Mental Health America California is a vital organization dedicated to improving the lives of Californians by addressing mental health challenges. California faces a complex mental health landscape, marked by significant disparities in access to care and a growing need for support services.
This guide explores the current state of mental health in California, the role of Mental Health America, and the critical issues impacting the well-being of residents.
From analyzing the prevalence of mental health conditions across different demographics to examining the effectiveness of existing policies and programs, we delve into the key factors shaping mental health outcomes in the state. We also highlight the crucial work of advocacy groups and organizations that champion mental health awareness and advocate for policy change.
Mental Health Landscape in California

California is a state with a diverse population and a complex mental health landscape. It faces a range of challenges in providing adequate and accessible mental health care to its residents. This section will delve into the current state of mental health resources and services, explore the prevalence of mental health conditions across different demographics, and identify key disparities and challenges in accessing mental health care within the state.
Mental Health Resources and Services in California
California has a robust system of mental health resources and services, encompassing a wide range of options, including community mental health centers, hospitals, private practices, and telehealth services. The state has made significant investments in mental health services, including expanding access to Medicaid and increasing funding for community-based programs.
However, despite these efforts, there are still significant gaps in access to care, particularly for underserved populations.
Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions in California
Mental health conditions are prevalent in California, affecting individuals of all ages, races, ethnicities, and socioeconomic backgrounds. According to the California Mental Health Services Authority (MHSA), approximately one in five adults in California experiences a mental health condition each year.
Mental health conditions are often linked to social determinants of health, such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to education and employment.
Challenges and Disparities in Access to Mental Health Care
Access to mental health care in California is influenced by several factors, including socioeconomic status, geographic location, and insurance coverage. Some of the key challenges and disparities in access to mental health care include:
- Limited Access to Providers:There is a shortage of mental health providers in California, particularly in rural and underserved areas. This shortage can make it difficult for individuals to find a qualified provider who accepts their insurance.
- Insurance Coverage:Many individuals in California lack adequate insurance coverage for mental health services. While the state has expanded Medicaid coverage, there are still gaps in coverage, particularly for individuals with pre-existing conditions or who are uninsured.
- Stigma and Discrimination:Mental health stigma and discrimination can prevent individuals from seeking help. Individuals may fear being judged or discriminated against by their families, friends, employers, or communities.
- Cultural and Language Barriers:Cultural and language barriers can also hinder access to mental health care. Individuals who speak a language other than English or who have different cultural beliefs about mental health may face challenges in finding culturally competent providers and accessing services.
Mental Health America’s Role in California

Mental Health America (MHA) plays a vital role in advocating for and improving mental health in California. As the nation’s leading mental health advocacy organization, MHA California works tirelessly to ensure that all Californians have access to quality mental health care and support.
Initiatives and Programs
MHA California implements various initiatives and programs to address the mental health needs of Californians. These programs aim to raise awareness, reduce stigma, and provide support to individuals and communities struggling with mental health challenges.
- Mental Health First Aid Training:MHA California offers Mental Health First Aid training to individuals in communities across the state. This program teaches participants how to identify, understand, and respond to signs of mental health challenges in themselves and others. It equips individuals with the skills to provide initial support and guide individuals towards appropriate resources.
- Advocacy and Policy:MHA California actively advocates for policies that promote mental health and well-being. The organization works closely with policymakers at the state and local levels to ensure that mental health is a priority in legislative and budgetary decisions. This includes advocating for increased funding for mental health services, improved access to care, and the implementation of evidence-based practices.
- Public Education and Awareness Campaigns:MHA California conducts public education and awareness campaigns to reduce stigma associated with mental illness and promote mental health literacy. These campaigns utilize various media platforms, including social media, print materials, and community events, to educate the public about mental health conditions, available resources, and the importance of seeking help.
- Support Groups and Peer Support Programs:MHA California supports the development and expansion of support groups and peer support programs across the state. These programs provide individuals with mental health challenges a safe and supportive environment to connect with others who share similar experiences, build coping skills, and access resources.
Collaboration and Partnerships
MHA California recognizes the importance of collaboration and partnerships in achieving its mission. The organization works closely with a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Local Organizations:MHA California collaborates with local organizations, such as community mental health centers, non-profit organizations, and faith-based groups, to expand access to mental health services and support in communities across the state. This collaboration involves sharing resources, coordinating services, and advocating for common goals.
- Government Agencies:MHA California partners with state and local government agencies, including the California Department of Mental Health and county mental health departments, to ensure the effective implementation of mental health policies and programs. This collaboration includes providing technical assistance, advocating for funding, and monitoring the quality of mental health services.
- Healthcare Providers:MHA California works with healthcare providers, including physicians, nurses, and therapists, to improve the integration of mental health care into primary care settings. This collaboration involves educating healthcare providers about mental health conditions, promoting screening and early intervention, and advocating for better coordination of care.
Impact on Mental Health Outcomes
MHA California’s work has had a significant impact on improving mental health outcomes in California. The organization’s initiatives and programs have contributed to:
- Increased Awareness and Reduced Stigma:MHA California’s public education and awareness campaigns have helped to increase awareness of mental health conditions and reduce the stigma associated with seeking help. This has encouraged more individuals to reach out for support and seek professional help.
- Improved Access to Care:MHA California’s advocacy efforts have resulted in increased funding for mental health services and improved access to care for individuals with mental health challenges. This has enabled more Californians to receive the treatment they need.
- Enhanced Support Systems:MHA California’s support for support groups and peer support programs has provided individuals with mental health challenges a sense of community and belonging. These programs have empowered individuals to build coping skills, access resources, and navigate their mental health journeys.
Mental Health Policy and Legislation in California
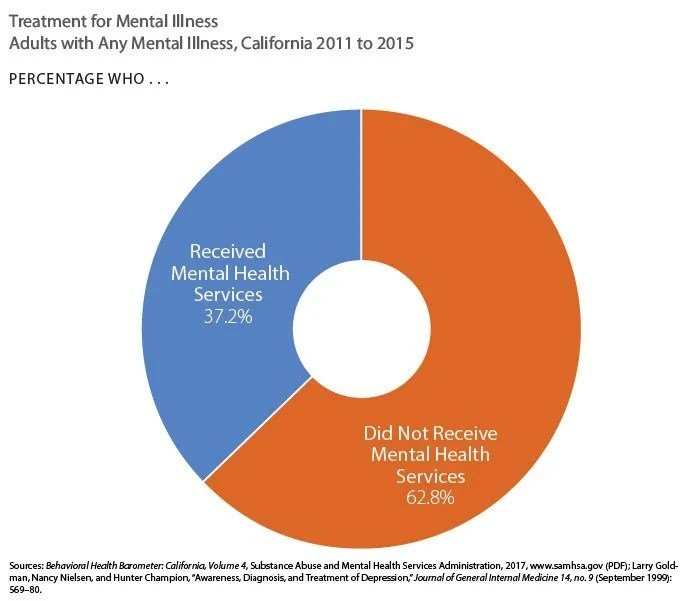
California has a long history of enacting legislation and policies aimed at improving mental health services and support. These efforts have been driven by a recognition of the significant burden of mental illness on individuals, families, and communities.
Mental Health Parity Laws
Mental health parity laws ensure that health insurance plans cover mental health and substance use disorder benefits at the same level as medical and surgical benefits. California was one of the first states to pass a mental health parity law in 1999, and has since strengthened these protections through subsequent legislation.
- The Mental Health Parity Act of 1999required health plans to provide mental health benefits that are comparable to medical and surgical benefits in terms of coverage, benefits, and treatment limitations.
- The Paul Wellstone and Pete Domenici Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008expanded these protections to include substance use disorder benefits.
These laws have helped to reduce disparities in access to mental health care by ensuring that individuals with mental illness have access to the same level of coverage as those with physical health conditions. However, some limitations remain, such as restrictions on coverage for out-of-network providers and limits on the number of therapy sessions.
Mental Health System Reform
California has undertaken significant efforts to reform its mental health system, aiming to create a more integrated and effective system of care.
- The Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) of 2004provided a dedicated funding stream for mental health services through a 1% tax on personal income. MHSA funding has been instrumental in expanding mental health services, including community-based programs, early intervention services, and crisis intervention services.
- The California Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) of 2004established a framework for local mental health planning and service delivery.
This legislation created Mental Health Boards in each county, responsible for overseeing the allocation of MHSA funds and ensuring that services meet the needs of the local community.
MHSA funding has also supported the development of innovative programs, such as Assertive Community Treatment (ACT) teams, which provide intensive, community-based services to individuals with severe mental illness. Despite these efforts, challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to services, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
Mental Health Prevention and Early Intervention
California has recognized the importance of preventing mental illness and intervening early to address mental health needs.
- The Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) of 2004includes funding for prevention and early intervention programs. These programs aim to promote mental health, build resilience, and reduce the risk of developing mental illness.
- The California Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) of 2004mandates that counties develop and implement mental health prevention and early intervention plans. These plans are intended to address specific needs in each community and promote early identification and treatment of mental health issues.
Prevention programs focus on factors that contribute to mental health, such as stress management, healthy coping skills, and social support. Early intervention programs aim to identify and support individuals who are experiencing early signs of mental illness.
Mental Health Workforce Development
California has faced a shortage of mental health professionals, which has limited access to care.
- The Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) of 2004includes funding for mental health workforce development initiatives. These initiatives aim to increase the number of qualified mental health professionals, particularly in underserved areas.
- The California Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) of 2004supports programs to train and support mental health professionals, including peer support specialists, who provide valuable services to individuals with mental illness.
These initiatives have helped to address the workforce shortage, but more efforts are needed to ensure that mental health professionals are available and accessible to all Californians.
Areas for Policy Improvement
While California has made significant strides in mental health policy, there are areas where further improvements are needed.
- Addressing the Mental Health Workforce Shortage: Continued efforts are needed to address the shortage of mental health professionals, particularly in underserved areas. This could include providing financial incentives for professionals to work in these areas, expanding training programs, and supporting the development of new models of care.
- Improving Access to Care: Many Californians still face barriers to accessing mental health care, such as long wait times, limited availability of services, and high costs. Policy improvements could focus on expanding access to affordable and culturally competent care, reducing wait times, and providing support for individuals who are navigating the mental health system.
- Enhancing Integration of Care: There is a need for better integration of mental health services with other healthcare systems, such as primary care and substance use disorder treatment. This could involve training primary care providers to screen for mental health issues, expanding mental health services in primary care settings, and developing seamless referral systems.
- Promoting Prevention and Early Intervention: California has made progress in prevention and early intervention, but more efforts are needed to address the root causes of mental illness and promote mental health at all ages. This could include expanding school-based mental health programs, supporting community-based prevention initiatives, and promoting public awareness of mental health issues.
These policy improvements would help to ensure that all Californians have access to the mental health services they need.
Mental Health Advocacy in California
Advocacy groups and organizations play a vital role in promoting mental health awareness and policy change in California. These groups employ a range of strategies to raise awareness, advocate for funding, and influence public opinion on mental health issues.
Mental Health America of California emphasizes the importance of overall well-being, recognizing that physical health is intertwined with mental health. A key aspect of this holistic approach is incorporating regular exercise, which can be achieved through various programs like the forever fitness initiative.
By promoting a balanced lifestyle that prioritizes both physical and mental wellness, Mental Health America of California strives to create a supportive environment for individuals to thrive.
Strategies Employed by Advocacy Groups
Advocacy groups in California utilize diverse strategies to advance mental health awareness and policy change. These strategies can be broadly categorized into:
- Public Education and Awareness Campaigns: These campaigns aim to destigmatize mental illness, educate the public about mental health conditions, and promote help-seeking behaviors. Advocacy groups use various mediums, including social media, public service announcements, and community events, to reach a broad audience.
- Lobbying and Policy Advocacy: Advocacy groups actively engage with policymakers at the state and local levels to advocate for legislation and policies that support mental health services and programs. This involves lobbying for increased funding, advocating for improved access to care, and promoting policies that address the root causes of mental health issues.
- Grassroots Organizing and Community Engagement: Advocacy groups mobilize community members to advocate for mental health issues. This can involve organizing rallies, protests, and letter-writing campaigns to raise awareness and pressure policymakers. They also work to build coalitions with other organizations and community leaders to amplify their message.
- Research and Data Analysis: Advocacy groups conduct research and collect data to inform their advocacy efforts. They analyze trends in mental health service utilization, identify gaps in care, and track the impact of policy changes on mental health outcomes. This evidence-based approach strengthens their advocacy efforts and provides policymakers with data to support policy decisions.
Effectiveness of Advocacy Efforts, Mental health america california
Advocacy efforts have had a significant impact on shaping mental health policy and practice in California. For example, advocacy groups have been instrumental in:
- Expanding Access to Mental Health Services: Advocacy groups have successfully lobbied for increased funding for mental health services, resulting in the expansion of community mental health centers, school-based mental health programs, and crisis intervention services.
- Promoting Mental Health Parity: Advocacy groups have played a key role in advocating for mental health parity laws, which require insurance plans to cover mental health services at the same level as physical health services.
- Addressing the Stigma of Mental Illness: Advocacy groups have launched public education campaigns to raise awareness about mental health conditions and challenge negative stereotypes. These campaigns have helped to destigmatize mental illness and encourage individuals to seek help.
Examples of Advocacy Groups in California
Several prominent advocacy groups in California are actively working to improve mental health services and outcomes. These include:
- Mental Health America of California: This organization advocates for policies that support mental health and well-being. They work to educate the public, promote mental health parity, and increase access to mental health services.
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) California: NAMI California provides support and advocacy for individuals and families affected by mental illness. They offer education, support groups, and advocacy programs to address the needs of the mental health community.
- The California Mental Health Services Authority (CalMHSA): CalMHSA is a state agency that provides funding and support for mental health services in California. They work with advocacy groups and other stakeholders to develop and implement mental health policies and programs.
Resources and Support for Mental Health in California
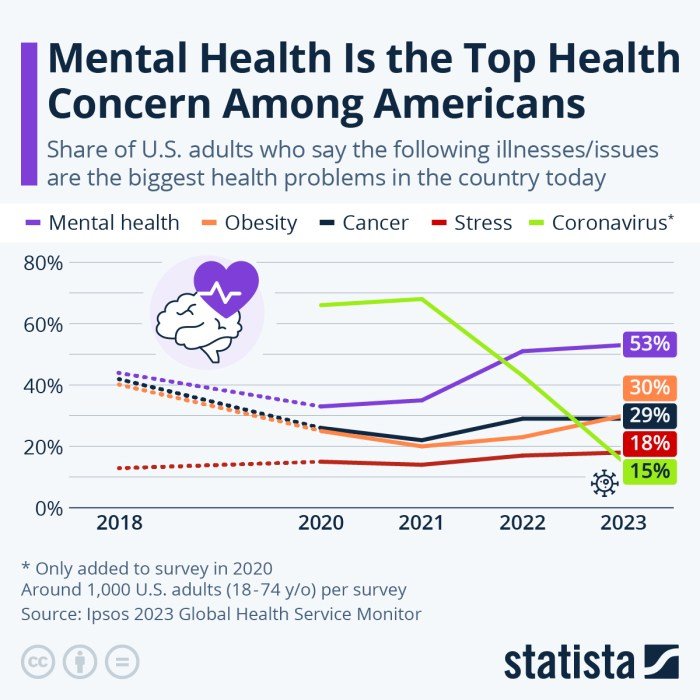
California offers a wide range of resources and support systems for individuals seeking mental health assistance. These resources cater to various needs and circumstances, ensuring access to appropriate care for all.
Crisis Hotlines
Crisis hotlines provide immediate support and resources for individuals experiencing a mental health crisis. They offer confidential and judgment-free support, connecting individuals with trained professionals who can provide guidance, resources, and referrals.
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline:988 – Provides 24/7 support for individuals in suicidal crisis or emotional distress.
- Crisis Text Line:Text HOME to 741741 – Offers free, 24/7 support through text messaging for individuals experiencing a mental health crisis.
- California Crisis Hotline:1-800-950-HOPE (4673) – Provides crisis counseling and referrals to mental health services for individuals in California.
Mental Health Clinics
Mental health clinics offer a range of services, including individual and group therapy, medication management, and case management. They provide comprehensive mental health care to individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
- California Mental Health Services Authority (CalMHSA): https://www.calmhsa.org/ – Offers a directory of mental health clinics and services across California.
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) California: https://www.namicalifornia.org/ – Provides support groups, education, and advocacy for individuals with mental illness and their families.
- Mental Health America (MHA) California: https://mha.org/california – Offers a range of resources and support services, including a directory of mental health providers and information on mental health conditions.
Support Groups
Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to connect with others who share similar experiences. They offer peer support, education, and resources for managing mental health challenges.
- NAMI California: https://www.namicalifornia.org/ – Offers a wide range of support groups for individuals with various mental health conditions and their families.
- Mental Health America (MHA) California: https://mha.org/california – Provides information on support groups and resources for individuals seeking peer support.
- The Trevor Project: https://www.thetrevorproject.org/ – Offers a crisis hotline and support services for LGBTQ youth experiencing mental health challenges.
Online Resources
Online resources provide a wealth of information, support, and tools for individuals seeking mental health information and support. They offer a convenient and accessible way to learn about mental health conditions, find resources, and connect with others.
- Mental Health America (MHA): https://mha.org/ – Offers a comprehensive website with information on mental health conditions, treatment options, and resources.
- National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): https://www.nimh.nih.gov/ – Provides research-based information on mental health conditions, treatments, and resources.
- Psychology Today: https://www.psychologytoday.com/ – Offers a directory of mental health professionals, articles on mental health topics, and information on mental health services.
Prevention and Early Intervention in California
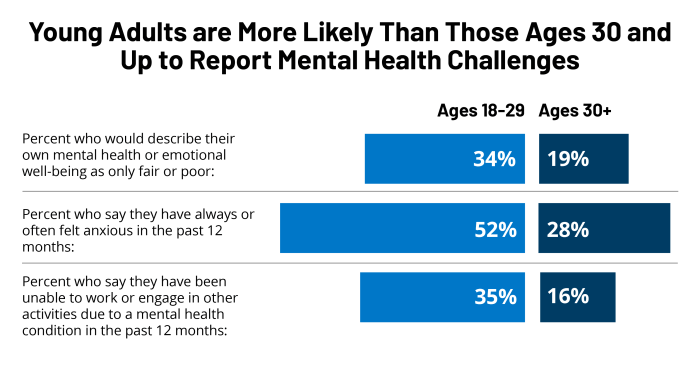
Mental health prevention and early intervention programs play a crucial role in California’s efforts to address the growing mental health crisis. By focusing on promoting mental well-being and addressing risk factors early on, these programs aim to prevent the development of mental health conditions and reduce the severity of existing conditions.
Effectiveness of Existing Initiatives
California has implemented a variety of prevention and early intervention initiatives, including school-based mental health programs, community-based support services, and public awareness campaigns. These programs have demonstrated some success in promoting mental health awareness, reducing stigma, and increasing access to care.
For example, the California Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) has funded a range of programs that provide early intervention services for children and youth, including mental health screenings, counseling, and support groups. These programs have been shown to improve mental health outcomes for children and youth, particularly those at risk for developing mental health conditions.
However, the effectiveness of these programs varies depending on factors such as program design, implementation, and funding. Some programs have been more successful than others in reaching their target populations and achieving desired outcomes.
Areas for Further Investment and Development
Despite the progress made, there are several areas where further investment and development are needed to enhance mental health prevention and early intervention efforts in California.
- Increased Funding:Many prevention and early intervention programs are underfunded, limiting their reach and effectiveness. Increased funding is needed to expand access to these programs and ensure they are adequately staffed and equipped to meet the needs of the population.
- Targeted Interventions:More targeted interventions are needed to address specific risk factors and populations. For example, programs that focus on early childhood development, substance abuse prevention, and suicide prevention can help to address key risk factors for mental health conditions.
- Improved Data Collection and Evaluation:Robust data collection and evaluation systems are needed to track the effectiveness of prevention and early intervention programs and identify areas for improvement. This information can be used to inform program design, implementation, and funding decisions.
- Increased Collaboration:Greater collaboration is needed between different sectors, including education, healthcare, and social services, to create a more comprehensive and integrated system of mental health prevention and early intervention services. This includes sharing data, coordinating services, and developing joint initiatives.
“Investing in mental health prevention and early intervention programs is not only the right thing to do, but it is also the smart thing to do. These programs can help to reduce the incidence of mental health conditions, improve the quality of life for individuals and families, and save money in the long run.”
Stigma and Discrimination in Mental Health

Mental health stigma and discrimination remain significant challenges in California, hindering individuals from seeking help and accessing necessary support. It’s essential to understand the prevalence and impact of stigma and discrimination, and how we can create a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with mental health conditions.
Prevalence and Impact of Stigma
Stigma and discrimination in mental health are widespread, impacting individuals in various ways. In California, the prevalence of mental health stigma is reflected in:
- Negative attitudes and beliefs:Many people still hold misconceptions about mental illness, associating it with weakness, dangerousness, or personal failure. This can lead to prejudice and discrimination, making individuals reluctant to seek help.
- Fear of judgment:The fear of being judged or discriminated against prevents many individuals from disclosing their mental health conditions to family, friends, or employers, hindering their ability to access support and resources.
- Social isolation:Stigma can lead to social isolation, as individuals may avoid social situations due to fear of being judged or discriminated against.
- Discrimination in employment, housing, and education:Individuals with mental health conditions may face discrimination in employment, housing, and education, further exacerbating their struggles and limiting their opportunities.
The impact of stigma and discrimination on individuals with mental health conditions is significant, leading to:
- Delayed help-seeking:Individuals may delay seeking help due to fear of judgment or discrimination, leading to worsening symptoms and increased risk of suicide.
- Non-adherence to treatment:Stigma can also lead to non-adherence to treatment, as individuals may feel ashamed or embarrassed to seek help.
- Reduced quality of life:Stigma can significantly impact individuals’ quality of life, leading to feelings of shame, isolation, and hopelessness.
Role of Education and Awareness Campaigns
Education and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in reducing stigma and promoting inclusivity. By promoting understanding and challenging misconceptions about mental illness, these initiatives can help create a more supportive environment for individuals with mental health conditions.
- Educating the public:Public education campaigns can raise awareness about mental health conditions, dispel myths, and promote understanding of the importance of seeking help.
- Sharing personal stories:Sharing personal stories of individuals with mental health conditions can help humanize the experience and challenge negative stereotypes.
- Promoting positive language:Encouraging the use of respectful and inclusive language when discussing mental health can help create a more supportive and understanding environment.
Cultural Sensitivity and Inclusivity
It is essential to consider cultural sensitivity and inclusivity when addressing mental health stigma and discrimination. Different cultures may have varying perceptions and attitudes towards mental illness, and it is crucial to recognize and respect these differences.
- Addressing cultural barriers:Organizations and communities need to address cultural barriers that may prevent individuals from seeking help, such as language differences, cultural beliefs, or lack of culturally appropriate services.
- Promoting culturally sensitive services:Providing culturally sensitive services that are tailored to the needs of diverse communities can help ensure that individuals feel comfortable and supported.
- Building trust and relationships:Building trust and relationships with diverse communities is essential to address stigma and discrimination effectively.
Community Initiatives and Organizational Efforts
Many communities and organizations in California are actively working to address stigma and discrimination related to mental health.
- Community-based mental health programs:Community-based mental health programs offer culturally sensitive services and support to individuals with mental health conditions, promoting access to care and reducing stigma.
- Peer support groups:Peer support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals with mental health conditions to connect with others who understand their experiences.
- Mental health awareness events:Mental health awareness events can raise awareness about mental health conditions, promote understanding, and encourage help-seeking.
- Anti-stigma campaigns:Anti-stigma campaigns aim to challenge negative stereotypes and promote positive attitudes towards mental health.
Mental Health and the Future of California: Mental Health America California
California is at a pivotal moment in its journey towards comprehensive mental health care. The state faces both challenges and opportunities in its pursuit of improved mental health outcomes for all residents. This section explores emerging trends and challenges in mental health care in California, examines the role of technology and innovation, and identifies key areas where the state can invest to achieve its goals.
Technology and Innovation in Mental Health
The rapid advancement of technology is transforming mental health care in California, creating opportunities for more accessible, personalized, and effective services. Technology plays a critical role in improving access to mental health care, particularly for underserved populations.
- Telehealth:Telehealth platforms allow individuals to connect with mental health professionals remotely, breaking down geographic barriers and increasing access to care, especially in rural areas. For example, the California Telehealth Network (CTN) provides telehealth services to underserved communities, including those in rural areas, and connects patients with mental health professionals via video conferencing, phone calls, and other technologies.
- Mobile Apps:Mobile applications offer self-management tools, mental health resources, and support networks, empowering individuals to take charge of their mental well-being. For example, the “Calm” and “Headspace” apps provide guided meditations, mindfulness exercises, and sleep aids. These apps can be especially helpful for individuals who may not feel comfortable seeking traditional mental health services.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI-powered tools are being used to personalize treatment plans, screen for mental health conditions, and provide support through chatbots and virtual assistants. For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide immediate support to individuals experiencing mental health crises, offering resources and guidance.
Community Engagement and Collaboration
Building a strong mental health system in California requires a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders. Community engagement plays a crucial role in ensuring that mental health services are responsive to the needs of diverse communities.
Mental Health America California provides valuable resources and support for individuals struggling with mental health challenges. It’s important to prioritize your well-being, and sometimes that means making changes to your routine. If your gym membership is no longer serving you, you can easily cancel it online by following the steps provided on this website: cancel planet fitness membership online.
Mental Health America California offers a variety of services, including support groups, counseling, and educational materials, to help individuals on their journey to wellness.
- Community-Based Organizations (CBOs):CBOs provide culturally competent mental health services and support to specific communities, fostering trust and engagement. For example, the Asian Pacific Islander Mental Health Association (APIMHA) offers culturally sensitive mental health services to the Asian American and Pacific Islander community.
- Schools:Schools are increasingly recognizing the importance of mental health and implementing programs to promote well-being and address mental health needs among students. For example, the California Department of Education has launched a comprehensive mental health initiative to support students’ mental health needs.
Mental Health America of California offers valuable resources and support for individuals facing mental health challenges. A healthy self-image is crucial for overall well-being, and understanding the connection between inner peace and outward appearance can be beneficial. Learning about the art of “blushing beauty,” as explored on this website , might offer insights into how to enhance self-confidence and cultivate a positive body image.
Ultimately, Mental Health America of California encourages individuals to prioritize their mental health and seek support when needed.
- Law Enforcement:Collaboration between law enforcement and mental health professionals is essential to address mental health crises and ensure appropriate responses. For example, the Crisis Intervention Team (CIT) program trains law enforcement officers to de-escalate situations involving individuals with mental illness.
Key Investment Areas for Mental Health in California
California has a unique opportunity to invest in initiatives that will significantly improve mental health outcomes for its residents. These investments should prioritize:
- Expanding Access to Care:Increasing the number of mental health professionals, particularly in underserved areas, is crucial to meet the growing demand for mental health services. California can invest in training programs to increase the workforce of mental health professionals and provide financial incentives to encourage professionals to work in underserved communities.
- Early Intervention and Prevention:Investing in early intervention and prevention programs can help identify mental health issues early on and reduce the severity of mental illness. This includes providing mental health screenings in schools, workplaces, and community settings.
- Integrating Mental Health into Primary Care:Integrating mental health services into primary care settings can help address mental health needs alongside physical health concerns. This approach can make mental health care more accessible and reduce stigma associated with seeking mental health services.
- Addressing Housing and Homelessness:Housing instability and homelessness are significant contributors to mental health issues. California can invest in affordable housing initiatives and programs that provide support services for individuals experiencing homelessness.
Last Word
The future of mental health in California depends on collaborative efforts, innovative solutions, and a commitment to addressing the unique needs of diverse communities. By understanding the challenges and opportunities facing the state, we can work together to create a more equitable and supportive system that prioritizes mental health for all Californians.
Top FAQs
What are some common mental health conditions in California?
Common mental health conditions in California include anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, and substance abuse. These conditions can affect people of all ages, backgrounds, and socioeconomic statuses.
How can I get help for mental health issues in California?
There are many resources available for individuals seeking mental health support in California. You can contact a crisis hotline, visit a mental health clinic, join a support group, or access online resources. The Mental Health America California website provides a comprehensive list of resources and contact information.
What is the role of Mental Health America in California?
Mental Health America California works to improve mental health outcomes by advocating for policy change, promoting mental health awareness, and providing resources and support services. They collaborate with local organizations, government agencies, and healthcare providers to address mental health challenges in the state.