Health alliance plans are a growing trend in the healthcare landscape, offering individuals and employers a unique approach to accessing quality medical care. These plans, often characterized by a strong network of providers and a focus on preventative care, aim to provide comprehensive health coverage while controlling costs.
Health alliances have evolved over time, driven by the need for more affordable and accessible healthcare options. They represent a departure from traditional insurance models, emphasizing collaboration between healthcare providers and members to achieve shared goals.
Introduction to Health Alliance Plans
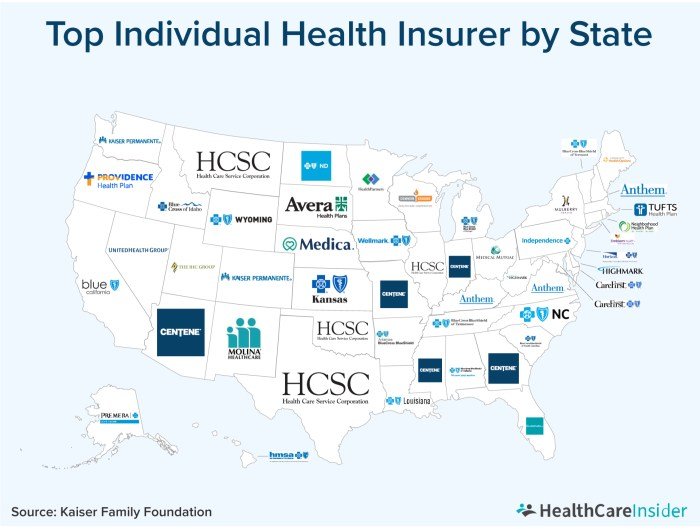
Health alliance plans, also known as health maintenance organizations (HMOs), are a type of managed care plan that provides comprehensive health coverage to members through a network of healthcare providers. They function as a middleman between healthcare providers and patients, offering a streamlined and cost-effective approach to healthcare access.Health alliance plans are designed to offer affordable healthcare while promoting preventive care and efficient utilization of healthcare resources.
They operate by negotiating discounted rates with healthcare providers within their network, creating a closed system where members can access care at a lower cost.
Historical Context and Evolution of Health Alliances
The concept of health alliances emerged in the mid-20th century as a response to rising healthcare costs and the increasing complexity of the healthcare system. The first HMOs were established in the 1930s, primarily for industrial workers. However, the widespread adoption of HMOs occurred in the 1970s, fueled by the rise of managed care and the passage of the Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973.
This legislation provided federal support for the development and expansion of HMOs, paving the way for their widespread acceptance as a viable alternative to traditional fee-for-service insurance.Since their inception, health alliances have undergone significant evolution, adapting to changes in the healthcare landscape and consumer preferences.
The advent of technology has led to the development of digital health platforms, allowing members to manage their health information and access care remotely. Moreover, the emphasis on value-based care has prompted health alliances to adopt new models that incentivize providers to deliver high-quality care at a lower cost.
Rationale Behind Health Alliances and Intended Benefits
Health alliances are designed to address several key challenges in the healthcare system, including:* Rising Healthcare Costs:By negotiating discounted rates with healthcare providers and promoting preventive care, health alliances aim to control costs and make healthcare more affordable for members.
Limited Access to Care
Health alliances offer access to a network of healthcare providers, ensuring that members can readily access the care they need.
Health alliance plans are becoming increasingly popular, offering a blend of affordability and personalized care. One company making waves in this space is Agilon Health, whose focus on value-based care has attracted attention. If you’re interested in investing in the future of healthcare, you might want to consider checking out agilon health stock.
Ultimately, the success of these plans hinges on their ability to deliver quality care at a sustainable cost, which is where companies like Agilon Health are playing a critical role.
Lack of Coordination of Care
Health alliances provide a coordinated approach to care, ensuring that members receive comprehensive and efficient healthcare services.The intended benefits of health alliances include:* Lower Premiums:By leveraging their bargaining power and promoting cost-effective care, health alliances can offer lower premiums compared to traditional fee-for-service insurance.
Improved Access to Care
Health alliances offer access to a network of healthcare providers, ensuring that members can readily access the care they need.
Enhanced Quality of Care
Health alliances emphasize preventive care and promote coordinated care, which can lead to improved health outcomes for members.
Health alliance plans often include fitness benefits, and NYU students have access to a fantastic resource: the NYU Fitness Center. This state-of-the-art facility provides a range of equipment and classes, making it easy for students to stay active and healthy while balancing their academic commitments.
Such partnerships between health alliance plans and universities can be mutually beneficial, promoting overall wellness and healthy lifestyles.
Greater Transparency
Health alliances typically provide clear and concise information about their services, costs, and provider network.
Key Features of Health Alliance Plans

Health alliance plans, also known as preferred provider organizations (PPOs), are a popular type of health insurance plan that offers a balance of flexibility and cost savings. They provide a wide network of healthcare providers and allow you to choose your doctor without needing a referral.
However, they typically involve some cost-sharing mechanisms, such as copays and deductibles, to manage healthcare expenses.
Network of Healthcare Providers
Health alliance plans establish a network of healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities, with whom they have negotiated discounted rates. You can choose your healthcare provider from within this network, ensuring you receive care at a lower cost.
Cost-Sharing Mechanisms
Health alliance plans employ cost-sharing mechanisms to share the cost of healthcare services between the insurance company and the insured individual.
- Copays:These are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, such as doctor visits or prescriptions.
- Deductibles:This is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in for covered services.
Coverage for Specific Medical Services
Health alliance plans typically cover a broad range of medical services, including:
- Preventive care:This includes routine checkups, screenings, and immunizations.
- Hospitalization:This covers costs associated with inpatient stays, surgery, and emergency room visits.
- Prescription drugs:Most plans offer coverage for prescription medications, although there may be formularies that limit the drugs covered.
- Mental health and substance abuse treatment:Many plans provide coverage for these services.
Administrative Processes
Health alliance plans typically involve administrative processes, such as:
- Pre-authorization:Some services may require pre-authorization from the insurance company before they are covered.
- Claims processing:You will need to submit claims to the insurance company for reimbursement of covered expenses.
- Customer service:Health alliance plans provide customer service to assist you with your insurance needs.
Comparison with Other Health Insurance Plans
Health alliance plans share similarities and differences with other types of health insurance plans, such as HMOs and POS plans.
- HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations):HMOs typically have a narrower network of providers and require referrals for specialist care. They often have lower premiums than PPOs but may have higher copays and deductibles.
- POS (Point-of-Service) Plans:POS plans offer a combination of HMO and PPO features. They allow you to see providers outside the network, but you may have to pay higher costs for out-of-network care.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Health Alliance Plans
Health alliance plans, also known as health purchasing alliances or health care cooperatives, are a relatively new model of health insurance that aims to provide affordable and high-quality health care by pooling resources and negotiating lower prices with providers. These plans offer several potential benefits for both individuals and employers, but they also come with some drawbacks and challenges.
Advantages of Health Alliance Plans
Health alliance plans can provide several advantages for individuals and employers, including:
- Lower Premiums:By pooling resources and negotiating lower prices with providers, health alliances can often offer lower premiums compared to traditional health insurance plans.
- Wider Network of Providers:Health alliances typically have a wider network of providers than traditional health insurance plans, giving individuals more choices when selecting a doctor or hospital.
- Improved Quality of Care:Health alliances can often negotiate higher quality standards with providers, leading to improved patient care and outcomes.
- Greater Transparency:Health alliances are often more transparent about their pricing and provider networks than traditional health insurance plans, giving individuals more information to make informed decisions about their health care.
- Increased Access to Care:Health alliances can help to increase access to care, particularly in underserved areas, by providing more affordable and convenient options for individuals.
Drawbacks of Health Alliance Plans
Despite their potential benefits, health alliance plans also have some drawbacks and challenges, including:
- Limited Availability:Health alliances are not widely available in all areas, and they may not be available to all individuals or employers.
- Administrative Complexity:Setting up and managing a health alliance can be complex and time-consuming, requiring significant administrative resources.
- Potential for Conflicts of Interest:Health alliances can face potential conflicts of interest if they are also involved in providing health care services.
- Lack of Standardization:There is no standardized model for health alliances, which can make it difficult to compare plans and understand their benefits and drawbacks.
- Limited Consumer Protection:Consumer protection laws for health alliances may not be as robust as those for traditional health insurance plans.
Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Health Alliances
The effectiveness and efficiency of health alliances depend on several factors, including:
- The Size and Scope of the Alliance:Larger alliances with a greater number of members have more bargaining power with providers and can negotiate lower prices.
- The Quality of Provider Networks:The quality of providers in the alliance’s network is crucial to ensuring high-quality care for members.
- Administrative Efficiency:The administrative efficiency of the alliance is important to keep costs low and ensure smooth operations.
- Transparency and Accountability:Transparency and accountability are essential for building trust with members and ensuring that the alliance is operating in their best interests.
- Regulatory Environment:The regulatory environment in which health alliances operate can have a significant impact on their success.
Types of Health Alliance Plans
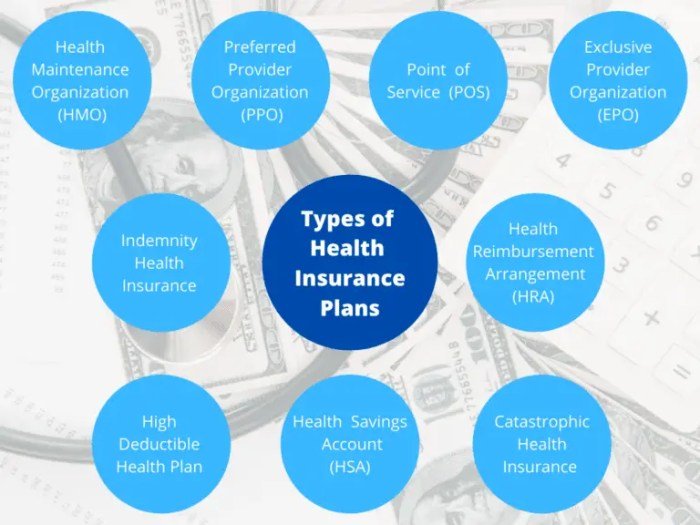
Health alliance plans, also known as health maintenance organizations (HMOs), offer a comprehensive approach to healthcare by integrating various medical services under one umbrella. They are distinguished by their network of providers, negotiated rates, and emphasis on preventive care. These plans are broadly categorized based on their geographic reach, target population, and specific health needs.
Geographic Coverage
Health alliance plans can vary significantly in their geographic coverage, ranging from local to national networks. This diversity reflects the needs of different populations and the capabilities of various health alliances.
Health alliance plans are designed to offer comprehensive health coverage, often including fitness benefits. Many plans provide access to a variety of gyms, and you might find that your plan covers planet fitness 24 hr locations. This could be a great option if you’re looking for a convenient and affordable way to stay active and healthy while taking advantage of your health alliance plan.
- Local Health Alliance Plans:These plans operate within a specific region, often serving a particular city or county. They have strong ties to local healthcare providers and are well-versed in the community’s health needs. Examples include the Kaiser Permanenteplan, which is prominent in California and other states, and Group Health Cooperative, primarily serving the Seattle metropolitan area.
- Regional Health Alliance Plans:These plans extend their coverage to multiple counties or states within a specific geographic region. They offer a wider network of providers and can cater to the needs of a larger population. An example is the Blue Shield of Californiaplan, which operates throughout the state of California, and UnitedHealthcare, which has a significant presence in many regions across the United States.
- National Health Alliance Plans:These plans provide coverage nationwide, allowing members to access healthcare services regardless of their location. They have extensive provider networks and often offer specialized programs for various health needs. Examples include Aetnaand Cigna, both of which have nationwide networks and offer a wide range of health plans.
Target Populations, Health alliance plans
Health alliance plans often tailor their services to specific target populations, such as employees, retirees, or individuals in particular industries. This targeted approach allows them to address the unique health needs of these groups.
- Employee Health Alliance Plans:These plans are commonly offered by employers to their employees as a benefit. They provide comprehensive healthcare coverage, including preventive care, medical services, and prescription drugs. Examples include plans offered by Anthemand Humana, which are popular choices for large employers.
- Retiree Health Alliance Plans:These plans are designed specifically for retirees and offer coverage tailored to their age-related health needs. They may include specialized programs for seniors, such as Medicare coordination and preventive screenings. Examples include Medicare Advantageplans offered by private insurance companies, which provide comprehensive coverage for Medicare beneficiaries.
- Industry-Specific Health Alliance Plans:Some health alliance plans focus on serving specific industries, such as education, healthcare, or manufacturing. They offer plans that address the unique health concerns of these industries, such as occupational hazards or specific health risks. An example is the Health Alliance Planin Michigan, which caters to the healthcare industry and offers plans that include specialized services for healthcare professionals.
Specific Health Needs
Health alliance plans also cater to individuals with specific health needs, such as mental health concerns, chronic conditions, or specialized care requirements.
- Mental Health Health Alliance Plans:These plans prioritize mental health services and offer comprehensive coverage for mental health conditions, including therapy, medication, and inpatient care. They often have a network of mental health professionals, such as therapists and psychiatrists, to provide specialized care. Examples include Beacon Health Optionsand Optum, which offer specialized mental health plans and services.
- Chronic Condition Health Alliance Plans:These plans provide support and resources for individuals with chronic conditions, such as diabetes, asthma, or heart disease. They offer disease management programs, medication assistance, and access to specialists. Examples include plans offered by UnitedHealthcare, which has programs for managing chronic conditions, and Anthem, which offers specialized plans for individuals with diabetes.
- Specialized Care Health Alliance Plans:Some health alliance plans offer specialized care for specific health needs, such as maternity care, cancer treatment, or organ transplantation. They have networks of providers who are experts in these areas and offer comprehensive care. Examples include plans offered by Kaiser Permanente, which has a strong reputation for maternity care, and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, which offers specialized plans for cancer patients.
Choosing the Right Health Alliance Plan

Navigating the world of health alliance plans can be overwhelming, especially with the multitude of options available. Selecting the right plan is crucial to ensuring adequate coverage and affordability. To make an informed decision, it’s essential to consider your individual needs, budget, and access to healthcare providers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Health Alliance Plan
Several factors influence the suitability of a health alliance plan. Understanding these factors can help you narrow down your choices and find a plan that meets your specific requirements.
- Individual Health Needs and Preferences: Your health status, pre-existing conditions, and anticipated healthcare needs play a significant role in plan selection. If you have chronic conditions or require frequent medical care, you might prioritize plans with extensive coverage and a robust network of providers.
Conversely, if you are generally healthy and rarely seek medical attention, a plan with lower premiums and limited coverage might suffice.
- Budget Constraints: The cost of healthcare is a major concern for most individuals. Health alliance plans offer varying premium structures, deductibles, and co-pays. It’s essential to carefully evaluate your budget and choose a plan that fits your financial capabilities. Consider the balance between premium affordability and the level of coverage provided.
- Geographic Location and Access to Healthcare Providers: Your location and access to healthcare providers are crucial factors. Ensure the plan you choose covers the doctors, hospitals, and specialists you need. Check the plan’s network to confirm the availability of preferred providers within your area.
Decision-Making Framework
A structured approach can simplify the process of choosing the right health alliance plan. The following framework can guide individuals and employers in making an informed decision:
Step 1: Define Your Needs and Priorities: Start by identifying your health needs, budget constraints, and preferences. Consider your health history, anticipated healthcare usage, and the importance of specific benefits.
Step 2: Research Available Plans: Explore different health alliance plans offered in your area. Gather information on premium costs, coverage details, provider networks, and other essential features. Utilize online resources, insurance brokers, and plan websites to obtain comprehensive data.
Step 3: Compare Plans and Identify Potential Options: Once you have gathered information on various plans, compare them based on your defined needs and priorities. Focus on key aspects like coverage, cost, provider network, and benefits.
Step 4: Consult with Healthcare Professionals and Financial Advisors: Seek advice from your doctor, pharmacist, or financial advisor to gain insights on plan selection. Their expertise can help you understand the intricacies of different plans and their implications for your health and finances.
Step 5: Make an Informed Decision: Based on your research, comparisons, and expert advice, choose the health alliance plan that best aligns with your needs, budget, and preferences.
Future Trends in Health Alliance Plans
Health alliances are dynamic entities constantly adapting to the evolving healthcare landscape. Emerging trends and technological advancements are shaping the future of these collaborations, influencing their structure, operations, and impact on healthcare delivery.
The Impact of Technology on Health Alliances
Technological advancements are playing a pivotal role in transforming health alliances, enabling them to operate more efficiently and effectively. Telehealth, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are among the key drivers of this evolution.
- Telehealth: Telehealth platforms are increasingly integrated into health alliance networks, expanding access to care, particularly in underserved areas. Virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and telemedicine services enhance patient engagement and reduce healthcare costs. For instance, a health alliance in a rural region might utilize telehealth to connect patients with specialists in urban centers, improving access to specialized care without the need for extensive travel.
- Data Analytics: Health alliances are leveraging data analytics to gain insights into patient populations, identify trends, and optimize resource allocation. By analyzing data from various sources, including claims, electronic health records, and patient surveys, alliances can develop targeted interventions, improve care coordination, and enhance population health management.
An example is a health alliance using data analytics to identify patients with high risk of developing chronic diseases, enabling early interventions and preventive measures.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into health alliance operations, automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing patient care. AI-powered chatbots can provide personalized health information and support, while AI algorithms can assist in disease prediction, risk assessment, and treatment planning. Imagine a health alliance utilizing AI to analyze patient data and identify individuals who might benefit from specific interventions, such as early detection programs for certain cancers.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of health alliance plans is crucial for individuals and employers seeking to navigate the complex world of healthcare. By carefully considering factors such as individual needs, budget constraints, and geographic location, one can make an informed decision about whether a health alliance plan is the right fit.
As healthcare continues to evolve, health alliances are poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery.
General Inquiries
What are the main advantages of joining a health alliance plan?
Health alliance plans typically offer benefits like lower premiums, access to a wider network of providers, and coordinated care, potentially leading to better health outcomes.
How do health alliances manage costs?
Health alliances often use strategies like negotiating lower rates with providers, promoting preventive care, and encouraging the use of cost-effective treatments to control healthcare expenses.
What are the key differences between health alliance plans and HMOs?
While both types of plans emphasize managed care, health alliances often have a more flexible network of providers and may offer greater choice in healthcare options compared to HMOs.