Expectancy: Life expectancy has been steadily increasing in the United States, but there are significant disparities across counties. Some counties have seen a decline in life expectancy, particularly in areas with high rates of poverty, unemployment, and limited access to healthcare.
- Mortality Rates: Mortality rates from preventable causes, such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, and diabetes, have been declining over time. However, disparities in mortality rates persist across counties and population groups.
- Premature Death: The number of years lost due to premature death has been decreasing, but disparities remain. Counties with higher poverty rates and lower levels of education tend to have higher rates of premature death.
- Self-Reported Health: The proportion of adults who report being in good or excellent health has been increasing, but there are still disparities across counties.
Disparities in Health Outcomes
Disparities in health outcomes exist across counties and population groups, reflecting underlying differences in social determinants of health.
- Race and Ethnicity: People of color consistently experience worse health outcomes than white people. This is due to a complex interplay of factors, including systemic racism, socioeconomic inequalities, and limited access to healthcare.
- Income: People with lower incomes tend to have worse health outcomes than those with higher incomes. This is due to factors such as limited access to healthy food, safe housing, and quality healthcare.
- Education: People with lower levels of education tend to have worse health outcomes than those with higher levels of education. This is due to factors such as lower-paying jobs, limited access to healthcare, and higher rates of unhealthy behaviors.
- Geography: Health outcomes can vary significantly across counties, with rural areas often facing greater challenges. Factors such as limited access to healthcare, lower employment opportunities, and higher rates of poverty contribute to these disparities.
Health Factors
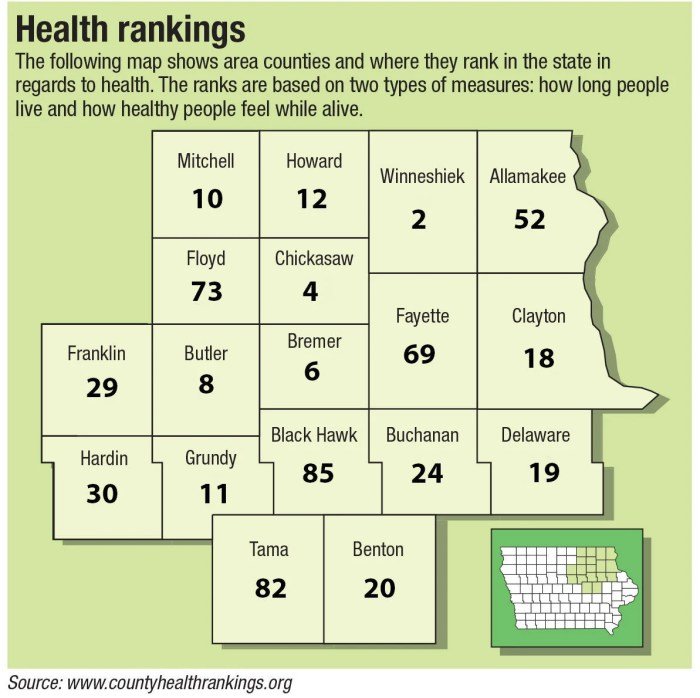
The County Health Rankings use a set of health factors to understand and measure the overall health of a county. These factors represent the key elements that influence the health of a community and are grouped into four distinct categories: health behaviors, clinical care, social and economic factors, and physical environment.
The County Health Rankings consider these factors to be essential for improving health outcomes. Each factor plays a crucial role in shaping the health of individuals and communities, and addressing these factors is key to creating a healthier environment for everyone.
Health Behaviors
Health behaviors are the choices and actions people take that affect their health. These behaviors can have a significant impact on health outcomes, both positive and negative. Understanding and addressing these behaviors is crucial for improving health and well-being in a community.
- Tobacco use: Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke contribute to various health problems, including heart disease, stroke, cancer, and lung disease.
- Alcohol and drug use: Excessive alcohol consumption and drug abuse can lead to various health issues, including liver disease, mental health problems, and accidents.
- Physical inactivity: Lack of physical activity increases the risk of obesity, heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
- Unhealthy diet: Diets high in saturated fat, sugar, and sodium and low in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contribute to various health problems, including obesity, heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
- Sexual behaviors: Risky sexual behaviors can lead to sexually transmitted infections (STIs), unplanned pregnancies, and other health problems.
Clinical Care
Clinical care encompasses the services provided by healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and other medical personnel. This category focuses on the quality and accessibility of healthcare services, which play a vital role in preventing and managing health conditions.
- Access to care: This refers to the ability of individuals to obtain necessary healthcare services when they need them. Factors that influence access to care include insurance coverage, distance to healthcare providers, and availability of transportation.
- Quality of care: The quality of healthcare services refers to the effectiveness, safety, and efficiency of the care provided.
- Preventive care: Preventive care services aim to identify and address health risks before they become serious problems. Examples include vaccinations, screenings for cancer and other diseases, and counseling on healthy behaviors.
Social and Economic Factors
Social and economic factors are the conditions in which people live, work, and learn. These factors can significantly influence health outcomes, and addressing them is crucial for creating healthier communities.
- Education: Education levels are linked to health outcomes. People with higher levels of education tend to have better health, live longer, and experience fewer health problems.
- Income: Income is a significant factor in health. People with lower incomes are more likely to experience poor health, have limited access to healthcare, and live in neighborhoods with fewer resources.
- Social support: Social support refers to the relationships and connections that individuals have with others. Strong social connections can provide emotional support, reduce stress, and promote healthy behaviors.
- Community safety: Living in a safe community can positively impact health outcomes. Safe communities reduce exposure to violence, crime, and environmental hazards.
- Discrimination: Discrimination based on race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, or other factors can negatively impact health outcomes.
Physical Environment
The physical environment encompasses the places where people live, work, learn, and play. This category includes factors such as air and water quality, access to safe and affordable housing, and the availability of parks and green spaces.
County health rankings often highlight the importance of overall well-being, which encompasses both physical and mental health. A thriving community might find solace in pampering themselves at a local spa like blooming beauty lounge , where relaxation and rejuvenation can contribute to a positive outlook.
Ultimately, county health rankings strive to create a holistic picture of community health, acknowledging that factors like mental well-being and access to self-care services play a significant role.
- Air quality: Air pollution can contribute to respiratory problems, heart disease, and other health issues.
- Water quality: Access to clean and safe drinking water is essential for good health.
- Housing quality: Housing quality can affect health outcomes.
- Access to healthy foods: Access to affordable and nutritious food is essential for good health.
- Access to safe and affordable transportation: Access to safe and affordable transportation is essential for people to access healthcare, employment, education, and other resources.
- Access to recreational opportunities: Parks, green spaces, and other recreational opportunities can promote physical activity and mental well-being.
Policy and Community Interventions
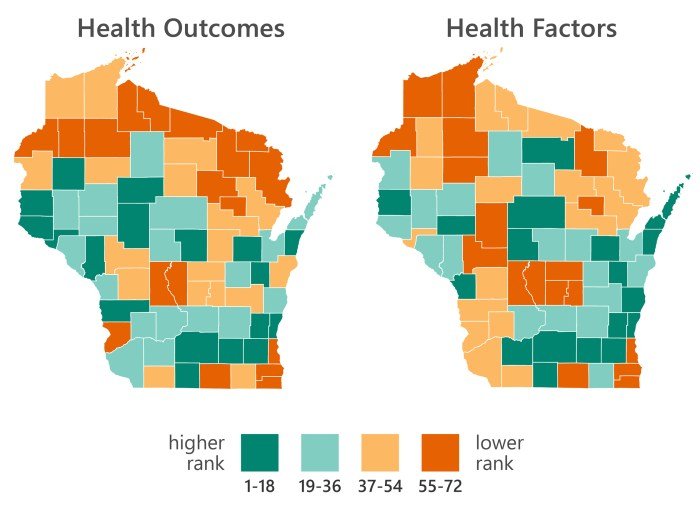
Improving county health rankings requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond individual behavior changes. Policy and community interventions play a crucial role in creating environments that support healthy choices and address the root causes of health disparities.
Policies to Improve Health Outcomes
Policies can significantly influence health outcomes by shaping the environment and providing access to resources.
- Smoke-free policies:Implementing smoke-free policies in public places and workplaces reduces exposure to secondhand smoke, leading to improved respiratory health and reduced risk of heart disease and cancer.
- Food policies:Policies that promote access to healthy foods, such as subsidies for farmers’ markets and incentives for grocery stores to stock fresh produce in low-income areas, can improve nutrition and reduce obesity rates.
- Physical activity policies:Policies that encourage physical activity, such as funding for parks and recreation programs, building bike lanes, and promoting walkable communities, can increase physical activity levels and reduce chronic diseases.
- Affordable housing policies:Providing affordable housing options reduces stress and improves mental health, leading to better overall health outcomes.
Community Interventions for Healthier Communities
Community interventions focus on creating supportive environments and promoting healthy behaviors through collaborative efforts.
- Community health centers:These centers provide accessible and affordable healthcare services to underserved populations, addressing health disparities and improving health outcomes.
- Health education programs:Community-based health education programs can raise awareness about health risks, promote healthy behaviors, and empower individuals to make informed choices.
- Community gardens:Community gardens provide opportunities for residents to grow their own fresh produce, improving nutrition and fostering a sense of community.
- Social support programs:Programs that provide social support, such as mentoring programs and support groups, can address social determinants of health and improve mental well-being.
Data Visualization and Analysis
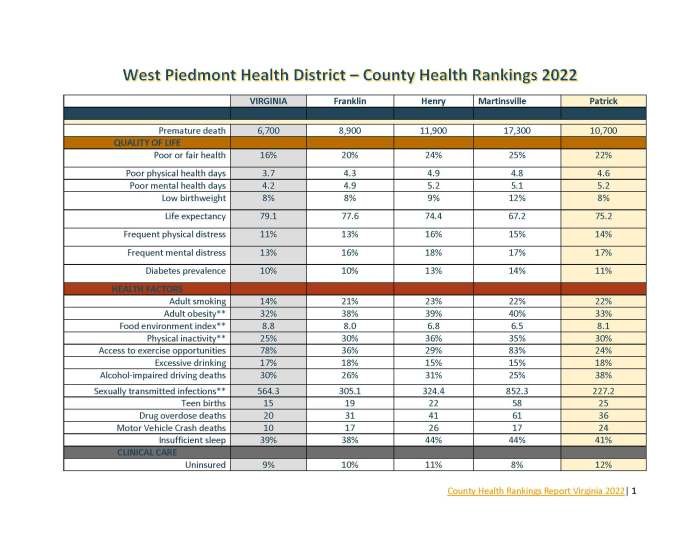
Data visualization and analysis are crucial components of the County Health Rankings, providing insights into the complex factors influencing health outcomes and offering opportunities for improvement. By leveraging visual representations and statistical methods, we can identify trends, patterns, and areas of strength and weakness across counties.
Interactive Table
An interactive table can effectively display the rankings of several counties, including their health outcomes, health factors, and policy scores. The table can be designed with sortable columns, allowing users to easily compare and analyze data based on different criteria.
For example, users could sort by overall health ranking, life expectancy, or prevalence of obesity to gain a deeper understanding of the factors influencing health outcomes in different counties.
Example: An interactive table could display the rankings of five counties in a state, including their overall health ranking, premature death rate, high school graduation rate, and percentage of adults with obesity. The table would allow users to sort the columns, highlighting counties with high premature death rates or low high school graduation rates, providing valuable insights into areas for improvement.
Geographic Map Visualization
A map visualization is an effective way to highlight the geographical distribution of county health rankings. Using color gradients or other visual cues, the map can represent the relative health rankings of counties, enabling users to quickly identify areas with higher or lower health outcomes.
This visual representation can be particularly helpful for understanding spatial patterns and identifying potential clusters of counties with similar health challenges.
Example: A map visualization could display the overall health rankings of counties in a state, using color gradients to represent the relative health rankings. Counties with higher overall health rankings would be represented with darker shades of green, while counties with lower rankings would be represented with darker shades of red. This visualization would quickly identify areas with high or low health outcomes, potentially highlighting the need for targeted interventions.
Data Analysis and Trends
Analyzing the data collected for the County Health Rankings can reveal important patterns and trends. For instance, examining the correlation between health factors and health outcomes can identify key areas for intervention. For example, a strong correlation between the prevalence of smoking and premature death rates might suggest that tobacco control programs could have a significant impact on improving health outcomes.
Example: Analyzing the data might reveal a strong correlation between the percentage of adults with diabetes and the rate of premature death in a state. This finding could indicate that addressing diabetes management and prevention could be a critical step in improving health outcomes in the state.
County health rankings can often highlight disparities in access to quality healthcare. Organizations like the Henry Austin Health Center play a vital role in addressing these disparities by providing essential services to underserved communities. By focusing on preventative care and health education, these centers contribute to improving overall health outcomes and ultimately enhancing county health rankings.
Implications and Recommendations

The County Health Rankings provide valuable insights into the health status of communities across the nation. These rankings serve as a powerful tool for policymakers, public health practitioners, and community leaders to identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance health outcomes.
Implications for Public Health Policy and Practice
The rankings highlight the interconnectedness of health factors and the need for a comprehensive approach to address health disparities. They underscore the importance of addressing social determinants of health, such as poverty, education, and access to healthcare, as these factors significantly influence health outcomes.
The rankings can inform the development of policies and programs that promote health equity and improve the overall health of communities.
Key Areas for Improvement and Recommendations
The rankings provide a framework for identifying key areas for improvement and developing targeted interventions.
County health rankings offer a snapshot of community well-being, highlighting areas where improvement is needed. A comprehensive approach to boosting health outcomes often involves implementing a program for health and wellness that addresses factors like nutrition, physical activity, and mental health.
By focusing on these areas, communities can work towards achieving better overall health rankings and creating a healthier environment for all.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health
- Promote Economic Opportunity:Investing in education, job training, and affordable housing can create opportunities for individuals and families to improve their socioeconomic status, which is directly linked to health outcomes.
- Reduce Poverty:Implementing policies that address income inequality and provide support to low-income families can help alleviate poverty, a major driver of health disparities.
- Improve Access to Healthcare:Expanding access to affordable healthcare, including preventive care and mental health services, is crucial for addressing health disparities and improving overall health.
- Enhance Education and Employment Opportunities:Investing in early childhood education and providing opportunities for lifelong learning can equip individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in the workforce and improve their health outcomes.
Promoting Healthy Behaviors
- Encourage Physical Activity:Creating safe and accessible spaces for physical activity, such as parks and walking trails, can encourage people to be more active, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Promote Healthy Eating:Implementing policies that encourage healthy food choices, such as providing healthy food options in schools and workplaces, can help reduce the prevalence of obesity and other diet-related diseases.
- Reduce Tobacco Use:Enacting smoke-free policies and providing cessation programs can help reduce tobacco use, a leading cause of preventable death.
- Address Substance Abuse:Providing access to addiction treatment and prevention programs can help address substance abuse, which has significant health and social consequences.
Improving Access to Quality Healthcare
- Expand Health Insurance Coverage:Ensuring that all individuals have access to affordable health insurance can improve access to preventive care and treatment, leading to better health outcomes.
- Strengthen the Primary Care System:Investing in primary care providers and supporting community health centers can provide essential healthcare services to underserved populations.
- Improve Mental Health Services:Expanding access to mental health services, including counseling and medication, can address the growing mental health crisis and improve overall well-being.
- Address Health Disparities:Implementing policies and programs that specifically target communities experiencing health disparities can help reduce inequities in health outcomes.
Using Rankings to Inform Community Health Initiatives and Resource Allocation, County health rankings
The rankings can be used to inform community health initiatives and resource allocation by:
- Identifying Priority Areas:The rankings highlight areas where health outcomes are particularly poor, providing a starting point for developing targeted interventions.
- Measuring Progress:The rankings can be used to track progress over time and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Advocating for Change:The rankings can be used to advocate for policies and programs that address the root causes of health disparities.
- Building Community Partnerships:The rankings can facilitate collaboration among stakeholders, including community organizations, healthcare providers, and policymakers, to address health challenges.
Last Word: County Health Rankings

County Health Rankings serve as a powerful tool for promoting health equity and improving the overall well-being of communities. By providing data-driven insights and fostering collaboration between policymakers, healthcare providers, and community leaders, these rankings can guide interventions that address the root causes of health disparities and create healthier communities for all.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of the County Health Rankings?
The County Health Rankings aim to provide a clear and concise picture of the health status of counties across the United States, highlighting areas where improvements can be made and promoting healthier communities.
How are counties ranked?
Counties are ranked based on a combination of health outcomes, health factors, and policy scores. The rankings are designed to reflect the overall health of a community, taking into account a variety of factors that influence well-being.
What are some examples of health factors that are considered in the rankings?
Health factors considered in the rankings include health behaviors (e.g., smoking, physical activity, obesity), access to healthcare, social and economic factors (e.g., education, income, poverty), and the physical environment (e.g., air quality, access to healthy food).