What is a health insurance deductible mean – What does a health insurance deductible mean? It’s a common question, and the answer can significantly impact your healthcare costs. Think of a deductible as a threshold you need to meet before your insurance kicks in to cover medical expenses.
Imagine you have a $1,000 deductible, and you need surgery costing $5,000. You’d pay the first $1,000 out of pocket, and your insurance would cover the remaining $4,000.
Deductibles are a key component of health insurance plans, influencing your premium costs and how much you pay for healthcare. They are designed to encourage responsible utilization of healthcare services and to help manage overall healthcare costs. Understanding deductibles is crucial for making informed decisions about your health insurance plan and managing your healthcare expenses.
What is a Health Insurance Deductible?

Imagine you have a car with insurance. If you get into an accident, you have to pay a certain amount out of pocket before the insurance kicks in. A health insurance deductible is similar. It’s the amount you pay for covered healthcare services before your health insurance starts paying its share.
Deductible in Action, What is a health insurance deductible mean
Let’s say your health insurance plan has a $1,000 deductible. You go to the doctor for a medical issue and the bill comes to $2,000. You’ll pay the first $1,000 out of pocket, and your insurance will cover the remaining $1,000.
Relationship Between Deductibles and Premiums
Deductibles and premiums are linked. A higher deductible typically means a lower monthly premium, and vice versa.
Why Do Health Insurance Plans Have Deductibles?
Health insurance deductibles are a common feature of many plans, and while they might seem like an extra cost, they play a crucial role in how health insurance works and how costs are managed. Deductibles act as a threshold you need to meet before your insurance starts covering your medical expenses.
In essence, you pay for a portion of your healthcare costs upfront, and once you’ve reached the deductible amount, your insurance kicks in to cover the remaining expenses.
Deductibles and Cost Management
Deductibles are designed to encourage responsible healthcare utilization and help manage healthcare costs. Here’s how:* Sharing Costs:Deductibles help share the cost of healthcare between the insurance company and the policyholder. By requiring policyholders to pay a portion of their healthcare costs upfront, deductibles incentivize them to be more mindful of their healthcare spending and seek care only when truly necessary.
A health insurance deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. It’s like a “gatekeeper” to your benefits. You might be wondering how to manage these costs, and that’s where institutions like western health university can be helpful.
They offer programs and resources to educate individuals about navigating the complexities of healthcare and insurance, including understanding deductibles and finding ways to minimize their impact.
Lower Premiums
Deductibles often correlate with lower premiums. By accepting a higher deductible, you agree to pay more out-of-pocket initially, but you can potentially save money on your monthly premiums.
Preventing Overutilization
Deductibles can help prevent unnecessary healthcare utilization. When individuals know they have to pay a certain amount before their insurance kicks in, they may be less likely to seek care for minor ailments or schedule unnecessary tests.
Pros and Cons of Having a Deductible
Having a deductible in your health insurance plan comes with both advantages and disadvantages:
Pros
- Lower Premiums:A higher deductible often translates to lower monthly premiums, making health insurance more affordable for some individuals.
- Financial Responsibility:Deductibles encourage individuals to be more mindful of their healthcare spending and make informed decisions about their care.
Cons
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses:Deductibles can result in significant out-of-pocket expenses, especially for individuals who require frequent or expensive medical care.
- Access to Care:High deductibles can deter individuals from seeking necessary care due to the fear of incurring substantial out-of-pocket costs, potentially leading to delayed care or untreated health issues.
Types of Deductibles
Deductibles can vary in how they are applied, and understanding these variations is crucial for making informed decisions about your health insurance plan. Here’s a breakdown of some common types of deductibles.
Individual vs. Family Deductibles
Health insurance plans often offer both individual and family deductibles. This distinction is important, especially for families with multiple members.
- Individual Deductible:This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in for each individual covered under the plan. For example, if you have a $1,000 individual deductible and incur $1,500 in medical expenses, you would pay the first $1,000 and your insurance would cover the remaining $500.
- Family Deductible:This is the total amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in for the entire family. The family deductible can be met by any individual on the plan, meaning that if one family member incurs $2,000 in medical expenses and another incurs $1,000, the family deductible might be met, and coverage would apply to subsequent expenses.
For example, if your family deductible is $3,000, once a combined $3,000 in medical expenses is incurred by the family, the insurance coverage would start applying to future expenses for all family members.
High vs. Low Deductibles
The level of your deductible directly influences your out-of-pocket costs. Choosing between a high or low deductible is a personal decision, and it depends on your individual circumstances and risk tolerance.
- High Deductible:High deductible plans typically have lower monthly premiums. However, you’ll pay more out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in. This type of plan can be a good option for individuals who are generally healthy and confident in their ability to manage smaller medical expenses.
For example, a high deductible plan might require you to pay $5,000 before coverage starts. This means you would be responsible for the first $5,000 of medical expenses.
- Low Deductible:Low deductible plans have higher monthly premiums but offer greater protection from high medical expenses. This type of plan can be a good option for individuals who have a history of health issues or are concerned about unexpected medical bills.
For example, a low deductible plan might require you to pay only $1,000 before coverage starts, providing greater protection from large medical bills.
Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Maximums

Deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums are two important concepts in health insurance that work together to determine how much you pay for your healthcare. Understanding these concepts is crucial for making informed decisions about your health insurance coverage and for planning your healthcare finances.
Relationship Between Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Maximums
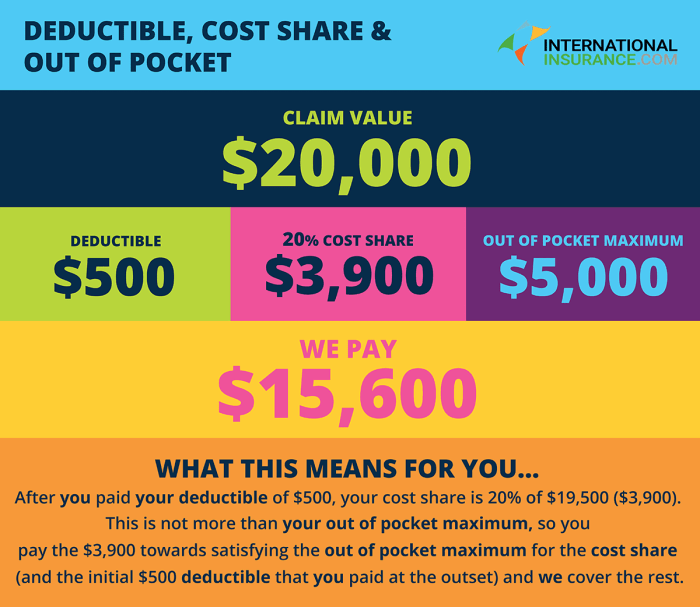
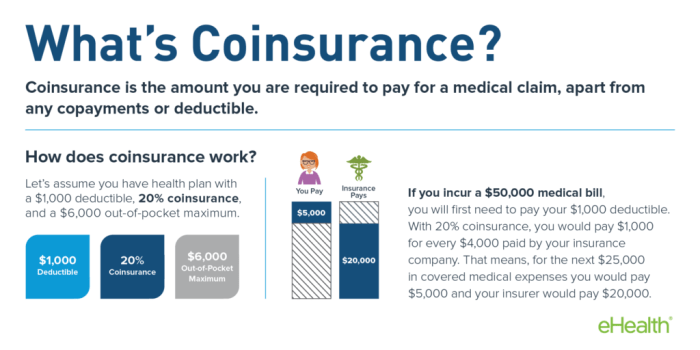
The deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare expenses before your health insurance plan starts paying. The out-of-pocket maximum is the most you will have to pay for covered healthcare expenses in a year, including deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
The out-of-pocket maximum includes your deductible, but it does not include your monthly premium.
An Example
Imagine you have a health insurance plan with a $1,000 deductible and a $5,000 out-of-pocket maximum. If you have $2,000 in covered healthcare expenses, you will pay the first $1,000 (your deductible) and your insurance company will pay the remaining $1,000.
If you have $7,000 in covered healthcare expenses, you will pay $5,000 (your out-of-pocket maximum) and your insurance company will pay the remaining $2,000.
Importance of Understanding Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Maximums
Understanding both deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums is essential for financial planning because they can significantly impact your healthcare costs. If you have a high deductible plan, you may be able to save on your monthly premiums, but you will have to pay more out-of-pocket for healthcare expenses.
Conversely, if you have a low deductible plan, you will have to pay more for your monthly premiums, but you will have to pay less out-of-pocket for healthcare expenses.
Factors Influencing Deductible Amounts: What Is A Health Insurance Deductible Mean
The amount of your health insurance deductible is influenced by a variety of factors, including your age, health status, and the level of coverage you choose. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your health insurance plan.
A health insurance deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. It’s like a financial threshold you need to cross before your plan starts sharing the cost of your medical care. So, if you’re looking to invest in your health and wellness, perhaps a luxurious retreat like cal a vie health spa california could be a worthwhile investment, even if you have to factor in a deductible for any related medical treatments.
Age
Your age is a significant factor in determining your deductible. Generally, older individuals tend to have higher deductibles than younger individuals. This is because older individuals are more likely to require medical care, and insurance companies adjust their premiums and deductibles to reflect this increased risk.
Health Status
Your health status also plays a role in determining your deductible. Individuals with pre-existing conditions may face higher deductibles than those who are considered healthy. This is because insurance companies assess the likelihood of individuals needing medical care and adjust their premiums and deductibles accordingly.
Coverage Level
The level of coverage you choose can significantly impact your deductible. Plans with higher coverage levels typically have lower deductibles. However, these plans also come with higher premiums. Conversely, plans with lower coverage levels may have higher deductibles but lower premiums.
Health Insurance Providers
Deductibles can vary significantly across different health insurance providers. Insurance companies have different pricing structures and risk assessments, leading to variations in deductible amounts. It’s essential to compare quotes from multiple providers to find the best value for your needs.
Choosing the Right Deductible
Selecting the right deductible is a crucial part of choosing a health insurance plan. It involves weighing your potential healthcare costs against your financial comfort level. This decision impacts how much you pay out-of-pocket for medical expenses and your monthly premium.
Deductible Selection Guide
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right deductible:
- Estimate Your Healthcare Needs:Consider your health history, family history, and current health status. If you have a chronic condition or are prone to frequent illnesses, you might benefit from a lower deductible. However, if you are generally healthy and have no major medical concerns, a higher deductible might be more cost-effective.
- Assess Your Financial Capacity:Evaluate your financial situation and your ability to pay a higher deductible if needed. Consider your savings, income, and emergency fund. A higher deductible might mean lower monthly premiums, but you’ll need to be prepared to cover a larger amount out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in.
- Compare Plans and Deductibles:Explore different health insurance plans and their corresponding deductibles. Compare the monthly premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums. Look for plans that offer a balance between affordability and coverage that aligns with your needs.
- Factor in Risk Tolerance:Consider your personal risk tolerance. Are you comfortable with the possibility of having to pay a significant amount out-of-pocket for healthcare? A higher deductible might offer lower premiums but could lead to a larger financial burden if you face a medical emergency.
Conversely, a lower deductible might provide peace of mind but come with higher monthly premiums.
Trade-offs in Deductible Selection
Choosing a higher or lower deductible involves trade-offs:
- Higher Deductible:A higher deductible usually translates to lower monthly premiums. This can be advantageous for individuals who are healthy and confident in their ability to pay a larger amount out-of-pocket in case of a medical emergency. However, it means you’ll need to cover more expenses before your insurance starts covering costs.
- Lower Deductible:A lower deductible means you’ll pay less out-of-pocket for medical expenses. This can be beneficial for individuals who are more risk-averse or have a history of frequent healthcare utilization. However, it typically comes with higher monthly premiums.
Assessing Personal Risk Tolerance and Financial Capacity
It’s essential to assess your personal risk tolerance and financial capacity when choosing a deductible. Consider these factors:
- Health History:If you have a history of chronic illnesses or frequent medical visits, a lower deductible might provide more financial security. However, if you’re generally healthy and have minimal healthcare needs, a higher deductible might be more cost-effective.
- Financial Stability:Evaluate your income, savings, and emergency fund. Can you afford to pay a larger deductible if needed? A higher deductible might save you money on premiums, but it could lead to financial strain if you face a significant medical expense.
- Future Healthcare Needs:Consider your future healthcare needs. Are you planning to start a family or anticipate needing more healthcare services in the coming years? If so, a lower deductible might be a better choice.
Deductibles and Preventive Care
Deductibles are a crucial aspect of health insurance plans, and understanding how they apply to preventive care services is essential for maximizing your health benefits. Preventive care services aim to prevent health issues before they arise, and they often come with special considerations regarding deductibles.
Deductibles and Preventive Care Services
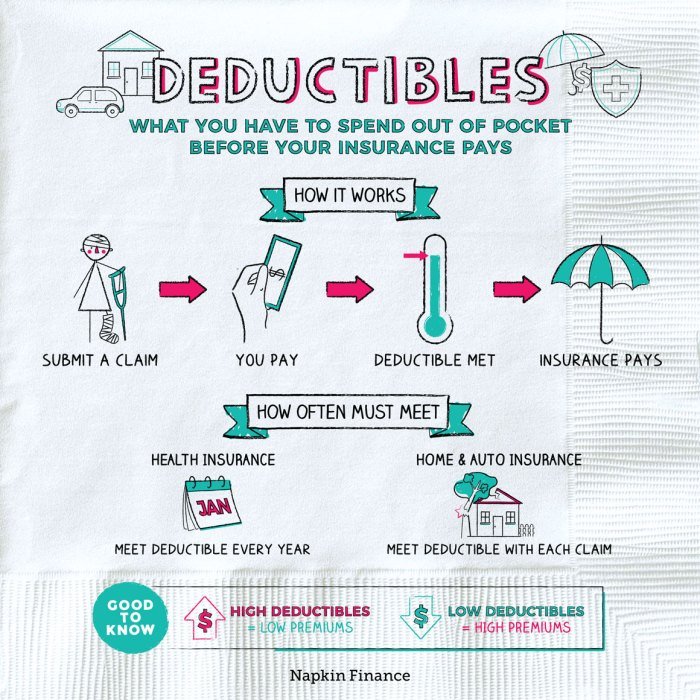
Preventive care services are generally designed to be accessible and affordable, and in many cases, they are exempt from deductibles. This means you may not have to pay anything out of pocket for these services, even if you haven’t met your deductible for the year.
Deductibles and Routine Checkups, Vaccinations, and Screenings
- Routine Checkups: These are typically covered without a deductible. This includes annual physical exams, well-woman visits, and routine checkups for children.
- Vaccinations: Most health insurance plans cover vaccinations without requiring you to meet your deductible. This includes vaccinations for common illnesses like influenza, measles, mumps, and rubella.
- Screenings: Many screenings, such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap tests, are also covered without a deductible. These screenings are essential for early detection of potential health issues.
Examples of Preventive Care Services Exempt from Deductibles
- Blood pressure checks
- Cholesterol screenings
- Diabetes screenings
- Cancer screenings
- Mental health screenings
Deductibles and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health savings accounts (HSAs) are tax-advantaged savings accounts available to individuals enrolled in high-deductible health insurance plans. HSAs offer a unique advantage in managing healthcare costs, particularly in relation to deductibles.
HSA Contributions and Deductible Payments
HSAs can be used to pay for deductible expenses, effectively reducing the out-of-pocket costs associated with healthcare services. Contributions to an HSA are made pre-tax, meaning you save on taxes and can accumulate funds to cover future medical expenses.
The funds can be withdrawn tax-free for qualified medical expenses, including deductible payments.
Example of Using an HSA to Pay Deductible Expenses
Imagine you have a high-deductible health insurance plan with a $2,000 deductible. You need to undergo a medical procedure that incurs $3,000 in expenses. Before the procedure, you have accumulated $1,500 in your HSA. You can use the $1,500 from your HSA to pay for the deductible, reducing your out-of-pocket cost to $500.
This demonstrates how an HSA can help you manage your healthcare costs, particularly the deductible portion.
Deductibles and Co-pays
Deductibles and co-pays are two key elements of health insurance plans that impact how much you pay for healthcare services. Understanding the difference between them and how they work together is essential for making informed decisions about your health insurance coverage.
Deductibles and Co-pays Explained
Deductibles and co-pays are both types of out-of-pocket expenses you pay for healthcare services. However, they differ in how they are applied:
- Deductible:A fixed amount you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance starts paying. Once you’ve met your deductible, your insurance company will typically cover a larger percentage of your medical expenses.
- Co-pay:A fixed amount you pay for specific medical services, such as doctor’s visits or prescriptions, regardless of whether you’ve met your deductible. Co-pays are usually a smaller amount than deductibles.
How Deductibles and Co-pays Work Together
Deductibles and co-pays work together to determine how much you pay for healthcare services. Here’s a breakdown:
You go to the doctor for a checkup. Your co-pay is $25. You then need to have surgery. Your insurance plan has a $1,000 deductible. You pay the $1,000 deductible for the surgery, and then your insurance covers the rest of the cost, except for any co-pays for follow-up appointments or prescriptions.
Example of Deductibles and Co-pays
Imagine you have a health insurance plan with a $1,000 deductible and a $25 co-pay for doctor’s visits. If you have a medical bill for $2,000, you would first pay the $1,000 deductible. Then, your insurance would cover the remaining $1,000, minus any applicable co-pays for services.
For example, if you had three doctor’s visits related to this medical issue, you would pay an additional $75 in co-pays ($25 per visit).
Deductibles and Out-of-Network Care

Your health insurance deductible applies to both in-network and out-of-network care, but the way it’s calculated and the potential costs can differ significantly. Out-of-network care, meaning services from providers not included in your insurance plan’s network, often comes with higher out-of-pocket costs.
A health insurance deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts covering costs. It’s like a barrier you need to overcome before your plan kicks in. If you’re interested in helping people navigate their mental health, consider pursuing online mental health nurse practitioner programs to become a qualified professional.
Once you’re a provider, you can help patients understand their insurance coverage, including deductibles, and guide them through the complexities of mental health care.
This is because your insurance company might not cover as much of the expenses, and you’ll likely face higher negotiated rates.
Out-of-Network Deductibles
When you receive out-of-network care, your insurance company might apply your deductible differently. Some plans may have a separate deductible for out-of-network services, meaning you’ll have to meet a separate threshold before your insurance starts covering any expenses. Other plans might combine your in-network and out-of-network deductibles, so you’ll be working towards a single total.
Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs
Out-of-network care can lead to significantly higher out-of-pocket costs due to:* Higher Negotiated Rates:Out-of-network providers can charge higher rates than in-network providers. Your insurance company might only cover a portion of these costs, leaving you with a larger balance to pay.
Limited Coverage
Your insurance plan may cover a smaller percentage of out-of-network expenses compared to in-network services. This means you’ll be responsible for a larger share of the costs.
Balance Billing
In some cases, out-of-network providers can “balance bill” you, meaning they can charge you the difference between their full fee and the amount your insurance company is willing to pay. This can lead to unexpected and substantial costs.
Navigating Out-of-Network Care
While out-of-network care often comes with higher costs, there are ways to navigate it more effectively and minimize expenses:* Check Your Plan:Before receiving out-of-network care, carefully review your insurance plan’s coverage for out-of-network services. Understand your deductible, copayments, and coinsurance rates for out-of-network services.
Get Pre-Authorization
In many cases, your insurance company may require pre-authorization for out-of-network care. This involves obtaining approval from your insurance company before receiving the service. Pre-authorization can help you avoid surprises and ensure your insurance will cover some of the costs.
Negotiate Rates
If you’re considering out-of-network care, try to negotiate rates with the provider. Some providers may be willing to negotiate a lower rate if you pay upfront or if you can provide proof of your insurance coverage.
Consider Alternatives
Before choosing out-of-network care, explore alternative options within your network. There might be qualified providers within your network who can offer similar services.
Know Your Rights
Be aware of your rights as a patient regarding out-of-network care. Your insurance company should provide information about your coverage and your rights under your plan.
Final Summary
Navigating health insurance can be complex, and understanding deductibles is essential. By understanding how deductibles work, you can make informed choices about your health insurance plan, manage your healthcare costs, and ensure you have the coverage you need. Remember to carefully consider your individual needs and financial situation when choosing a deductible amount.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a deductible affect my premium?
Generally, a higher deductible means a lower premium, and a lower deductible means a higher premium. It’s a trade-off between upfront costs and potential savings on future healthcare expenses.
What happens if I don’t meet my deductible?
You’ll be responsible for paying the full cost of your medical expenses until you reach your deductible. After you meet your deductible, your insurance will cover the remaining costs according to your plan’s coverage.
Are there any exceptions to deductibles?
Some preventive care services, like routine checkups and vaccinations, may be exempt from deductibles. Check your insurance plan for details.
Can I use a Health Savings Account (HSA) to pay my deductible?
Yes, you can use HSA funds to pay for deductible expenses. HSAs are tax-advantaged accounts specifically designed to help cover healthcare costs, including deductibles.