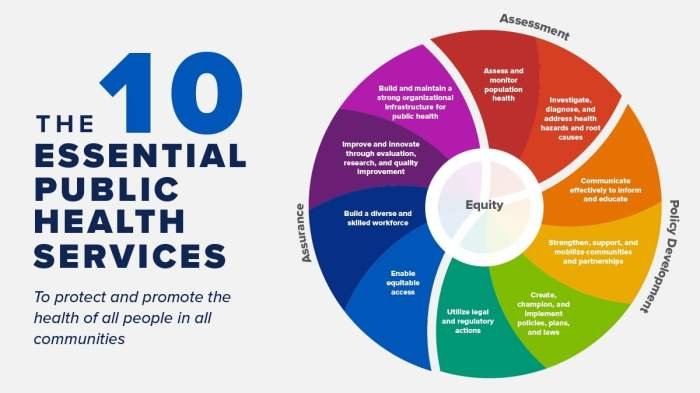
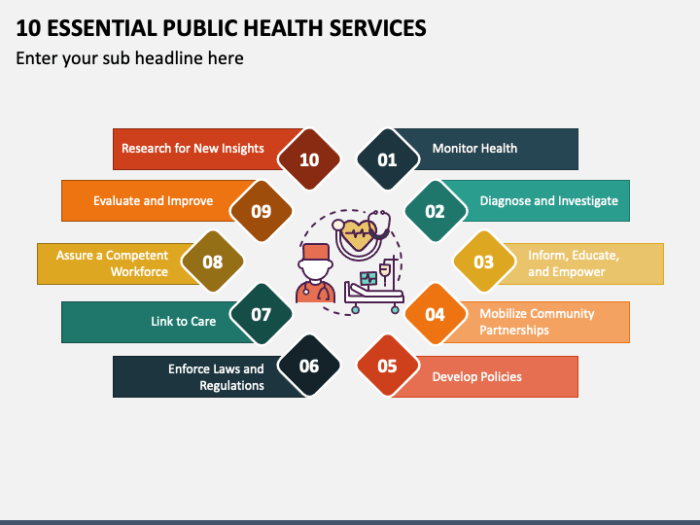
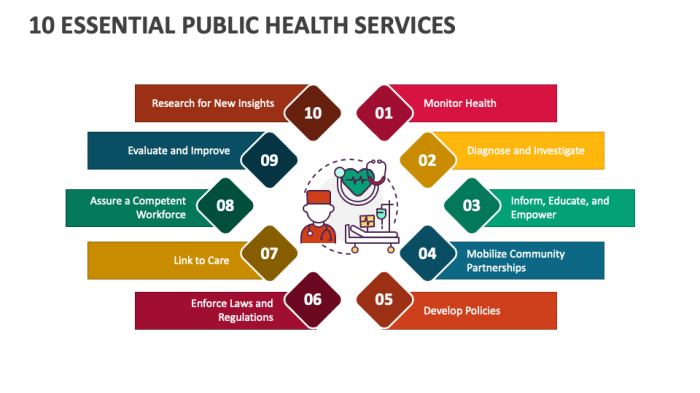
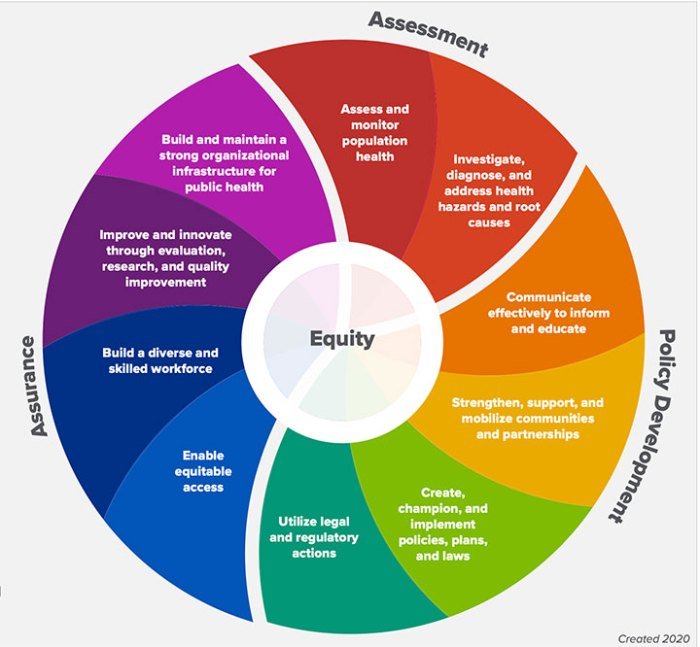
The 10 essential services of public health serve as a vital framework for promoting health and preventing disease across communities. These services, encompassing a broad range of activities, aim to address the multifaceted factors that influence individual and collective well-being.
From promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing infectious diseases to ensuring access to quality healthcare and advocating for health equity, these services work in concert to create a healthier society.
Public health professionals play a crucial role in implementing these services, collaborating with various stakeholders to address health challenges and improve health outcomes. By working together, we can foster a healthier environment, empower individuals to make informed choices, and build a more resilient and equitable society.
Health Promotion and Education
Public health plays a crucial role in promoting healthy behaviors and preventing disease. By educating individuals and communities about health risks, promoting healthy choices, and creating supportive environments, public health professionals strive to improve the overall well-being of the population.
Successful Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns have been instrumental in addressing various health issues. These campaigns often leverage different communication strategies, including mass media, social media, community outreach, and partnerships with organizations.
- The “Truth” Campaign:This anti-smoking campaign launched in the late 1990s targeted youth by exposing the tobacco industry’s deceptive marketing practices and the harmful effects of smoking. The campaign was highly successful in reducing youth smoking rates.
- The “Got Milk?” Campaign:This campaign, launched in the 1990s, aimed to increase milk consumption and promote calcium intake for strong bones. The campaign used catchy slogans and celebrity endorsements to effectively reach a wide audience.
- The “This is Your Brain on Drugs” Campaign:This campaign, launched in the 1980s, aimed to educate youth about the harmful effects of drug use. The campaign used graphic images and powerful messages to deter drug use.
Tailoring Health Messages
Tailoring health messages to different populations and communities is essential for effective health promotion. This involves considering factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and cultural beliefs.
- Age-Specific Messages:Health messages should be tailored to the developmental stage and needs of different age groups. For example, messages about nutrition and physical activity for children will differ from those for older adults.
- Cultural Sensitivity:Health messages should be culturally sensitive and avoid language or imagery that may be offensive or inappropriate to certain groups.
- Community Engagement:Public health professionals should engage with communities to understand their specific health needs and concerns. This can help ensure that health messages are relevant and resonate with the target audience.
Disease Prevention and Control
Disease prevention and control is a cornerstone of public health, aiming to protect and improve the health of populations by preventing the occurrence of diseases and controlling their spread. It involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing a wide range of strategies, from individual-level interventions to large-scale public health programs.
Strategies for Preventing and Controlling Diseases
Effective disease prevention and control strategies are crucial for safeguarding public health. These strategies can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Primary prevention: This involves preventing the initial occurrence of disease by addressing the underlying causes and risk factors. Examples include:
- Vaccination programs to prevent infectious diseases
- Health education campaigns promoting healthy lifestyles
- Regulations and policies to control environmental hazards
- Secondary prevention: This focuses on early detection and intervention to prevent disease progression and complications. Examples include:
- Screening programs for early detection of diseases like cancer
- Case management and treatment for individuals with existing diseases
- Contact tracing and quarantine measures to control outbreaks
Examples of Public Health Interventions
Public health interventions have played a significant role in reducing the burden of numerous diseases.
- Vaccination: The widespread implementation of vaccination programs has dramatically reduced the incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases like polio, measles, and rubella. For example, the eradication of smallpox through global vaccination efforts is a testament to the power of this intervention.
From promoting healthy lifestyles to ensuring access to quality healthcare, the 10 essential services of public health are crucial for a thriving community. A key player in delivering these services are community health workers, who often act as a bridge between healthcare providers and underserved populations.
If you’re passionate about making a difference in your community, you can find a wealth of opportunities in community health workers jobs , where you can contribute directly to the success of these essential public health services.
- Tobacco Control: Public health campaigns, regulations, and policies aimed at reducing tobacco use have led to significant declines in smoking rates and associated diseases like lung cancer and heart disease.
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Public health efforts to promote appropriate antibiotic use and prevent the spread of resistant bacteria are crucial to address the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance.
Importance of Surveillance and Outbreak Response
Surveillance and outbreak response are critical components of disease prevention and control.
- Surveillance: Continuous monitoring of disease trends and patterns allows public health authorities to identify emerging threats, track disease outbreaks, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Outbreak Response: Prompt and effective response to disease outbreaks is essential to contain their spread and minimize their impact on public health. This involves a coordinated effort by public health agencies, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders.
Environmental Health
Environmental health focuses on the connection between the environment and human well-being. It encompasses a wide range of factors, from air and water quality to exposure to hazardous substances, and how these factors impact our health.
Environmental Factors and Human Health
Environmental factors play a significant role in determining our health outcomes. These factors can be broadly categorized into:
- Physical Environment: This includes elements like air and water quality, climate change, and exposure to hazardous substances. For instance, poor air quality can lead to respiratory problems, while contaminated water can cause various illnesses.
- Biological Environment: This refers to living organisms that can impact human health, such as bacteria, viruses, and insects. For example, mosquito-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever are significant public health concerns in many regions.
- Social Environment: This encompasses factors like poverty, access to healthcare, and education. These factors can influence exposure to environmental hazards and the ability to cope with health risks.
Public Health Initiatives Addressing Environmental Health Concerns
Public health plays a crucial role in mitigating environmental health risks. Some key initiatives include:
- Air Quality Monitoring and Regulation: Public health agencies monitor air quality and set standards for pollutants. This helps to identify and address sources of pollution, such as industrial emissions and vehicle exhaust.
- Safe Drinking Water Programs: Public health programs ensure access to safe drinking water by monitoring water quality and implementing treatment processes to remove contaminants.
- Waste Management and Recycling: Public health initiatives promote proper waste disposal and recycling to reduce environmental pollution and protect public health.
- Environmental Education and Awareness: Public health campaigns raise awareness about environmental health risks and empower individuals to make informed decisions that protect their health and the environment.
Ensuring Access to Safe Drinking Water and Sanitation
Access to safe drinking water and sanitation is fundamental to human health. Public health plays a crucial role in ensuring this access through:
- Water Treatment and Distribution Systems: Public health agencies oversee the construction and maintenance of water treatment plants and distribution systems to provide safe and reliable water supply.
- Sanitation Infrastructure: Public health initiatives promote the development and maintenance of sanitation infrastructure, including toilets, sewage systems, and waste disposal facilities.
- Hygiene Education and Promotion: Public health campaigns educate communities about proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing, to prevent the spread of diseases.
Maternal and Child Health
Maternal and child health (MCH) is a critical component of public health, encompassing the well-being of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum, as well as the health and development of children from birth to adolescence. MCH programs aim to ensure healthy pregnancies, safe deliveries, and optimal child development, ultimately contributing to a healthier population.
Importance of Prenatal Care and Early Childhood Interventions
Prenatal care is essential for the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Regular prenatal visits allow healthcare providers to monitor the mother’s health, identify and manage potential complications, and provide education and support. Early childhood interventions, on the other hand, focus on promoting the cognitive, social, and emotional development of children from birth to age five.
These interventions can help to prevent developmental delays, promote school readiness, and improve long-term health outcomes.
Public Health Programs Supporting Maternal and Child Health Outcomes
Public health programs play a vital role in supporting maternal and child health outcomes. These programs provide a range of services, including:
- Prenatal care and delivery services
- Immunizations and disease prevention
- Nutrition and breastfeeding support
- Early childhood education and development programs
- Mental health services for mothers and children
- Family planning and reproductive health services
Role of Public Health in Reducing Infant Mortality and Improving Child Development
Public health efforts are crucial in reducing infant mortality rates and improving child development. Public health programs and interventions that address factors contributing to infant mortality include:
- Access to quality prenatal care
- Safe sleep practices for infants
- Breastfeeding promotion and support
- Early identification and treatment of birth defects
- Prevention of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Public health interventions that support child development include:
- Early childhood education and development programs
- Nutrition programs for children
- Lead poisoning prevention
- Injury prevention programs
- Mental health services for children
Injury Prevention and Control
Injuries are a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, affecting people of all ages. Injury prevention and control are essential public health priorities, aiming to reduce the incidence and severity of injuries.
Types of Injuries and Risk Factors
Injuries can be classified into various categories, each with associated risk factors.
- Unintentional Injuries: These include falls, motor vehicle crashes, poisonings, drownings, and fires. Risk factors vary depending on the type of injury but often include age, environment, and behavior. For instance, falls are more common among older adults, while motor vehicle crashes are more frequent among young adults.
- Intentional Injuries: These include violence, suicide, and self-harm. Risk factors include mental health issues, substance abuse, and social determinants of health. For example, exposure to violence in the home or community can increase the risk of intentional injury.
Public Health Interventions for Injury Prevention
Public health interventions are designed to address the underlying causes of injuries and promote safety.
- Environmental Modifications: These include changes to physical environments to reduce injury risk. Examples include installing traffic calming measures, improving road design, and providing safer playgrounds.
- Behavioral Interventions: These aim to change individual behaviors that contribute to injuries. Examples include promoting safe driving practices, encouraging the use of helmets, and promoting responsible alcohol consumption.
- Legislation and Policy: These can help to enforce safety standards and reduce injury risk. Examples include seatbelt laws, smoke detector regulations, and gun control measures.
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: These aim to raise public awareness about injury risks and prevention strategies. Examples include public service announcements, educational materials, and community outreach programs.
Data Collection and Analysis in Injury Prevention, 10 essential services of public health
Data collection and analysis are crucial for understanding the nature and causes of injuries, identifying trends, and evaluating the effectiveness of prevention programs.
- Surveillance Systems: These collect data on injuries, including incidence, severity, and risk factors. Examples include the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS) and the National Vital Statistics System (NVSS).
- Injury Databases: These store and analyze injury data, providing insights into injury patterns and trends. Examples include the National Trauma Data Bank (NTDB) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) database.
- Research Studies: These can provide further insights into the causes and prevention of injuries. Examples include randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and case-control studies.
Mental Health
Mental health is a crucial component of overall well-being, encompassing our emotional, psychological, and social health. It influences how we think, feel, and behave. When individuals experience good mental health, they are able to cope with life’s challenges, build strong relationships, and contribute meaningfully to their communities.
Conversely, mental health problems can significantly impact individuals and communities, leading to decreased productivity, strained relationships, and increased healthcare costs.
Public Health Programs Addressing Mental Health Needs
Public health programs play a vital role in promoting mental health and addressing mental health needs within communities. These programs are designed to provide support, resources, and services to individuals and families facing mental health challenges.
The 10 essential services of public health cover a wide range of crucial areas, from promoting healthy lifestyles to ensuring access to quality healthcare. In California, the state’s vast network of healthcare facilities plays a significant role in delivering these services.
One such example is the california health care facility , which provides a comprehensive range of services, including preventative care, treatment, and rehabilitation. By working together, public health agencies and healthcare facilities can effectively address the health needs of the population and create a healthier future for all.
- Mental Health Awareness Campaigns:These campaigns aim to educate the public about mental health issues, reduce stigma, and promote help-seeking behaviors. They often involve public service announcements, social media campaigns, and community events.
- Early Intervention Programs:Early intervention programs focus on identifying and addressing mental health concerns in children and adolescents. They may include screening for mental health disorders, providing support to families, and connecting individuals to appropriate services.
- Mental Health Treatment Services:Public health programs may provide access to mental health treatment services, including individual therapy, group therapy, medication management, and crisis intervention. These services can be offered through community mental health centers, hospitals, and private practices.
- Support Groups and Peer Support Networks:These programs connect individuals with others who share similar experiences, providing a sense of belonging, support, and understanding. They can help individuals cope with mental health challenges and build resilience.
The Role of Public Health in Reducing Stigma and Promoting Mental Health Awareness
Stigma associated with mental health issues can prevent individuals from seeking help, leading to delayed treatment and worsening symptoms. Public health plays a crucial role in reducing stigma and promoting mental health awareness.
- Public Education and Outreach:Public health agencies conduct educational campaigns to raise awareness about mental health issues, dispel myths, and promote understanding. They can use various channels, including social media, community events, and partnerships with schools and workplaces.
- Training for Professionals:Public health agencies train healthcare professionals, educators, and community leaders on mental health issues, best practices for mental health care, and how to recognize and respond to mental health concerns.
- Advocacy for Policy Change:Public health agencies advocate for policies that promote mental health, such as increased funding for mental health services, improved access to care, and integration of mental health into primary care settings.
Nutrition and Physical Activity: 10 Essential Services Of Public Health
A healthy lifestyle is a cornerstone of overall well-being, and two essential pillars of this lifestyle are proper nutrition and regular physical activity. Public health initiatives play a vital role in promoting these habits, aiming to improve the health and well-being of communities.
The Importance of Healthy Eating and Physical Activity
A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, provides the body with the essential nutrients it needs to function optimally. Regular physical activity, on the other hand, helps maintain a healthy weight, strengthens muscles and bones, improves cardiovascular health, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer.
Public Health Programs Promoting Healthy Diets and Active Lifestyles
Public health agencies and organizations implement various programs to encourage healthy eating and physical activity. These programs often target different populations, from children and adolescents to adults and older adults, and employ a variety of strategies.
While public health focuses on essential services like disease prevention and health promotion, it’s also important to remember the role of personal well-being. A unique hair and beauty salon, like this one , can contribute to a sense of self-care and confidence, which in turn supports overall health and well-being.
Just as public health initiatives strive to create a healthier society, a well-maintained appearance can contribute to a positive self-image, ultimately enhancing individual health and happiness.
- School-Based Nutrition Programs: These programs aim to promote healthy eating habits among children and adolescents by providing nutritious meals and snacks in schools, teaching nutrition education, and implementing policies to limit the sale of unhealthy foods.
- Community Gardens: Community gardens provide residents with access to fresh produce and opportunities to learn about gardening and healthy eating. These gardens can be particularly beneficial in underserved communities with limited access to fresh, affordable food.
- Physical Activity Campaigns: Public health campaigns encourage physical activity by promoting walking, biking, and other forms of active transportation, organizing community fitness events, and providing access to recreational facilities.
Addressing Food Insecurity and Access to Healthy Food
Food insecurity, the lack of consistent access to enough food for an active, healthy life, is a significant public health issue. It can lead to malnutrition, chronic diseases, and other health problems. Public health plays a crucial role in addressing food insecurity by:
- Expanding Access to Food Assistance Programs: Public health agencies work to ensure that individuals and families in need have access to programs like SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program) and WIC (Women, Infants, and Children) that provide food assistance.
- Supporting Community Food Banks and Pantries: Public health agencies often partner with community food banks and pantries to provide food to those who are struggling with food insecurity.
- Promoting Farmers’ Markets and Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) Programs: These initiatives provide access to fresh, locally grown produce and support local farmers.
Access to Healthcare
Access to quality healthcare is a fundamental pillar of public health, ensuring that individuals and communities can access necessary medical services to maintain and improve their well-being. Public health plays a crucial role in advocating for equitable access to healthcare, working to remove barriers and promote health equity for all.
The Importance of Health Insurance and Public Health Programs
Health insurance serves as a vital financial safety net, protecting individuals and families from the potentially crippling costs of medical care. Public health programs, such as Medicaid and Medicare, play a crucial role in providing healthcare coverage to low-income, elderly, and disabled individuals who might otherwise lack access.
- Medicaidis a federal-state partnership program that provides health insurance coverage to low-income individuals and families, including children, pregnant women, and people with disabilities.
- Medicareis a federal program that provides health insurance to people aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities.
Public health programs also implement initiatives to expand access to healthcare services, such as:
- Community health centersprovide primary and preventive care services to underserved populations in rural and urban areas.
- Mobile clinicsoffer healthcare services to individuals in remote or underserved areas, bringing care directly to those who may lack transportation or access to traditional healthcare facilities.
Challenges Faced by Underserved Populations
Underserved populations, including those living in poverty, racial and ethnic minorities, and individuals residing in rural areas, often face significant barriers to accessing healthcare.
- Financial barriers:The cost of healthcare, including deductibles, co-pays, and premiums, can be a significant financial burden for low-income individuals and families.
- Geographic barriers:Limited access to transportation, particularly in rural areas, can make it difficult for individuals to reach healthcare facilities.
- Language barriers:Communication challenges can arise when individuals do not speak English fluently, hindering their ability to navigate the healthcare system and receive culturally competent care.
- Cultural barriers:Cultural beliefs and practices can sometimes influence individuals’ willingness to seek healthcare, leading to delays in accessing necessary medical attention.
Public health professionals work to address these challenges through various strategies, including:
- Advocating for policies:Public health advocates push for policies that expand access to healthcare, such as increasing funding for Medicaid and Medicare, and promoting affordable health insurance options.
- Outreach and education:Public health initiatives educate communities about available healthcare resources, dispel myths and misconceptions, and encourage individuals to seek preventive care.
- Community engagement:Public health professionals work closely with community organizations and leaders to identify and address local healthcare needs, ensuring that services are tailored to the specific needs of the population.
Public Health Policy and Advocacy

Public health plays a crucial role in shaping health policy and advocating for health equity. It aims to create a healthier society by influencing the development and implementation of policies that promote well-being and prevent disease. This involves identifying health issues, analyzing their root causes, and proposing solutions that address these issues at a population level.
The Role of Public Health in Shaping Health Policy
Public health professionals use their expertise to inform policymakers about health issues and provide evidence-based recommendations for policy solutions. They play a vital role in:
- Identifying health priorities:Public health professionals conduct research and surveillance to identify emerging health threats and monitor the health status of populations. This information helps prioritize public health interventions and allocate resources effectively.
- Developing policy recommendations:Based on their understanding of health issues and effective interventions, public health professionals develop evidence-based recommendations for policy changes. These recommendations can include policies aimed at promoting healthy behaviors, preventing disease, and improving access to healthcare.
- Evaluating policy effectiveness:Public health professionals play a crucial role in evaluating the effectiveness of policies and programs. They collect data, analyze results, and provide feedback to policymakers to ensure that interventions are working as intended and make adjustments as needed.
Advocating for Health Equity
Public health professionals are also advocates for health equity, which means ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to achieve their full health potential. This involves addressing the social determinants of health, which are the factors that influence health outcomes beyond individual choices.
- Identifying disparities:Public health professionals conduct research to identify health disparities, which are differences in health outcomes between different population groups. These disparities often reflect underlying social and economic inequalities.
- Advocating for policy changes:Public health professionals advocate for policy changes that address the root causes of health disparities. This may involve advocating for policies that promote economic opportunity, improve access to education, or reduce discrimination.
- Building coalitions:Public health professionals work with other organizations and individuals to build coalitions and raise awareness about health equity issues. This collaboration can amplify their message and increase the likelihood of policy change.
Examples of Successful Public Health Advocacy Campaigns
There are numerous examples of successful public health advocacy campaigns that have led to significant improvements in public health.
- The Campaign for Smoke-Free Air:This campaign, spearheaded by public health organizations, led to the enactment of smoke-free laws in many countries, significantly reducing exposure to secondhand smoke and improving public health.
- The Childhood Immunization Campaign:Public health professionals played a crucial role in advocating for widespread childhood immunization programs, which have dramatically reduced the incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- The Campaign for Safe Drinking Water:This campaign led to the development of regulations and standards for safe drinking water, protecting millions of people from waterborne diseases.
Collaboration Between Public Health Professionals and Policymakers
Effective public health policy requires close collaboration between public health professionals and policymakers. This collaboration ensures that:
- Policy decisions are informed by evidence:Public health professionals provide policymakers with evidence-based information about health issues and effective interventions.
- Policies are implemented effectively:Public health professionals can provide technical assistance and support to policymakers in implementing new policies.
- Policies are evaluated and improved:Public health professionals monitor the impact of policies and provide feedback to policymakers to ensure that they are achieving their intended outcomes.
Public Health Research and Evaluation
Public health research and evaluation are crucial components of a robust public health system. They provide the evidence base for effective interventions, policies, and programs aimed at improving population health. Research helps us understand the causes and consequences of health issues, while evaluation assesses the effectiveness of our efforts to address them.
The Importance of Public Health Research
Public health research plays a vital role in informing policy and practice by providing evidence-based insights into health issues.
- Identifying Health Problems:Research helps identify emerging health threats and patterns of disease, allowing for early interventions and targeted public health programs.
- Understanding Risk Factors:By investigating risk factors, research helps identify modifiable factors that contribute to disease development, guiding the development of effective prevention strategies.
- Evaluating Interventions:Research provides evidence on the effectiveness of various interventions, such as vaccination programs, health education campaigns, and policy changes, allowing for informed decision-making and resource allocation.
- Developing New Interventions:Research is essential for developing innovative and effective interventions, including new vaccines, treatments, and public health programs.
The Role of Public Health Evaluation
Public health evaluation is a systematic process for assessing the effectiveness, efficiency, and impact of public health programs and interventions.
- Measuring Outcomes:Evaluation measures the impact of interventions on health outcomes, such as disease incidence, mortality rates, and quality of life.
- Assessing Program Effectiveness:Evaluation helps determine whether interventions are achieving their intended goals and whether they are cost-effective.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement:Evaluation provides valuable feedback on program implementation, identifying areas for improvement and optimization.
- Ensuring Accountability:Evaluation ensures accountability by demonstrating the value and impact of public health programs to stakeholders, including funders, policymakers, and the public.
Examples of Public Health Research Contributions
Public health research has a long history of contributing to improvements in health outcomes.
- Vaccination Programs:Research on the effectiveness of vaccines has led to the development and widespread use of vaccines, dramatically reducing the incidence of preventable diseases such as polio, measles, and rubella.
- Tobacco Control:Research on the health effects of tobacco smoking has led to public health policies aimed at reducing smoking prevalence, such as smoke-free laws and tobacco taxes, resulting in significant declines in smoking rates and tobacco-related deaths.
- HIV/AIDS Prevention:Research on HIV transmission and prevention has led to the development of effective interventions, such as antiretroviral therapy, safe sex practices, and needle exchange programs, significantly reducing HIV incidence and improving the lives of people living with HIV.
Closing Summary
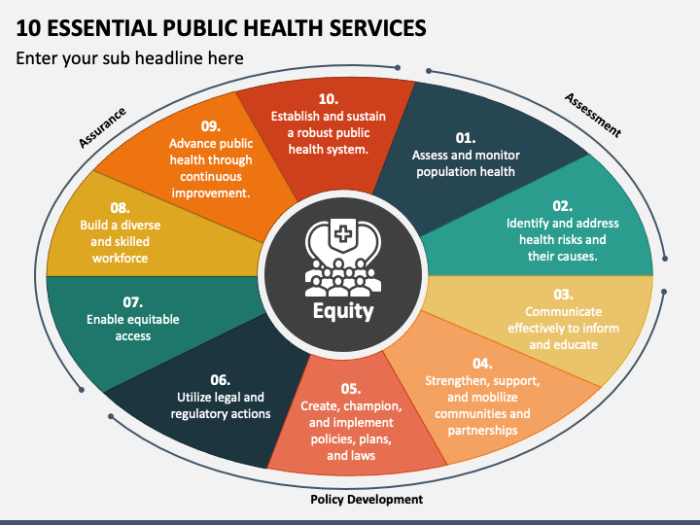
The 10 essential services of public health are a testament to the power of collective action in improving health outcomes. By understanding and implementing these services, we can create a society where health is valued, protected, and accessible to all.
From promoting healthy behaviors to addressing environmental hazards, these services lay the foundation for a healthier future.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the role of public health in promoting healthy behaviors?
Public health promotes healthy behaviors by educating individuals and communities about healthy choices, providing resources and support, and creating environments that encourage healthy living. This includes promoting physical activity, healthy eating, tobacco cessation, and safe sex practices.
How does public health ensure access to quality healthcare services?
Public health works to ensure access to quality healthcare by advocating for affordable health insurance, supporting community health centers, and promoting culturally competent healthcare services. It also addresses barriers to healthcare access, such as transportation and language limitations.
What are some examples of successful public health campaigns?
Examples of successful public health campaigns include the anti-smoking campaigns that have led to significant reductions in smoking rates, the immunization programs that have eradicated or significantly reduced the incidence of many infectious diseases, and the campaigns promoting safe sex practices that have helped to reduce the spread of HIV/AIDS.