The benefits of eggplant for health are numerous, making this versatile vegetable a valuable addition to any diet. From its heart-healthy properties to its potential role in managing blood sugar levels, eggplant offers a wide range of advantages. With its rich nutritional profile, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, eggplant can contribute to overall well-being and support a healthy lifestyle.
Eggplant, also known as aubergine, is a member of the nightshade family and boasts a unique flavor and texture. It is a low-calorie, nutrient-dense food that can be incorporated into various culinary dishes. Whether grilled, roasted, or fried, eggplant adds a delicious and nutritious element to meals.
Nutritional Profile of Eggplant: Benefits Of Eggplant For Health

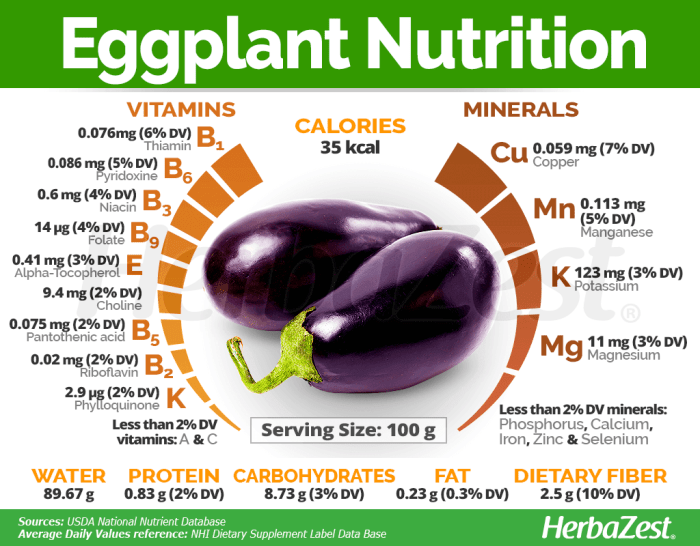
Eggplant, a versatile and flavorful vegetable, is a nutritional powerhouse packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Its low calorie content and high fiber make it a healthy addition to any diet. Let’s delve into the detailed nutritional profile of eggplant.
Eggplant, a versatile vegetable, offers a range of health benefits, including its ability to aid in digestion and support heart health. When it comes to the well-being of those we cherish, a heartfelt prayer for health of loved one can provide solace and strength.
Similarly, incorporating eggplant into a balanced diet can contribute to overall well-being, offering a delicious and nutritious way to support good health.
Key Nutrients in Eggplant
Eggplant is an excellent source of various essential nutrients, including:
- Vitamins:Eggplant is rich in vitamin K, which plays a crucial role in blood clotting and bone health. It also contains vitamin C, an antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production. Vitamin B6, another vital component, is involved in brain function and energy metabolism.
- Minerals:Eggplant is a good source of potassium, a mineral that helps regulate blood pressure and muscle function. It also provides magnesium, which supports muscle and nerve function, and manganese, which is essential for bone health and metabolism.
- Antioxidants:Eggplant is packed with antioxidants, including nasunin, which is a powerful antioxidant found in the skin. Nasunin helps protect brain cells from damage and may have anti-inflammatory properties. Other antioxidants present in eggplant include anthocyanins, which give the vegetable its vibrant purple color and have been linked to various health benefits.
Nutritional Content Per Serving
A typical serving of eggplant (about 1 cup cooked) provides the following nutrients:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 20 |
| Protein | 1 gram |
| Carbohydrates | 4 grams |
| Fiber | 3 grams |
| Vitamin K | 10% of the Daily Value (DV) |
| Vitamin C | 5% of the DV |
| Potassium | 6% of the DV |
| Magnesium | 4% of the DV |
Comparison with Other Vegetables
Compared to other vegetables, eggplant is relatively low in calories and carbohydrates. However, it stands out with its high fiber content, making it a filling and satisfying food choice. Eggplant also boasts a unique profile of antioxidants, particularly nasunin, which sets it apart from many other vegetables.
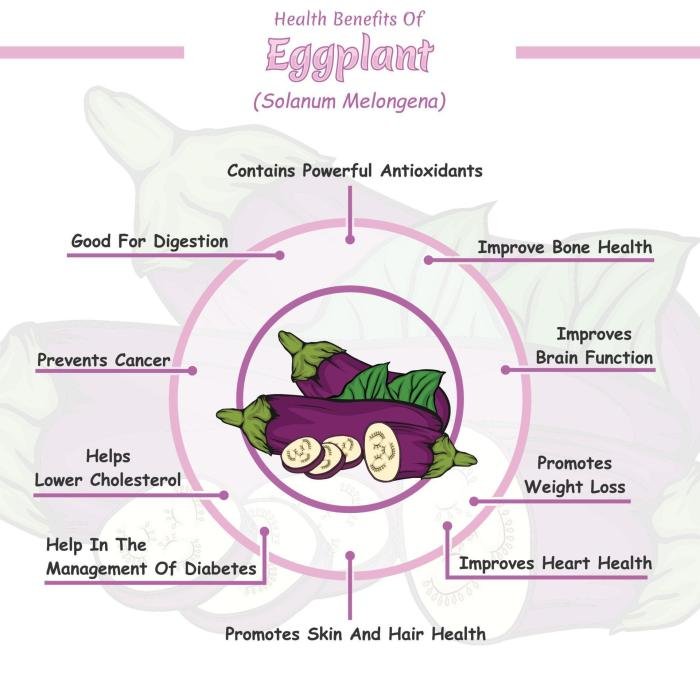
Health Benefits of Eggplant

Eggplant, a versatile and flavorful vegetable, is not only a culinary delight but also a powerhouse of nutrients that contribute to overall well-being. Its rich nutritional profile, brimming with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, makes it a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Let’s explore the various health benefits of eggplant.
Heart Health
Eggplant can play a significant role in promoting heart health. It is a good source of dietary fiber, which helps lower cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive tract, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. Additionally, eggplant contains potassium, a mineral that helps regulate blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium.
Blood Sugar Management
Eggplant is a low-glycemic index (GI) food, meaning it does not cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This makes it an ideal choice for individuals managing blood sugar levels, particularly those with type 2 diabetes. Its fiber content also helps regulate blood sugar by slowing down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
Eggplant is a versatile and nutritious vegetable that offers a range of health benefits, including its ability to aid in weight management and promote heart health. While exploring these advantages, you might also want to check out ulta beauty fenty for a range of beauty products.
Returning to eggplant, it’s a great source of fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Antioxidant Benefits
Eggplant is packed with antioxidants, including nasunin, which is particularly abundant in the skin. Antioxidants protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that contribute to aging and chronic diseases. Nasunin, in particular, has been shown to protect brain cells from oxidative stress.
Digestive Health
Eggplant is an excellent source of dietary fiber, which is essential for digestive health. Fiber adds bulk to stool, making it easier to pass and preventing constipation. It also promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which play a crucial role in digestion and overall gut health.
Culinary Uses of Eggplant
Eggplant, with its versatility and unique flavor, is a staple ingredient in cuisines worldwide. It can be prepared in numerous ways, from simple to elaborate, lending itself to both traditional and modern dishes.
Eggplant Cooking Methods
The texture of eggplant can be altered depending on the cooking method employed. Here are some popular techniques:
- Grilling:Grilling brings out the natural sweetness of eggplant and creates a smoky flavor. It’s ideal for preparing eggplant slices, kebabs, or whole eggplants.
- Roasting:Roasting eggplant in the oven intensifies its flavor and creates a soft, tender texture. It’s perfect for making baba ghanoush, eggplant parmesan, or stuffed eggplants.
- Frying:Frying eggplant results in a crispy exterior and a soft interior. It’s often used in dishes like eggplant fritters, eggplant chips, and eggplant stir-fries.
- Sautéing:Sautéing eggplant in a pan with oil and spices is a quick and easy way to cook it. It’s ideal for adding eggplant to curries, stews, or pasta dishes.
Eggplant Dishes from Around the World
Eggplant features prominently in diverse cuisines, showcasing its adaptability and culinary appeal. Here are some examples:
| Region | Dish | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Middle East | Baba ghanoush | A creamy dip made from roasted eggplant, tahini, garlic, lemon juice, and olive oil. |
| Italy | Parmigiana di melanzane | A layered casserole of eggplant, tomato sauce, mozzarella cheese, and Parmesan cheese. |
| India | Baingan Bharta | A smoky and flavorful dish made from roasted eggplant mashed with spices, onions, and tomatoes. |
| Japan | Nasu Dengaku | Grilled eggplant glazed with a sweet and savory miso sauce. |
| Thailand | Gaeng Keow Wan Gai | A green curry with chicken, eggplant, bamboo shoots, and coconut milk. |
Selecting and Storing Eggplant

Choosing the right eggplant is crucial for a delicious and satisfying culinary experience. Freshness and ripeness are key factors to consider when selecting eggplant at the grocery store. Additionally, understanding how to store eggplant properly will help maintain its quality and freshness, ensuring it stays flavorful and ready for use.
Choosing Fresh Eggplant
To select fresh eggplant, look for firm, glossy skin with a vibrant color. The eggplant should feel heavy for its size, indicating good hydration. Avoid eggplants with soft spots, wrinkles, or blemishes, as these are signs of spoilage. Additionally, inspect the stem; it should be green and firm.
- Color:The skin should be a deep, rich purple, without any signs of browning or discoloration.
- Firmness:The eggplant should feel firm to the touch, not soft or mushy. Gently press on the skin; it should spring back slightly.
- Size:Choose an eggplant that is appropriate for your recipe. Smaller eggplants are often more tender and flavorful, while larger eggplants can be more versatile.
- Stem:The stem should be green and firm, not wilted or brown.
- Weight:A fresh eggplant should feel heavy for its size, indicating good hydration.
Storing Eggplant, Benefits of eggplant for health
Storing eggplant properly will help extend its shelf life and maintain its freshness.
- Refrigerator:Unwashed eggplants can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a week. Wrap the eggplant loosely in plastic wrap or a paper towel to prevent moisture buildup.
- Freezing:Eggplant can be frozen for up to 3 months. To freeze, cut the eggplant into cubes or slices, blanch them in boiling water for 2-3 minutes, then drain and cool completely. Place the blanched eggplant in a freezer-safe bag or container.
Identifying Spoiled Eggplant
Spoiled eggplant will have a number of telltale signs.
- Softness:A spoiled eggplant will feel soft and mushy when pressed.
- Wrinkles:The skin will have wrinkles or blemishes, indicating dehydration.
- Discoloration:The skin will be brown or discolored, and the flesh may be brown or mushy.
- Mold:The eggplant may have mold growing on the skin or flesh.
- Unpleasant Odor:A spoiled eggplant will have a foul odor.
Eggplant in Traditional Medicine

Eggplant, a versatile vegetable with a long history of culinary and medicinal use, has been a staple in traditional medicine systems around the world for centuries. Its diverse applications in various cultures demonstrate its significance as a natural remedy.
Traditional Uses of Eggplant
Traditional medicine systems often rely on the belief that certain foods possess specific healing properties. Eggplant, with its unique composition of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, has been incorporated into various traditional remedies.
- Ayurveda:In Ayurveda, a traditional Indian system of medicine, eggplant is considered a cooling and detoxifying food. It is believed to balance the Pitta dosha, associated with fire and heat, and promote digestive health.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM):In TCM, eggplant is categorized as a cool and slightly bitter food, believed to clear heat and toxins, promote urination, and alleviate swelling.
- Folk Medicine:In various folk medicine traditions, eggplant has been used to treat a range of ailments, including skin conditions, inflammation, and digestive issues.
Traditional Remedies and Beliefs
Throughout history, eggplant has been used in a variety of traditional remedies.
- Skin Conditions:The application of eggplant pulp or juice has been traditionally used to soothe skin irritations, reduce inflammation, and treat acne.
- Digestive Issues:Eggplant is believed to aid digestion, relieve constipation, and reduce bloating due to its fiber content and potential anti-inflammatory properties.
- Inflammation:Some traditional medicine systems use eggplant to reduce inflammation and pain, particularly in conditions like arthritis.
Comparing Traditional Uses with Modern Science
While some traditional uses of eggplant align with modern scientific findings, others require further research.
Eggplant, a versatile and flavorful vegetable, offers numerous health benefits, including its ability to lower cholesterol and support healthy blood sugar levels. For more comprehensive advice on integrating eggplant and other nutritious foods into your diet, consider consulting with a health care consulting company who can provide personalized guidance and support.
This vegetable’s rich antioxidant profile can also help protect against inflammation and oxidative stress, contributing to overall well-being.
- Antioxidant Properties:Modern research supports the traditional belief that eggplant is rich in antioxidants, which can protect against oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Fiber Content:Eggplant’s fiber content aligns with its traditional use for digestive health, as fiber aids in promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects:Studies have shown that certain compounds in eggplant, such as nasunin, may possess anti-inflammatory properties, supporting its traditional use for conditions like arthritis.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, eggplant is a remarkable vegetable that offers a multitude of health benefits. From its heart-protective qualities to its potential role in managing blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation, eggplant plays a significant role in promoting overall well-being. Its versatility in the kitchen allows for diverse culinary creations, making it an enjoyable and nutritious addition to any diet.
Questions Often Asked
Is eggplant good for weight loss?
Eggplant is a low-calorie vegetable, making it a good choice for weight management. Its fiber content can help promote feelings of fullness, which may reduce overall calorie intake.
Can eggplant cause allergies?
While eggplant allergies are rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to nightshade vegetables, including eggplant. Symptoms can range from mild skin irritation to more severe reactions like difficulty breathing.
How much eggplant should I eat per week?
There is no specific recommended intake for eggplant. However, incorporating it into your diet a few times per week can provide a range of health benefits.