Health Heart Month shines a spotlight on the importance of cardiovascular health, reminding us that our hearts are the engines that power our lives. Every beat, every pump, is a testament to the incredible complexity of this vital organ, and it’s crucial to understand how to keep it functioning optimally.
Heart disease is a leading cause of death globally, impacting millions of individuals and families. It’s a complex condition with a multitude of risk factors, but it’s also a condition that can be prevented and managed through proactive lifestyle changes and early intervention.
Heart Health Awareness: Health Heart Month

February is American Heart Month, a time dedicated to raising awareness about heart disease and promoting healthy lifestyle choices. This annual event is crucial because heart disease is a leading cause of death in the United States, impacting millions of individuals and their families.
The Importance of Heart Health
Heart health is essential for overall well-being. A healthy heart enables your body to function properly by delivering oxygen-rich blood to all organs and tissues. When your heart is healthy, you have more energy, can enjoy physical activities, and are less likely to experience health problems.
February is American Heart Month, a time to focus on our cardiovascular health. This includes making positive changes to our lifestyle, which can be as simple as making small, sustainable adjustments to our daily routine. For tips on incorporating healthy habits into your life, check out this helpful article on health starting.
By taking these steps, you can help improve your heart health and live a longer, healthier life.
Heart Disease Prevalence and Impact
Heart disease is a serious health concern with a significant impact on individuals and communities. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 1 in 4 deaths in the United States is caused by heart disease. This translates to about 655,000 deaths annually.
Examples of Heart Disease Impact
Heart disease can affect individuals and communities in various ways. For example, individuals with heart disease may experience:
- Limited physical activity
- Increased healthcare costs
- Reduced quality of life
- Emotional stress and anxiety
On a community level, heart disease can lead to:
- Increased healthcare burdens on local hospitals and clinics
- Loss of productivity due to absenteeism and disability
- Economic strain on families and communities
Risk Factors and Prevention

Heart disease is a serious condition that can have devastating consequences. It’s important to understand the risk factors for heart disease and take steps to prevent it.
Modifiable Risk Factors
Modifiable risk factors are those that can be changed through lifestyle modifications. These factors are particularly important to address as they can significantly influence your risk of developing heart disease.
- High Blood Pressure:High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, puts extra strain on your heart and blood vessels. It’s a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
- High Cholesterol:Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood. High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often called “bad” cholesterol, can build up in your arteries and increase your risk of heart disease.
- Smoking:Smoking damages your blood vessels and increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, and lung cancer.
- Physical Inactivity:Lack of regular physical activity increases your risk of heart disease, obesity, and other health problems.
- Unhealthy Diet:A diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, salt, and sugar increases your risk of heart disease.
- Obesity:Being overweight or obese increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and other health problems.
- Diabetes:Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body regulates blood sugar. It increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
- Stress:Chronic stress can increase your risk of heart disease by raising your blood pressure and heart rate.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Non-modifiable risk factors are those that you cannot change. While you cannot control these factors, understanding them is crucial for making informed decisions about your health.
- Age:Your risk of heart disease increases with age.
- Family History:If you have a family history of heart disease, your risk is higher.
- Genetics:Some people inherit genes that increase their risk of heart disease.
Strategies for Preventing Heart Disease
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease.
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet:Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, salt, and sugar.
- Get Regular Physical Activity:Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Don’t Smoke:If you smoke, quit. If you don’t smoke, don’t start.
- Manage Stress:Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
- Get Regular Checkups:See your doctor regularly for checkups and screenings.
Sample Heart-Healthy Lifestyle Plan
Here is a sample heart-healthy lifestyle plan:
- Eat a balanced diet:Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, salt, and sugar.
- Exercise regularly:Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain a healthy weight:If you are overweight or obese, talk to your doctor about a safe and effective weight loss plan.
- Don’t smoke:If you smoke, quit. If you don’t smoke, don’t start.
- Manage stress:Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
- Get regular checkups:See your doctor regularly for checkups and screenings.
Healthy Habits for a Healthy Heart
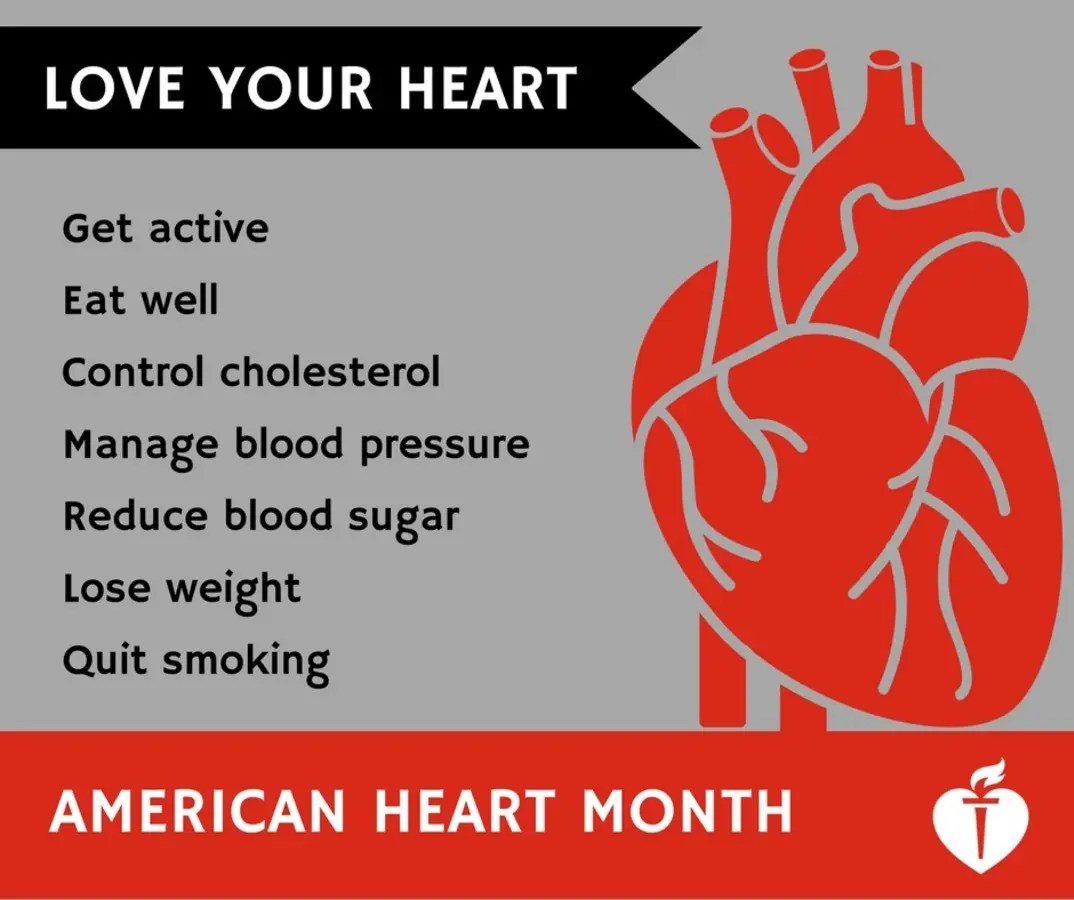
Adopting healthy habits is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. These habits encompass dietary choices, physical activity, stress management, and weight control. By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease and improve your overall well-being.
Heart-Healthy Dietary Guidelines
Following a heart-healthy diet is fundamental to protecting your cardiovascular system. This involves making conscious choices about the foods you consume.
- Limit saturated and trans fats:These unhealthy fats, found in red meat, butter, and processed foods, can raise your LDL (bad) cholesterol levels.
- Choose lean protein sources:Opt for lean meats, poultry without skin, fish, beans, and tofu as sources of protein.
- Increase your intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains:These foods are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals that promote heart health.
- Reduce your sodium intake:Excessive sodium can raise blood pressure, increasing your risk of heart disease. Choose fresh or frozen foods over processed foods, which are often high in sodium.
- Limit your intake of added sugars:Sugary drinks and processed foods contribute to weight gain and can negatively impact heart health.
Incorporating Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy heart. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Find activities you enjoy:This will make it easier to stick to your exercise routine. Consider activities like brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
- Break up your exercise into shorter intervals:Even short bursts of activity can benefit your heart health. Aim for 10 minutes of exercise at a time, several times a day.
- Incorporate physical activity into your daily routine:Take the stairs instead of the elevator, walk or bike to work, or park further away from your destination.
- Find a workout buddy:Having a friend to exercise with can help you stay motivated and accountable.
Managing Stress and Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease. Finding healthy ways to manage stress is crucial for heart health. Maintaining a healthy weight is also essential, as excess weight can put extra strain on your heart.
- Practice relaxation techniques:Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress levels.
- Get enough sleep:Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help your body recover and manage stress effectively.
- Seek support from friends and family:Talking to loved ones about your stress can provide emotional support and help you cope.
- Engage in hobbies and activities you enjoy:Spending time on activities you find pleasurable can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
- Eat a balanced diet and exercise regularly:These healthy habits can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Heart-Healthy Recipes
Here are some examples of heart-healthy recipes that you can incorporate into your diet:
- Grilled Salmon with Roasted Vegetables:Salmon is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. Pair it with roasted vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and peppers for a nutritious and flavorful meal.
- Lentil Soup:Lentils are a good source of fiber and protein, making them a heart-healthy choice. This soup is also low in calories and fat.
- Quinoa Salad with Grilled Chicken:Quinoa is a complete protein and a good source of fiber. Combine it with grilled chicken, chopped vegetables, and a light vinaigrette for a satisfying and heart-healthy salad.
- Whole-Wheat Pasta with Tomato Sauce:Choose whole-wheat pasta for added fiber and pair it with a tomato-based sauce for a healthy and flavorful meal.
Heart Disease Symptoms and Diagnosis

Understanding the symptoms of heart disease is crucial for early detection and intervention. Recognizing these signs can potentially save lives. Early diagnosis allows for prompt treatment, reducing the risk of complications and improving long-term health outcomes.
Common Symptoms of Heart Disease
Heart disease can manifest in various ways, and symptoms can vary depending on the specific condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort: This is often described as a tightness, pressure, squeezing, or aching sensation in the chest. It may radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, or back.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during exertion or when lying down, can be a sign of heart problems.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness or weakness can indicate heart disease, especially if it is new or worsening.
- Swelling in the legs or ankles: Fluid retention in the lower extremities can be a symptom of heart failure.
- Irregular heartbeat: A fluttering or racing heart, or a feeling of skipped beats, can signal an underlying heart condition.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: This can occur due to a decrease in blood flow to the brain.
- Pain or numbness in the arms or legs: This can be a sign of peripheral artery disease, a condition that affects blood flow to the extremities.
Diagnosing Heart Disease
Diagnosing heart disease involves a comprehensive evaluation that includes a medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
February is American Heart Month, a time to focus on cardiovascular health. A key component of heart health is regular exercise, and a master fitness trainer can help you create a personalized plan that fits your needs and goals. By working with a qualified professional, you can gain the knowledge and support to make lasting changes that benefit your heart and overall well-being throughout the year.
- Medical history: The doctor will ask about your family history of heart disease, lifestyle habits, and any existing medical conditions.
- Physical examination: The doctor will listen to your heart and lungs, check your blood pressure, and assess your overall health.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Various tests and procedures are used to diagnose heart disease. These may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This test measures the electrical activity of the heart and can detect abnormalities in heart rhythm or structure.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test creates images of the heart’s structure and function.
- Stress test: This test monitors heart function during exercise or medication-induced stress to assess its ability to handle increased workload.
- Cardiac catheterization: This procedure involves inserting a thin tube into a blood vessel to visualize the heart chambers and arteries.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can measure cholesterol levels, blood sugar, and other markers that may indicate heart disease.
Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing heart disease. Regular checkups and preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart disease. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional immediately.
February is American Heart Month, a time to focus on cardiovascular health. Aspire Health Partners Inc. aspire health partners inc is a great resource for learning about heart health and finding the support you need. By taking steps to improve our heart health, we can all live longer, healthier lives.
Treatment and Management

Once heart disease is diagnosed, treatment focuses on managing symptoms, preventing further damage, and improving quality of life. Treatment options vary depending on the specific type and severity of the disease, as well as the individual’s overall health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are crucial for managing heart disease. These changes can help reduce risk factors, improve heart health, and prevent complications. Here are some key lifestyle modifications:
- Quit Smoking:Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your heart.
- Healthy Diet:A heart-healthy diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy products. It limits saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, added sugars, and sodium.
- Regular Exercise:Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Physical activity strengthens the heart, lowers blood pressure, and improves cholesterol levels.
- Weight Management:Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for heart health. Losing even a small amount of weight can make a significant difference.
- Stress Management:Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Medications
Medications play a vital role in managing heart disease. They can help control symptoms, reduce risk factors, and prevent complications. Here are some common types of medications used for heart disease:
- Statins:Lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Beta-blockers:Slow the heart rate and lower blood pressure, reducing the workload on the heart.
- ACE inhibitors:Relax blood vessels and reduce blood pressure, improving blood flow to the heart.
- Aspirin:Reduces blood clotting, preventing heart attacks and strokes.
- Nitrates:Dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart and relieving chest pain.
- Diuretics:Remove excess fluid from the body, reducing blood pressure and relieving fluid buildup.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehabilitation programs are supervised exercise and education programs designed to help people recover from heart attacks, heart surgery, or other heart conditions. These programs offer:
- Structured Exercise:Gradual and safe exercise program tailored to individual needs and abilities.
- Education:Information about heart health, risk factors, medications, and lifestyle changes.
- Counseling:Support and guidance from healthcare professionals, including nurses, doctors, and exercise physiologists.
- Stress Management:Techniques for coping with stress and anxiety.
- Nutrition Counseling:Advice on healthy eating habits to support heart health.
Managing Heart Disease Effectively
Managing heart disease requires a lifelong commitment to healthy habits and close collaboration with your healthcare provider. Here are some tips for effective management:
- Follow Your Treatment Plan:Take your medications as prescribed and attend all scheduled appointments.
- Monitor Your Symptoms:Pay attention to any changes in your health and report them to your doctor promptly.
- Make Healthy Lifestyle Changes:Adopt a heart-healthy diet, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
- Get Support:Join a support group or talk to a therapist to cope with the emotional challenges of heart disease.
- Ask Questions:Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor or other healthcare providers any questions you have about your condition or treatment.
Heart Health Resources and Support

Navigating the world of heart health can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone. There are numerous resources and support systems available to help you stay informed, manage your health, and connect with others who understand.
Reputable Organizations and Resources
Access to reliable information is crucial for making informed decisions about your heart health. Many organizations dedicate themselves to providing accurate and up-to-date resources.
- American Heart Association (AHA):This organization offers a wealth of information on heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. They provide educational materials, research updates, and advocacy efforts to promote heart health.
- American College of Cardiology (ACC):The ACC is a professional medical society dedicated to cardiovascular care.
Their website provides information for both healthcare professionals and the public on various heart-related topics.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI):This institute, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), conducts research and provides information on heart health, lung diseases, and blood disorders. Their website features resources on heart disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):The CDC offers comprehensive information on heart disease, including risk factors, prevention strategies, and statistics. Their website provides valuable resources for understanding and managing heart health.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in heart health management. They provide personalized guidance, diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing support.
- Primary Care Physicians:Your primary care physician can conduct regular checkups, monitor your risk factors, and refer you to specialists if needed.
- Cardiologists:Cardiologists specialize in diagnosing and treating heart conditions. They may perform tests, prescribe medications, and recommend lifestyle changes.
- Cardiac Surgeons:Cardiac surgeons perform surgery on the heart and surrounding vessels to treat conditions like coronary artery disease or heart valve problems.
- Other Specialists:Depending on your specific needs, you may also work with other specialists, such as vascular surgeons, electrophysiologists, or cardiac rehabilitation therapists.
Support Groups and Community Initiatives, Health heart month
Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community.
- Support Groups:Many organizations offer support groups for individuals living with heart disease or their families. These groups provide a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and connect with others.
- Community Initiatives:Local communities often organize events and programs focused on heart health awareness and prevention.
These initiatives may include educational workshops, screenings, and fitness activities.
Finding Reliable Information and Staying Informed
The internet offers a vast amount of information, but it’s essential to be discerning about the sources you rely on.
- Look for Reputable Sources:When seeking information online, prioritize websites from established organizations like the AHA, ACC, NHLBI, and CDC.
- Be Critical of Information:Question claims that seem too good to be true or lack supporting evidence.
- Consult Healthcare Professionals:Always discuss any concerns or questions you have with your doctor or other healthcare professionals.
- Stay Up-to-Date:Regularly check websites from reputable organizations for the latest research and recommendations on heart health.
Final Thoughts
By embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle, we empower ourselves to live longer, healthier lives. Health Heart Month serves as a reminder that taking care of our hearts is not just about avoiding disease, but about maximizing our quality of life and enjoying every beat to the fullest.
Top FAQs
What are some simple steps I can take to improve my heart health?
Start by incorporating regular physical activity into your routine, making heart-healthy dietary choices, and managing stress effectively. These small changes can have a significant impact on your overall cardiovascular well-being.
How can I get involved in Health Heart Month?
There are many ways to participate! You can spread awareness on social media, donate to heart health organizations, or volunteer your time to support heart health initiatives in your community.
Is there a specific age when I should start focusing on heart health?
It’s never too early or too late to prioritize heart health. Even young adults can benefit from adopting healthy habits that will safeguard their cardiovascular well-being in the long run.