Community health workers jobs are essential to providing healthcare access and improving health outcomes in underserved communities. These dedicated individuals act as bridges between healthcare systems and the people they serve, offering a wide range of services and support.
From conducting outreach and education to providing direct care and advocacy, community health workers play a crucial role in addressing health disparities and promoting well-being. They often work in diverse settings, including rural areas, urban neighborhoods, and community centers, reaching individuals who may face barriers to accessing traditional healthcare services.
The Role of Community Health Workers

Community health workers (CHWs) play a crucial role in improving health outcomes within communities by serving as a bridge between healthcare systems and individuals, especially those who are underserved.
Responsibilities of Community Health Workers
CHWs are responsible for a wide range of tasks that contribute to the well-being of communities. Their responsibilities often include outreach, education, and support services.
- Outreach:CHWs actively engage with community members to identify individuals in need of healthcare services, such as those who are uninsured, have limited access to transportation, or are hesitant to seek medical attention. They conduct home visits, participate in community events, and utilize various communication channels to reach out to individuals.
- Education:CHWs provide health education to individuals and groups on various topics, including disease prevention, healthy lifestyle choices, and the importance of seeking regular medical care. They often tailor their educational materials and presentations to meet the specific needs and cultural backgrounds of their communities.
- Support Services:CHWs offer practical support to individuals and families facing health challenges. They may assist with navigating the healthcare system, scheduling appointments, and connecting individuals with social services and other resources. They also provide emotional support and encouragement to individuals who are managing chronic illnesses or experiencing difficult life circumstances.
Examples of Community Health Worker Tasks
CHWs perform diverse tasks depending on the specific needs of their communities and the organizations they work with. Here are some examples of common tasks:
- Conducting health screenings:CHWs may conduct blood pressure checks, diabetes screenings, and other health assessments in community settings.
- Providing health education workshops:CHWs can facilitate workshops on topics such as nutrition, exercise, smoking cessation, and mental health.
- Assisting with medication adherence:CHWs can help individuals manage their medications by providing reminders, troubleshooting issues, and connecting them with pharmacists.
- Facilitating support groups:CHWs can lead support groups for individuals with chronic illnesses or those who are facing specific health challenges.
- Advocating for community health needs:CHWs can advocate for policies and programs that address the health needs of their communities.
Impact of Community Health Workers on Health Outcomes
CHWs have a significant impact on improving health outcomes within communities. They contribute to:
- Increased access to healthcare:CHWs help bridge the gap in access to healthcare by reaching out to underserved populations and connecting them with services.
- Improved health literacy:CHWs educate individuals about health issues and empower them to make informed decisions about their health.
- Enhanced disease management:CHWs support individuals in managing chronic illnesses, improving medication adherence, and preventing complications.
- Improved health behaviors:CHWs promote healthy lifestyle choices and encourage individuals to engage in preventive health measures.
- Stronger community health systems:CHWs play a vital role in strengthening community health systems by building trust, fostering communication, and connecting individuals with resources.
Job Market Trends for Community Health Workers
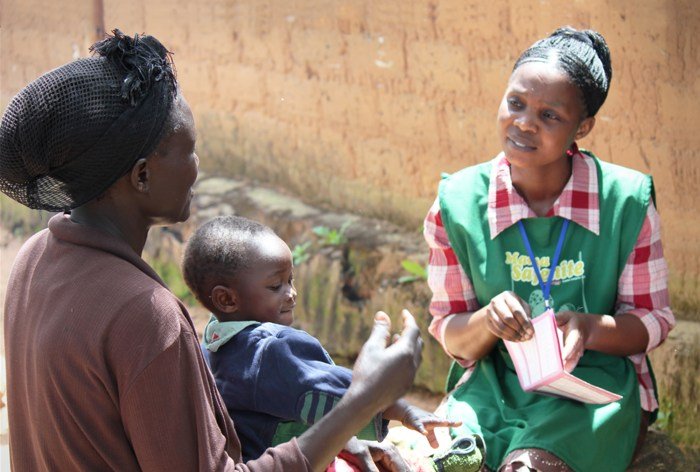

The demand for community health workers (CHWs) is steadily increasing across various regions and sectors globally. This growth is driven by several factors, including the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the need to improve access to healthcare services in underserved communities.
Community health workers play a vital role in connecting individuals with essential healthcare resources. For example, they might help patients navigate the online portal, luminis health mychart , to access their medical records or schedule appointments. By bridging the gap between healthcare systems and communities, community health workers contribute to improved health outcomes for everyone.
Current Demand for Community Health Workers
The demand for CHWs varies significantly depending on the region and the specific health challenges faced by the community. In the United States, the demand for CHWs is particularly high in rural areas and urban neighborhoods with limited access to healthcare services.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has also contributed to the growth of the CHW workforce by expanding health insurance coverage and increasing the need for outreach and care coordination.
- Rural Areas:In rural areas, CHWs play a crucial role in connecting individuals with healthcare services, providing health education, and promoting healthy behaviors. The shortage of healthcare providers in rural areas makes CHWs essential for ensuring access to care.
- Urban Underserved Communities:In urban areas, CHWs are often deployed to address health disparities in underserved communities. They work with vulnerable populations, such as individuals experiencing homelessness, refugees, and those with chronic conditions, to improve health outcomes.
- Public Health Initiatives:CHWs are increasingly involved in public health initiatives, such as disease prevention and health promotion programs. They play a vital role in educating communities about health risks, promoting healthy behaviors, and facilitating access to preventive services.
Factors Driving the Growth of Community Health Worker Jobs
Several factors are driving the growth of CHW jobs, including:
- Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases:The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity, is creating a growing need for community-based health services. CHWs are well-suited to provide ongoing support and care coordination for individuals with chronic conditions.
- Aging Population:As the population ages, the demand for healthcare services will continue to rise. CHWs can help address the needs of older adults, providing support with medication management, transportation, and social services.
- Focus on Health Equity:There is a growing focus on health equity, which aims to ensure that everyone has access to quality healthcare services. CHWs play a vital role in addressing health disparities by providing culturally sensitive care and connecting individuals with resources.
- Technological Advancements:Technological advancements, such as telehealth and mobile health applications, are creating new opportunities for CHWs to provide care remotely and improve access to services.
Future Outlook for Community Health Workers
The future outlook for CHWs is positive, with continued growth expected in the coming years. As the healthcare system shifts towards a more community-based approach, the role of CHWs will become even more critical.
- Emerging Health Challenges:CHWs will play a key role in addressing emerging health challenges, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and climate change. They can provide essential support and education to communities during health emergencies and help promote resilience in the face of environmental stressors.
- Integration into Healthcare Systems:CHWs are increasingly being integrated into healthcare systems, working alongside physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. This integration will enhance the effectiveness of care and improve coordination between different levels of care.
- Policy Support:Policymakers are increasingly recognizing the value of CHWs and providing support for their training, certification, and employment. This policy support will further strengthen the CHW workforce and enable them to contribute more effectively to the healthcare system.
Essential Skills and Qualifications

Community health workers (CHWs) play a crucial role in bridging the gap between healthcare systems and underserved communities. They often work in challenging environments, requiring a diverse skillset and qualifications to effectively connect with individuals and families. This section delves into the essential skills and qualifications typically sought in CHW positions.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
| Skill/Qualification | Description | Importance | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication Skills | Ability to communicate effectively with diverse populations, including those with limited English proficiency, different cultural backgrounds, and varying levels of health literacy. | Crucial for building trust and rapport with clients, effectively conveying health information, and providing culturally sensitive support. | Active listening, clear and concise speaking, nonverbal communication, empathy, cultural sensitivity. |
| Interpersonal Skills | Strong interpersonal skills are essential for working collaboratively with community members, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders. | Essential for building relationships, fostering trust, and coordinating care effectively. | Teamwork, conflict resolution, problem-solving, collaboration, leadership. |
| Cultural Competence | Understanding and respecting the cultural beliefs, values, and practices of the community served. | Ensures culturally appropriate health education, outreach, and support services. | Awareness of cultural differences, sensitivity to cultural norms, ability to adapt communication styles. |
| Community Engagement | Ability to engage with community members, build relationships, and mobilize resources to address health needs. | Essential for identifying health issues, promoting health behaviors, and advocating for community resources. | Community outreach, program development, advocacy, partnership building. |
| Health Education and Promotion | Knowledge of health issues, risk factors, and prevention strategies, as well as the ability to effectively educate individuals and communities. | Critical for promoting healthy behaviors, reducing health disparities, and improving health outcomes. | Health education materials, community health campaigns, workshops, presentations. |
| Data Collection and Reporting | Ability to gather, record, and analyze data to monitor program effectiveness and identify trends. | Essential for program evaluation, reporting, and informing decision-making. | Data entry, data analysis, program evaluation, report writing. |
| Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking | Ability to analyze situations, identify problems, and develop solutions to address community health needs. | Essential for navigating complex health issues, adapting to changing circumstances, and finding innovative solutions. | Problem identification, solution generation, decision-making, resource allocation. |
| Technology Skills | Familiarity with basic technology tools, such as computers, smartphones, and health information systems. | Essential for accessing resources, communicating with clients, and documenting services. | Email, internet, mobile apps, telehealth platforms. |
| Organizational Skills | Ability to manage time, prioritize tasks, and work independently and as part of a team. | Essential for efficient service delivery, meeting deadlines, and managing multiple responsibilities. | Time management, task prioritization, scheduling, resource management. |
| Resilience and Adaptability | Ability to handle stress, adapt to challenging situations, and maintain a positive attitude. | Essential for working in diverse and demanding environments, dealing with difficult clients, and overcoming obstacles. | Stress management, problem-solving, emotional regulation, flexibility. |
Relevant Certifications and Training Programs
Several certifications and training programs are available for individuals seeking to enhance their skills and qualifications as community health workers. These programs often cover topics such as:
- Health education and promotion
- Cultural competence and sensitivity
- Community engagement and mobilization
- Data collection and analysis
- Program evaluation and reporting
- Health policy and advocacy
- Ethics and professionalism
Some recognized certifications include:
- Certified Community Health Worker (CCHW) by the National Association of Community Health Workers (NACHW)
- Certified Health Education Specialist (CHES) by the National Commission for Health Education Credentialing (NCHEC)
- Certified Health Information Manager (CHIM) by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA)
These certifications demonstrate a commitment to professional development and can enhance career opportunities for CHWs.
Education and Training Pathways: Community Health Workers Jobs

Becoming a community health worker requires a blend of practical skills, cultural sensitivity, and knowledge of health resources. The path to becoming a community health worker varies depending on individual experience and career goals. There are multiple educational pathways, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Formal Education, Community health workers jobs
Formal education pathways offer structured learning environments with standardized curricula. These programs often provide a comprehensive understanding of health concepts, community engagement strategies, and the role of a community health worker.
- Associate’s Degree in Community Health: This two-year degree program provides a strong foundation in public health principles, health education, and community outreach. It equips graduates with the knowledge and skills necessary to work in a variety of community health settings.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Public Health or a related field: A four-year bachelor’s degree provides a more in-depth understanding of health systems, health policy, and research methodologies. This pathway is ideal for individuals seeking leadership roles or advanced careers in community health.
Advantages
- Structured learning environment: Formal education programs provide a systematic and organized approach to learning, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of community health principles and practices.
- Credibility and recognition: A formal degree or certificate demonstrates a commitment to professional development and enhances credibility in the job market.
- Networking opportunities: Formal programs often provide opportunities to connect with other professionals in the field, expanding networks and potential career paths.
Disadvantages
- Time commitment: Formal education programs require significant time and financial investment, which may not be feasible for everyone.
- Limited practical experience: While formal programs offer theoretical knowledge, they may not always provide sufficient hands-on experience in community settings.
Certificate Programs
Certificate programs offer a focused and accelerated approach to acquiring the necessary skills and knowledge for a community health worker role. These programs typically cover essential topics like health education, community outreach, and cultural competency.
- Community Health Worker Certificate: These programs provide a foundation in community health principles, outreach strategies, and the role of a community health worker. They are often offered by community colleges, universities, and health organizations.
- Specialized Certificates: Some programs offer specialized certificates in areas like diabetes management, mental health, or substance abuse. These certificates enhance expertise in specific health areas.
Advantages
- Flexibility and affordability: Certificate programs are often shorter and more affordable than degree programs, making them a viable option for individuals with time and financial constraints.
- Targeted skills: Certificate programs focus on specific skills and knowledge relevant to community health work, providing a practical and relevant education.
- Faster entry into the workforce: Certificate programs allow individuals to enter the workforce more quickly compared to degree programs.
Disadvantages
- Limited scope: Certificate programs may not provide the same breadth of knowledge as degree programs, potentially limiting career advancement opportunities.
- Less recognition: While certificates demonstrate skills and knowledge, they may not carry the same level of recognition as a degree in some job markets.
On-the-Job Training
On-the-job training provides practical experience and mentorship within a community health setting. This approach involves learning from experienced community health workers, participating in outreach programs, and gaining hands-on experience in real-world scenarios.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Sample Curriculum for a Community Health Worker Training Program
A comprehensive community health worker training program should address a wide range of topics, including:
- Introduction to Community Health: This module introduces the core concepts of community health, including the social determinants of health, health disparities, and the role of community health workers.
- Health Education and Promotion: This module focuses on the principles of health education, including effective communication techniques, behavior change strategies, and the development of health promotion programs.
- Community Outreach and Engagement: This module explores strategies for building relationships with community members, conducting needs assessments, and developing culturally appropriate outreach programs.
- Cultural Competency and Diversity: This module emphasizes the importance of understanding and respecting diverse cultures, beliefs, and practices. It covers topics like cultural sensitivity, language barriers, and health disparities.
- Health Resources and Systems: This module provides an overview of health resources available in the community, including healthcare providers, social services, and community organizations. It also explores the navigation of health systems and the referral process.
- Data Collection and Reporting: This module introduces methods for collecting and analyzing data related to community health needs and program outcomes. It covers topics like data privacy, ethical considerations, and report writing.
- Professional Ethics and Advocacy: This module explores ethical considerations in community health work, including confidentiality, informed consent, and advocacy for vulnerable populations.
- Practical Skills and Applications: This module provides hands-on training in essential skills like conducting health screenings, facilitating group discussions, and developing community partnerships.
Career Advancement Opportunities
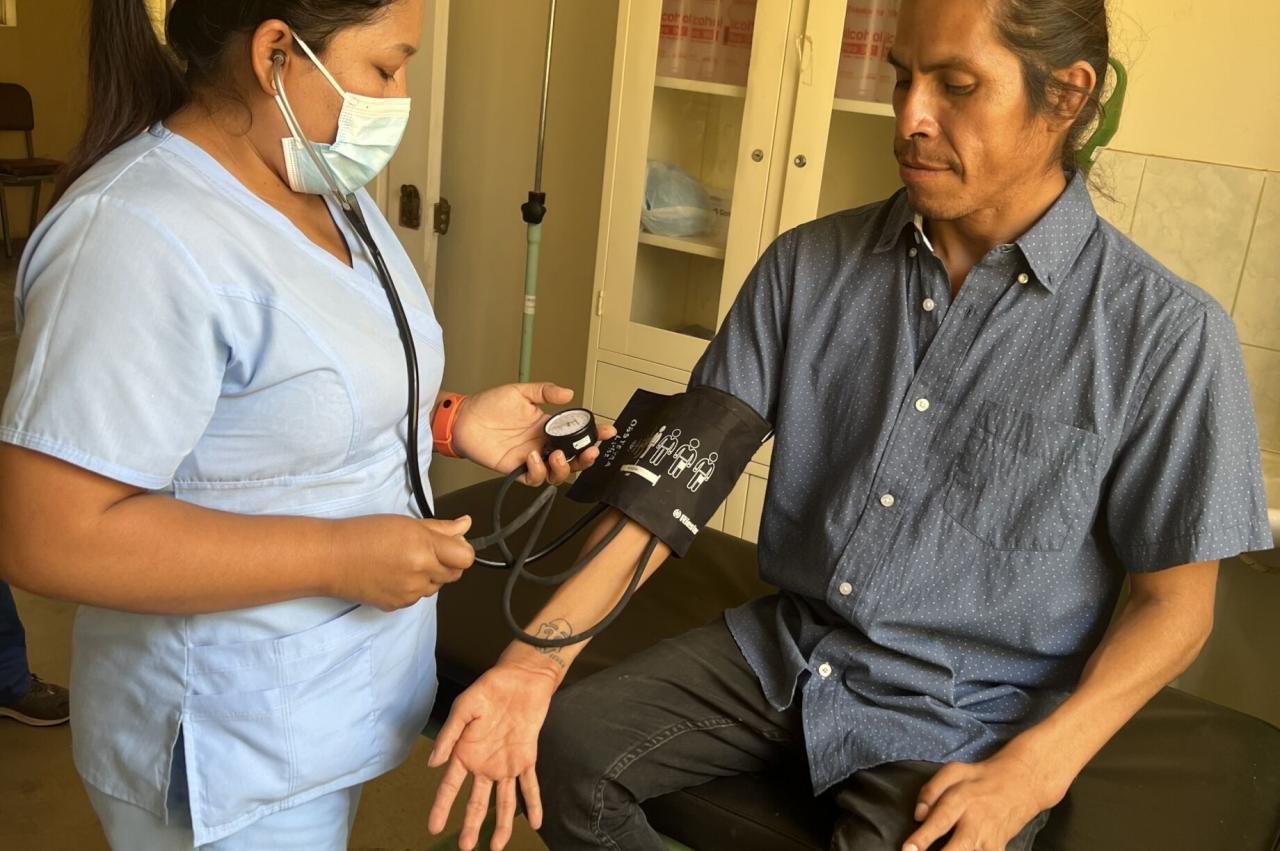
Community health workers (CHWs) play a vital role in improving health outcomes and addressing health disparities. While their work is often focused on direct patient care and community outreach, there are numerous opportunities for career advancement and professional growth.
CHWs can pursue various paths, including specialization, leadership roles, and higher education, to expand their knowledge, skills, and responsibilities. This section explores these opportunities, providing insights on how CHWs can enhance their career prospects and make a greater impact on the health of their communities.
Specialization Opportunities
CHWs can specialize in specific areas of public health, focusing their expertise on particular populations or health concerns. This specialization allows them to gain in-depth knowledge and skills in their chosen area, increasing their value to employers and expanding their career options.
- Maternal and Child Health:CHWs can specialize in supporting pregnant women, new mothers, and infants, providing education, counseling, and support services. This specialization may involve working with programs like the Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program or providing prenatal care in underserved communities.
- Chronic Disease Management:CHWs can specialize in helping individuals manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and asthma. This specialization may involve providing education, support groups, and home visits to help patients adhere to their treatment plans.
- Mental Health:CHWs can specialize in providing mental health support to individuals and families, addressing issues such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse. This specialization may involve working with community mental health centers, schools, or faith-based organizations.
- Substance Abuse:CHWs can specialize in working with individuals struggling with substance abuse, providing support, counseling, and referrals to treatment programs. This specialization may involve working with organizations like the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) or local addiction recovery centers.
Leadership Roles
CHWs can progress into leadership roles within their organizations or communities. These roles involve taking on greater responsibility for program development, staff supervision, and community engagement.
- Program Coordinator:CHWs can become program coordinators, overseeing the implementation and evaluation of specific health programs within their organizations. This role may involve managing budgets, coordinating staff, and working with community partners.
- Community Health Manager:CHWs can advance to community health manager positions, leading teams of CHWs and coordinating health services for specific communities. This role may involve developing and implementing community health plans, advocating for health policy changes, and building partnerships with local organizations.
- Community Health Advocate:CHWs can become community health advocates, raising awareness of health issues, promoting health policies, and mobilizing community members to address health disparities. This role may involve working with local government, community organizations, and advocacy groups.
Higher Education Pathways
CHWs can pursue higher education to enhance their knowledge and skills, opening up opportunities for advancement and specialization.
- Associate’s Degree in Health Sciences:CHWs can earn an associate’s degree in health sciences, providing them with a foundational understanding of public health principles, disease prevention, and health promotion. This degree can prepare them for roles such as health educator, community health specialist, or outreach coordinator.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Public Health:CHWs can pursue a bachelor’s degree in public health, gaining a comprehensive understanding of public health issues, interventions, and policy. This degree can prepare them for leadership roles such as program manager, community health director, or health policy analyst.
- Master’s Degree in Public Health:CHWs can obtain a master’s degree in public health, specializing in areas such as epidemiology, health policy, or health education. This advanced degree can prepare them for research positions, academic roles, or leadership positions within government agencies or non-profit organizations.
Community health workers play a vital role in promoting wellness within their communities. They often connect individuals with resources and services, including those related to beauty and self-care. For instance, they might recommend the ulta 21 days beauty program, which provides personalized guidance and products for a healthy glow.
By promoting holistic well-being, community health workers empower individuals to lead fulfilling lives.
Professional Development Opportunities
CHWs can enhance their career prospects through ongoing learning and networking. Many organizations and programs support the professional development of CHWs, offering training, mentorship, and networking opportunities.
- The National Association of Community Health Workers (NACHW):NACHW provides training, certification, and networking opportunities for CHWs. They offer online courses, webinars, and conferences on a variety of topics related to community health work.
NACHW’s mission is to advance the community health worker profession through education, advocacy, and research.
- The Community Health Worker Education and Training Program (CHW-ETP):CHW-ETP is a national program that provides training and resources for CHWs. They offer online courses, workshops, and technical assistance to support CHWs in their work.
- State and Local Health Departments:Many state and local health departments offer training and professional development opportunities for CHWs. These programs may focus on specific health issues, such as chronic disease management, mental health, or substance abuse.
- Universities and Colleges:Some universities and colleges offer certificate programs or degree programs specifically designed for CHWs. These programs provide CHWs with the knowledge and skills needed to advance their careers.
Challenges and Rewards of the Profession
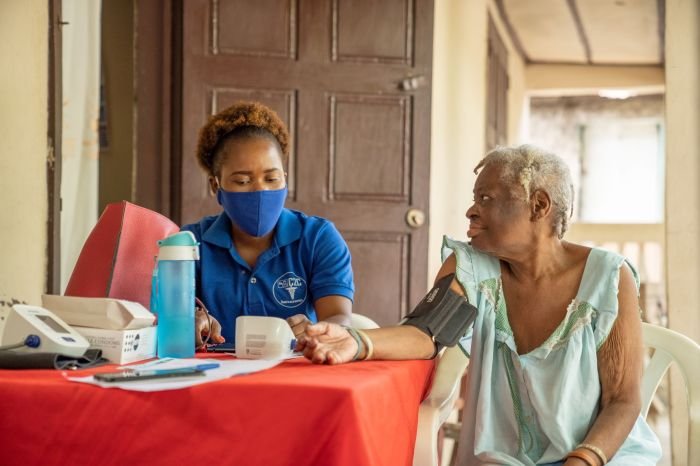

The role of a community health worker, while deeply rewarding, also presents a unique set of challenges. Understanding these challenges and the intrinsic rewards is crucial for individuals considering this career path. This section explores the common hurdles faced by community health workers, highlighting the motivating factors that make this profession fulfilling.
Common Challenges Faced by Community Health Workers
Community health workers often navigate a demanding environment characterized by limited resources, heavy workloads, and emotional strain.
- Heavy Workload:Community health workers often manage large caseloads, requiring them to juggle multiple tasks and responsibilities simultaneously. This can lead to feelings of being overwhelmed and burnt out.
- Resource Limitations:Community health workers may operate with limited access to resources, such as transportation, technology, or funding. This can hinder their ability to effectively deliver services and support their clients.
- Emotional Demands:Working with vulnerable populations often exposes community health workers to difficult situations, including poverty, illness, and social injustices. This can take a toll on their emotional well-being.
Rewarding Aspects of the Profession
Despite the challenges, community health workers find deep satisfaction in their work, knowing they are making a tangible difference in people’s lives.
- Direct Impact on Individuals and Communities:Community health workers witness firsthand the positive impact of their efforts on the lives of individuals and communities. They play a crucial role in improving health outcomes, promoting well-being, and empowering individuals to take control of their health.
- Building Trust and Relationships:Community health workers often work closely with individuals and families, building trust and strong relationships. This allows them to provide culturally sensitive and tailored support, fostering a sense of connection and belonging.
- Advocating for Health Equity:Community health workers are passionate advocates for health equity, working to address health disparities and improve access to care for marginalized communities. They use their lived experiences and cultural understanding to champion the needs of their communities.
Strategies for Managing Stress and Maintaining a Healthy Work-Life Balance
Managing stress and maintaining a healthy work-life balance is crucial for community health workers to thrive in their profession.
- Self-Care Practices:Prioritizing self-care is essential. This includes engaging in activities that promote physical and mental well-being, such as exercise, mindfulness, and spending time with loved ones.
- Setting Boundaries:Establishing clear boundaries between work and personal life is crucial for preventing burnout. This involves setting limits on work hours and avoiding work-related tasks outside of designated work time.
- Seeking Support:Community health workers should seek support from colleagues, supervisors, or mental health professionals when needed. Joining professional organizations or support groups can provide valuable connections and resources.
Resources for Community Health Workers

Community health workers (CHWs) play a vital role in improving health outcomes, particularly for underserved populations. Accessing the right resources can enhance their skills, knowledge, and effectiveness in their work. This section will explore the various resources available to CHWs, including professional organizations, online communities, and training materials.
Professional Organizations
Professional organizations provide a platform for CHWs to connect with peers, stay informed about industry trends, and access valuable resources.
Community health workers play a crucial role in connecting individuals with essential resources, and sometimes that can involve navigating the bustling streets of New York City. For example, if a client needs to access beauty products or services, a community health worker might direct them to ulta beauty 51 w 34th st new york ny 10001 , a popular destination for beauty supplies.
By understanding the needs of their communities, community health workers can provide valuable support and guidance in a wide range of areas, including access to healthcare, social services, and even beauty products.
- National Association of Community Health Workers (NACHW)
- Website: https://www.nachw.org/
- Description: NACHW is a national organization dedicated to advancing the community health worker profession. It offers advocacy, training, and resources to support CHWs.
- Benefits: Membership provides access to networking opportunities, professional development resources, and advocacy efforts.
- Community Health Worker Association of Oregon (CHWAO)
- Website: https://www.chwaoregon.org/
- Description: CHWAO focuses on supporting and advocating for CHWs in Oregon. It offers training, networking events, and policy initiatives.
- Benefits: Membership provides access to resources specific to Oregon’s CHW landscape, including training opportunities and advocacy support.
- National Coalition of Community Health Workers (NCCHW)
- Website: https://www.ncchw.org/
- Description: NCCHW is a national organization dedicated to advancing the community health worker profession. It offers advocacy, training, and resources to support CHWs.
- Benefits: Membership provides access to networking opportunities, professional development resources, and advocacy efforts.
Online Communities
Online communities provide a space for CHWs to connect with peers, share experiences, and seek support.
- CHW Network
- Website: https://www.chwnetwork.org/
- Description: CHW Network is a national online community for CHWs, offering resources, forums, and networking opportunities.
- Benefits: Members can access a wealth of information, connect with other CHWs, and participate in discussions related to the profession.
- Community Health Worker Facebook Groups
- Description: Several Facebook groups are dedicated to CHWs, providing a platform for sharing information, asking questions, and connecting with peers.
- Benefits: These groups offer a convenient way to stay updated on industry news, share experiences, and seek support from other CHWs.
Training Materials
Access to quality training materials is crucial for CHWs to stay updated on best practices and enhance their skills.
- NACHW Training Resources
- Website: https://www.nachw.org/training/
- Description: NACHW offers a variety of training resources, including online courses, webinars, and workshops, covering various aspects of the CHW profession.
- Benefits: These resources provide CHWs with opportunities to enhance their skills, stay updated on best practices, and earn certifications.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Website: https://www.cdc.gov/communityhealthworkers/
- Description: The CDC provides resources and guidance for CHWs, including training materials, best practices, and information on various health issues.
- Benefits: CHWs can access evidence-based information and training materials to enhance their knowledge and skills.
- Online Learning Platforms
- Description: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer online courses and certifications related to community health, health education, and related fields.
- Benefits: These platforms provide flexible learning options for CHWs to enhance their skills and knowledge at their own pace.
Accessing and Utilizing Resources Effectively
- Identify Your Needs:Before exploring resources, identify your specific needs and goals. What skills do you want to improve? What information are you seeking?
- Network:Connect with other CHWs, attend conferences, and join online communities to learn about available resources and best practices.
- Stay Updated:Regularly check the websites of professional organizations and online communities for new resources, training opportunities, and industry updates.
- Seek Mentorship:Find a mentor or experienced CHW who can guide you through the resources available and provide support.
Final Review

The impact of community health workers is undeniable, as they contribute to healthier communities and empower individuals to take charge of their health. As the demand for these professionals continues to grow, their dedication and commitment will remain essential in shaping a more equitable and accessible healthcare system.
FAQ Compilation
What are the typical salaries for community health workers?
Salaries for community health workers vary depending on factors such as location, experience, and employer. It’s advisable to research salary ranges in your specific area.
What are the most common job titles for community health workers?
Some common job titles include Community Health Worker, Outreach Worker, Health Educator, Patient Navigator, and Case Manager.
What are the benefits of working as a community health worker?
Benefits include making a direct impact on people’s lives, working in a dynamic and rewarding field, and contributing to positive social change.