Health sciences learning centers are more than just classrooms; they are dynamic hubs where aspiring healthcare professionals hone their skills, expand their knowledge, and prepare for a rewarding career in medicine. These centers serve as vital pillars in modern education, offering students immersive experiences that go beyond traditional textbook learning.
From state-of-the-art simulation labs to hands-on clinical experiences, health sciences learning centers provide a holistic approach to education, ensuring students develop the critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical skills essential for success in the healthcare field.
The Role of Health Sciences Learning Centers
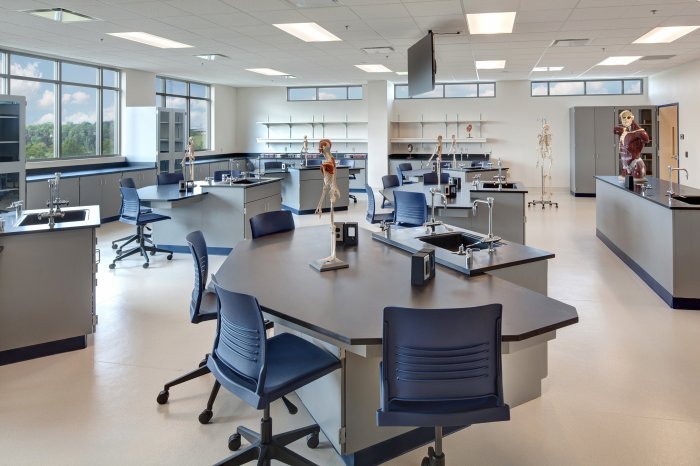

Health sciences learning centers are essential components of modern education, playing a crucial role in preparing students for successful careers in the healthcare field. These centers offer a variety of resources and services that support student learning, professional development, and the advancement of healthcare practices.
Types of Health Sciences Learning Centers
Health sciences learning centers come in various forms, each with its unique features and services.
- Simulation Centers:These centers provide realistic simulations of clinical environments, allowing students to practice skills and procedures in a safe and controlled setting. They often feature high-fidelity mannequins, virtual reality technology, and standardized patients who can interact with students and provide feedback.
- Skills Labs:These labs are equipped with equipment and tools used in healthcare settings, such as microscopes, anatomical models, and medical instruments. They provide students with hands-on experience in performing procedures and using medical technology.
- Computer Labs:These labs offer access to specialized software, databases, and online resources relevant to healthcare education. Students can utilize these resources for research, learning, and clinical practice.
- Study Centers:These centers provide students with a dedicated space for studying, collaborating, and accessing academic resources. They often offer quiet study areas, group study rooms, and access to tutors and faculty.
Impact on Student Learning and Professional Development
Health sciences learning centers have a significant impact on student learning and professional development.
- Enhanced Skills and Knowledge:Through hands-on practice, simulation experiences, and access to specialized resources, students develop essential skills and knowledge needed for their chosen healthcare profession.
- Improved Confidence and Competence:The safe and controlled environment of learning centers allows students to practice and refine their skills without the pressure of real-life clinical situations, boosting their confidence and competence.
- Increased Patient Safety:By providing opportunities for students to practice and improve their skills in a controlled setting, learning centers contribute to increased patient safety by reducing medical errors.
- Preparation for the Workplace:The resources and services offered by learning centers prepare students for the demands of the healthcare workplace, equipping them with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in their careers.
Curriculum and Learning Resources: Health Sciences Learning Center

Health sciences learning centers provide a diverse range of curriculum and learning resources to support students in their pursuit of healthcare careers. These centers offer a comprehensive learning environment that combines theoretical knowledge with practical skills development, preparing students for the challenges of the healthcare field.
Curriculum Overview
The curriculum at a health sciences learning center is tailored to meet the specific needs of each program of study. For example, programs in nursing, medical assisting, and pharmacy technician training will have distinct curricula that address the core competencies required for those professions.
A typical curriculum might include:
- Fundamental Sciences:Biology, chemistry, anatomy, physiology, and microbiology form the foundation of understanding human health and disease. These courses provide students with a strong scientific base upon which to build their healthcare knowledge.
- Clinical Skills:Hands-on training is a critical component of health sciences education. Students develop essential clinical skills through simulation labs, clinical rotations, and real-world experiences under the supervision of qualified instructors. These skills include patient assessment, vital sign measurement, medication administration, wound care, and basic life support.
- Healthcare Systems and Ethics:Students gain an understanding of the healthcare system, including its organization, policies, and regulations. They also learn about ethical principles that guide healthcare practice, ensuring they can make informed decisions in complex situations.
- Communication and Interpersonal Skills:Effective communication is essential for healthcare professionals. Students develop strong communication skills through role-playing scenarios, group discussions, and real-life interactions with patients and colleagues.
- Technology and Informatics:The healthcare industry is increasingly reliant on technology. Students learn about electronic health records, medical imaging, telehealth, and other technologies that are transforming healthcare delivery.
Learning Resources
Health sciences learning centers provide a rich array of learning resources to enhance student understanding and skill development. These resources can be categorized as follows:
| Resource Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Textbooks and Reference Materials | Comprehensive textbooks, specialized reference books, and online databases provide students with detailed information on various healthcare topics. | Human Anatomy & Physiology by Elaine N. Marieb and Katja Hoehn, Pharmacology for Nurses by Linda Lane, Medical Terminology: A Programmed Approach by Alice M. Dorland |
| Simulations and Virtual Reality | Interactive simulations and virtual reality environments allow students to practice clinical skills in a safe and controlled setting. | SimMan 3G patient simulator, virtual reality surgery simulations, online anatomy and physiology labs |
| Laboratory Equipment | Well-equipped laboratories provide students with hands-on experience using medical equipment and performing laboratory procedures. | Microscopes, centrifuges, blood pressure monitors, electrocardiograph machines, and sterile supplies |
| Online Learning Platforms | Online platforms offer a variety of learning resources, including interactive modules, video lectures, and assessment tools. | Khan Academy, Coursera, edX, and online medical journals |
| Faculty and Staff | Experienced faculty members and support staff provide guidance, mentorship, and personalized instruction to students. | Professors, instructors, clinical preceptors, librarians, and academic advisors |
Technology Integration
Technology plays a vital role in modern health sciences education. Learning centers leverage technology to enhance the learning experience in various ways:
- Online Learning Management Systems:Platforms like Canvas, Blackboard, and Moodle facilitate course delivery, communication, and assessment. Students can access course materials, submit assignments, and participate in online discussions through these systems.
- Interactive Learning Tools:Educational software, simulations, and virtual reality applications provide engaging and interactive learning experiences. These tools allow students to visualize complex concepts, practice clinical skills, and explore different scenarios.
- Mobile Learning:Mobile devices provide students with access to learning resources anytime, anywhere. Learning centers often provide mobile apps and online platforms that allow students to access course materials, participate in quizzes, and communicate with instructors.
- Telehealth and Virtual Care:Learning centers may incorporate telehealth and virtual care experiences into their curriculum, allowing students to interact with patients remotely and observe virtual consultations. This provides students with exposure to the evolving landscape of healthcare delivery.
Teaching and Learning Strategies

Health sciences learning centers are designed to foster an active and engaging learning environment. They utilize a variety of teaching and learning strategies to enhance student understanding and prepare them for their future careers in healthcare.
Innovative Teaching Methodologies
Health sciences learning centers are at the forefront of educational innovation, employing a range of teaching methodologies to enhance student engagement and understanding. These approaches move beyond traditional lecture-based learning and embrace active learning strategies.
Health sciences learning centers are invaluable resources for students seeking a comprehensive understanding of the human body and its intricacies. One particularly compelling area of study is the impact of mental health, which is often explored through the lens of film.
For instance, the article film mental health provides insightful analysis of how movies can depict and raise awareness about mental health challenges. By examining these portrayals, health sciences students gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of mental well-being and its influence on individuals and society.
- Problem-Based Learning (PBL):PBL presents students with real-world healthcare scenarios that require them to apply their knowledge and critical thinking skills to find solutions. Students work in groups to analyze the problem, research relevant information, and develop a plan of action. This approach fosters teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills.
- Simulation-Based Learning:Simulation-based learning utilizes realistic simulations to replicate real-life healthcare situations. Students can practice procedures, interact with simulated patients, and make decisions in a safe and controlled environment. This hands-on experience helps students develop clinical skills and confidence.
- Team-Based Learning (TBL):TBL emphasizes collaborative learning and active participation. Students work in teams to prepare for and participate in in-class activities. This approach encourages peer learning, discussion, and the development of teamwork skills.
- Flipped Classroom:The flipped classroom model reverses traditional learning by having students access lectures and other materials outside of class. Class time is then dedicated to interactive activities, group work, and problem-solving. This approach allows for more individualized learning and personalized feedback.
- Technology-Enhanced Learning:Health sciences learning centers utilize technology to enhance the learning experience. Interactive software, online simulations, virtual reality, and other digital tools provide students with engaging and interactive learning opportunities.
Comparison of Traditional and Active Learning
Traditional lecture-based learning is a time-honored approach, but it can sometimes be passive and less engaging. Active learning approaches, on the other hand, encourage student participation and engagement.
| Traditional Lecture-Based Learning | Active Learning Approaches |
|---|---|
| Passive learning environment | Active participation and engagement |
| Focus on content delivery | Emphasis on application and problem-solving |
| Limited opportunities for interaction | Collaborative learning and group work |
| Assessment through exams and quizzes | Variety of assessment methods, including projects, presentations, and simulations |
Case Studies, Simulations, and Clinical Experiences
Case studies, simulations, and clinical experiences play a crucial role in health sciences education. They provide students with opportunities to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios and develop essential clinical skills.
- Case Studies:Case studies present students with detailed descriptions of patient scenarios. Students analyze the case, identify relevant information, and formulate a diagnosis and treatment plan. This approach helps students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills.
- Simulations:Simulations allow students to practice clinical procedures and interact with simulated patients in a safe and controlled environment. This hands-on experience helps students develop technical skills, confidence, and decision-making abilities. Simulations can range from simple scenarios using mannequins to highly sophisticated virtual reality environments.
- Clinical Experiences:Clinical experiences provide students with the opportunity to observe and participate in real-world healthcare settings. This hands-on experience allows students to apply their knowledge, develop clinical skills, and gain a deeper understanding of the healthcare system. Clinical experiences are typically supervised by healthcare professionals and may include shadowing, assisting with patient care, and performing basic procedures.
Faculty and Staff

The success of a health sciences learning center hinges on the expertise and dedication of its faculty and staff. They play crucial roles in shaping the learning experience, fostering student growth, and advancing the field of healthcare education.
Roles and Responsibilities
The faculty and staff within a health sciences learning center are responsible for a diverse range of tasks, contributing to a comprehensive and effective learning environment.
- Instruction and Curriculum Development:Faculty members design, develop, and deliver engaging curricula that align with current healthcare standards and best practices. They are responsible for creating and implementing innovative teaching strategies, utilizing various learning technologies, and ensuring the content is relevant, accurate, and up-to-date.
- Mentorship and Guidance:Faculty and staff provide individual and group mentorship to students, offering guidance on academic and professional development. They provide support for students’ personal and academic challenges, fostering a positive and supportive learning environment.
- Assessment and Evaluation:Faculty members develop and administer assessments that measure student learning outcomes and identify areas for improvement. They use data-driven approaches to evaluate the effectiveness of teaching strategies and make adjustments to curriculum and instruction as needed.
- Research and Innovation:Faculty members often engage in research activities, contributing to the advancement of healthcare knowledge and practice. They may also participate in projects that explore innovative teaching methodologies and technologies, enhancing the learning experience for students.
- Administrative and Operational Support:Staff members provide essential administrative support, managing schedules, coordinating resources, and ensuring the smooth operation of the learning center. They play a vital role in facilitating a welcoming and efficient learning environment for students and faculty.
Qualifications and Expertise
Educators in health sciences learning centers possess a wide range of qualifications and expertise, ensuring that students receive high-quality instruction and mentorship.
- Academic Credentials:Faculty members typically hold advanced degrees in their respective fields, such as medicine, nursing, pharmacy, or allied health professions. They possess in-depth knowledge of their subject areas and are qualified to teach and mentor students.
- Clinical Experience:Many faculty members have extensive clinical experience, bringing real-world knowledge and insights to the classroom. This practical experience allows them to connect theory with practice, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of healthcare concepts and procedures.
- Teaching Skills:Educators in health sciences learning centers are skilled in teaching diverse student populations, employing various teaching methods and technologies to cater to different learning styles. They are adept at creating engaging and interactive learning environments that foster critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- Professional Development:Faculty members continuously engage in professional development activities to stay abreast of the latest advancements in healthcare education, research, and practice. They attend conferences, workshops, and seminars to enhance their teaching skills, pedagogical approaches, and content knowledge.
Mentorship and Guidance
Mentorship plays a crucial role in the success of students in health sciences programs. Faculty and staff provide guidance and support throughout their academic journey, helping them navigate the complexities of the field and develop the necessary skills and knowledge to excel.
- Academic Advising:Faculty members provide academic advising to students, helping them select courses, develop study plans, and manage their academic workload. They also offer guidance on research opportunities, internships, and career paths.
- Professional Development:Faculty and staff provide mentorship and guidance on professional development, helping students prepare for licensure exams, professional conferences, and job applications. They offer advice on networking, resume building, and interview skills.
- Personal Support:Mentors provide a supportive and encouraging environment for students, helping them address personal challenges, manage stress, and maintain a healthy work-life balance. They offer guidance on navigating the emotional and psychological demands of the healthcare profession.
Student Experiences and Outcomes

Health sciences learning centers play a crucial role in shaping the experiences and outcomes of students, fostering their engagement, motivation, and overall development as future healthcare professionals. These centers offer a unique learning environment that complements traditional classroom instruction and equips students with the essential skills and knowledge needed to excel in their chosen fields.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Health sciences learning centers significantly impact student engagement and motivation by providing a dynamic and interactive learning environment. The hands-on nature of these centers allows students to actively participate in their learning, applying theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios. This active engagement fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter, making learning more enjoyable and meaningful.
- Simulations and Case Studies:Learning centers often feature state-of-the-art simulation labs where students can practice clinical skills in a safe and controlled environment. These simulations provide realistic scenarios, allowing students to apply their knowledge and develop critical thinking skills. Case studies further enhance the learning process by presenting complex medical situations that require students to analyze information, make diagnoses, and develop treatment plans.
- Peer-to-Peer Learning:Learning centers encourage collaboration among students, creating a supportive and interactive learning environment. Peer-to-peer learning fosters a sense of community, where students can learn from each other’s experiences and perspectives. This collaborative approach enhances problem-solving abilities and promotes teamwork, essential skills for future healthcare professionals.
- Technology Integration:Learning centers often integrate technology into their learning activities, providing students with access to digital resources, interactive simulations, and online learning platforms. This technology-driven approach makes learning more engaging and accessible, allowing students to learn at their own pace and explore topics in greater depth.
Health sciences learning centers offer a diverse range of resources, from anatomical models to virtual simulations. But did you know that understanding the science behind beauty can be just as important? Beauty and Co provides a comprehensive overview of the latest trends and techniques in the beauty industry, helping students gain a deeper understanding of the science behind skincare, makeup, and hair care.
Student Projects, Research, and Community Outreach
Health sciences learning centers provide opportunities for students to engage in projects, research, and community outreach initiatives, enriching their learning experience and developing their skills beyond the classroom. These activities allow students to apply their knowledge in real-world settings, fostering a deeper understanding of the healthcare field and its impact on society.
- Research Projects:Learning centers often support student research projects, allowing students to investigate specific health topics under the guidance of faculty mentors. This hands-on experience provides valuable research skills and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Community Outreach Initiatives:Learning centers encourage students to participate in community outreach initiatives, providing healthcare services to underserved populations. These initiatives expose students to the social determinants of health and the challenges faced by vulnerable communities, fostering a sense of social responsibility and promoting health equity.
- Interprofessional Collaboration:Learning centers often facilitate interprofessional collaboration projects, bringing together students from different healthcare disciplines to work on real-world healthcare challenges. This experience fosters communication, teamwork, and a holistic understanding of the healthcare system.
Career Paths and Success Stories, Health sciences learning center
Health sciences learning centers play a vital role in preparing students for successful careers in the healthcare field. By providing a comprehensive learning environment that fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills, these centers equip students with the necessary tools to thrive in their chosen professions.
- Career Development Services:Learning centers often offer career development services, including career counseling, resume workshops, and job placement assistance. These services provide students with the guidance and support they need to navigate the job market and secure fulfilling careers.
- Alumni Network:Learning centers often maintain alumni networks, connecting graduates with current students and faculty. This network provides valuable mentorship opportunities and helps students build professional connections that can lead to career advancement.
- Success Stories:Numerous graduates from health sciences learning centers have gone on to achieve remarkable success in their careers, becoming leading healthcare professionals, researchers, and educators. Their achievements demonstrate the effectiveness of these centers in preparing students for the demands of the healthcare field.
Future Trends and Innovations
Health sciences learning centers are dynamic entities that must adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare education. Understanding emerging trends and embracing innovative approaches are crucial for these centers to remain relevant and effective.
Emerging Trends in Health Sciences Education
The field of health sciences education is undergoing a period of significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology, changing healthcare needs, and a growing emphasis on patient-centered care.
- Personalized Learning:Tailoring educational experiences to individual learner needs and preferences is becoming increasingly prevalent. Learning centers can leverage technology to provide personalized learning pathways, adaptive assessments, and individualized feedback. This approach allows students to learn at their own pace and focus on areas where they need additional support.
- Interprofessional Education:The healthcare workforce is increasingly collaborative, with professionals from different disciplines working together to provide comprehensive care. Learning centers can facilitate interprofessional education by creating opportunities for students from various healthcare professions to learn and work together. This approach promotes teamwork, communication, and a shared understanding of different roles.
- Simulation-Based Learning:Simulation technology allows students to practice clinical skills in a safe and controlled environment. Learning centers can incorporate advanced simulation technologies, such as virtual reality and haptic feedback, to provide immersive and realistic training experiences. This approach enhances clinical competency and reduces the risk of errors in real-world settings.
Health sciences learning centers are vital for students to gain practical experience, and they often feature partnerships with local businesses. For instance, some centers might collaborate with canvas beauty brands to provide students with hands-on experience in product development or marketing.
These collaborations offer valuable insights into the industry and enhance the overall learning experience.
- Data Analytics and Learning:Data analytics can provide valuable insights into student performance, learning patterns, and program effectiveness. Learning centers can utilize data analytics to identify areas for improvement, personalize learning experiences, and optimize resource allocation. This approach allows for data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement in educational quality.
Role of Technology in Shaping the Future of Learning Centers
Technology is a transformative force in health sciences education, enabling new possibilities for learning and teaching. Learning centers can leverage technology to create engaging, interactive, and personalized learning experiences.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS):LMS platforms provide a centralized hub for course content, assignments, assessments, and communication. They facilitate online learning, blended learning models, and personalized learning pathways. Examples include Moodle, Canvas, and Blackboard.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):VR and AR technologies create immersive and interactive learning experiences, allowing students to practice clinical skills in simulated environments. They offer realistic scenarios, haptic feedback, and real-time feedback, enhancing clinical competency and reducing the risk of errors in real-world settings.
- Mobile Learning:Mobile devices provide students with access to learning materials anytime, anywhere. Learning centers can develop mobile apps, online courses, and interactive content to support mobile learning. This approach allows students to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI can personalize learning experiences, provide intelligent tutoring, and automate administrative tasks. AI-powered chatbots can provide immediate assistance to students, and AI-based assessment tools can provide personalized feedback and identify areas for improvement.
Vision for the Future of Health Sciences Learning Centers
The future of health sciences learning centers will be characterized by a focus on personalized learning, interprofessional education, simulation-based learning, and data-driven decision-making. These centers will be dynamic and innovative spaces that leverage technology to create engaging and effective learning experiences.
- Learning Centers as Innovation Hubs:Learning centers will serve as hubs for innovation in health sciences education, fostering the development and implementation of new teaching and learning methods. They will partner with technology companies, researchers, and healthcare professionals to explore emerging trends and develop cutting-edge educational solutions.
- Blended Learning Models:Learning centers will embrace blended learning models that combine online and face-to-face instruction. This approach allows students to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule while benefiting from the collaborative and interactive aspects of traditional classroom learning.
- Data-Driven Assessment and Feedback:Learning centers will utilize data analytics to track student progress, identify learning gaps, and provide personalized feedback. This approach will allow for continuous improvement in educational quality and ensure that students are equipped with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in their chosen healthcare profession.
- Community Engagement:Learning centers will actively engage with the community, providing health education programs, conducting outreach activities, and fostering partnerships with healthcare organizations. This approach will promote community health, enhance the learning experience for students, and strengthen the center’s role in the healthcare ecosystem.
Last Word

As healthcare continues to evolve at a rapid pace, health sciences learning centers are at the forefront of innovation, embracing cutting-edge technologies and adapting to emerging trends. These centers are not just preparing students for today’s healthcare landscape; they are shaping the future of medicine by fostering a new generation of compassionate, skilled, and adaptable healthcare professionals.
FAQ Corner
What are the benefits of studying at a health sciences learning center?
Health sciences learning centers offer a variety of benefits, including access to state-of-the-art facilities, experienced faculty, and opportunities for hands-on learning. They also provide a supportive environment for students to develop their skills and prepare for a successful career in healthcare.
What are the different types of health sciences learning centers?
There are many different types of health sciences learning centers, including those that focus on specific areas of healthcare, such as nursing, pharmacy, or medical technology. Some centers are affiliated with hospitals or universities, while others are independent organizations.
How do I find a health sciences learning center that’s right for me?
When choosing a health sciences learning center, it’s important to consider your interests, career goals, and the programs offered. You should also research the center’s reputation, faculty, and facilities.