Why health information management takes center stage? This field plays a crucial role in the efficient and effective delivery of healthcare. It’s the backbone of patient care, ensuring accurate and timely information is available to healthcare providers. This allows for informed decision-making, leading to better patient outcomes.
From managing patient records and ensuring data privacy to implementing electronic health records and navigating complex legal and ethical considerations, health information management professionals are essential in today’s healthcare landscape. They are the guardians of patient information, working behind the scenes to ensure the smooth flow of critical data that impacts patient care.
Importance of Health Information Management

Health information management (HIM) plays a crucial role in the healthcare delivery system, ensuring the accuracy, accessibility, and security of patient health information. It is a vital component of efficient and effective healthcare operations.
Impact of Accurate and Timely Health Information on Patient Care
Accurate and timely health information is fundamental to providing high-quality patient care. When healthcare providers have access to comprehensive and reliable patient data, they can make informed decisions about treatment plans, medication prescriptions, and overall patient management.
- Improved Diagnosis and Treatment:Accurate medical records allow healthcare providers to diagnose conditions more effectively and tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs.
- Reduced Medical Errors:Timely access to complete patient information minimizes the risk of medication errors, duplicate testing, and other medical mishaps.
- Enhanced Patient Safety:HIM professionals ensure the confidentiality and security of patient information, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration:Well-organized health information facilitates seamless communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and optimal patient outcomes.
Contributions of Health Information Management to Healthcare Quality and Efficiency
HIM professionals contribute significantly to healthcare quality and efficiency through various activities.
- Data Analysis and Reporting:HIM professionals analyze health information to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in healthcare delivery. This data is essential for quality assurance, performance monitoring, and decision-making.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:HIM professionals ensure compliance with various healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), by maintaining accurate and secure patient records. This protects patient privacy and ensures legal compliance.
- Cost Reduction:Efficient health information management systems can streamline administrative processes, reduce duplicate testing, and optimize resource allocation, leading to cost savings for healthcare organizations.
- Research and Public Health:De-identified patient data is used for research purposes, contributing to advancements in medical knowledge and public health initiatives.
Key Functions of Health Information Management Professionals

Health information management (HIM) professionals play a crucial role in the healthcare system, ensuring the accuracy, privacy, and security of patient health information. Their responsibilities extend beyond record-keeping, encompassing a wide range of activities that directly impact patient care, research, and public health.
HIM professionals are responsible for the entire lifecycle of health information, from its creation to its use and disposal. This includes collecting, organizing, analyzing, and protecting patient data. They work closely with healthcare providers, administrators, and other stakeholders to ensure that information is readily available when needed and that it meets the highest standards of quality and integrity.
Types of Health Information Management Professionals
The field of health information management encompasses a diverse range of professionals with specialized skills and responsibilities.
Here are some of the most common types of HIM professionals:
- Registered Health Information Technician (RHIT): RHITs are responsible for the day-to-day operations of health information departments, including chart preparation, coding, and data entry. They ensure the accuracy and completeness of patient records and assist with the release of health information.
- Registered Health Information Administrator (RHIA): RHIA’s are highly skilled professionals who oversee the entire health information management system. They develop and implement policies and procedures, manage staff, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. They also play a key role in data analysis, performance improvement, and research.
- Certified Health Data Analyst (CHDA): CHDAs are experts in data analysis and interpretation. They use their skills to extract meaningful insights from health information to improve patient care, identify trends, and support research initiatives. They also play a role in developing and implementing data quality programs.
- Certified Tumor Registrar (CTR): CTRs specialize in the collection and analysis of cancer data. They work in hospitals and cancer registries to ensure the accuracy and completeness of cancer information for research, surveillance, and public health purposes.
Contributions to Patient Safety and Privacy
HIM professionals contribute significantly to patient safety and privacy by ensuring the accuracy, accessibility, and security of health information.
Here are some examples of how HIM professionals contribute to patient safety and privacy:
- Accurate Coding and Data Entry: HIM professionals play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy of patient information by assigning codes to diagnoses, procedures, and medications. Accurate coding is essential for billing, research, and public health reporting. It also helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care.
- Security and Privacy of Health Information: HIM professionals are responsible for protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient information. They implement and maintain security protocols, train staff on privacy practices, and respond to data breaches. This ensures that patient information is protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Data Analysis and Performance Improvement: HIM professionals analyze health information to identify trends and patterns that can improve patient care. They use data to measure the effectiveness of treatments, identify areas for improvement, and track patient outcomes. This information helps healthcare providers make data-driven decisions to improve patient safety and quality of care.
Health Information Systems and Technology

Technology plays a crucial role in modern health information management, transforming how healthcare data is collected, stored, analyzed, and used. This integration has led to the development of sophisticated health information systems (HIS) that streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve patient care.
Types of Health Information Systems
Health information systems are designed to manage various aspects of healthcare operations. They can be broadly categorized into different types based on their specific functions.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs are digital versions of patient medical records that contain comprehensive health information, including medical history, medications, allergies, lab results, and imaging reports. They provide a centralized and readily accessible platform for healthcare providers to access and manage patient data.
- Patient Portals: Patient portals are secure online platforms that allow patients to access their health information, schedule appointments, request refills, and communicate with their healthcare providers. These portals empower patients to take an active role in managing their health.
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS): HIS are designed specifically for hospitals and encompass various modules to manage administrative, clinical, and financial operations. These systems streamline processes like patient registration, scheduling, billing, and inventory management.
- Practice Management Systems (PMS): PMS are used by physician offices and other healthcare practices to manage patient appointments, billing, and administrative tasks. These systems improve efficiency and simplify day-to-day operations.
- Clinical Data Warehouses: Clinical data warehouses collect and store large volumes of healthcare data from various sources, such as EHRs, lab systems, and billing systems. This data is then analyzed to identify trends, improve patient care, and support research.
Benefits of Electronic Health Records
EHRs offer numerous benefits for patients, healthcare providers, and the healthcare system as a whole.
- Improved Patient Care: EHRs provide healthcare providers with real-time access to comprehensive patient data, enabling them to make more informed decisions and provide more personalized care. The ability to track patient progress, monitor medication adherence, and identify potential risks helps to improve patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Efficiency: EHRs automate many administrative tasks, such as scheduling appointments, generating reports, and managing billing, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care. They also reduce the risk of errors associated with manual record-keeping.
- Increased Patient Engagement: Patient portals allow patients to actively participate in their healthcare by accessing their medical records, scheduling appointments, and communicating with their providers. This increased engagement can lead to better health outcomes.
- Reduced Costs: EHRs can help to reduce healthcare costs by streamlining processes, improving efficiency, and reducing errors. They can also facilitate better coordination of care, which can help to prevent unnecessary hospitalizations and readmissions.
Challenges of Implementing Electronic Health Records
While EHRs offer significant benefits, their implementation also presents challenges.
- High Initial Costs: The purchase, installation, and ongoing maintenance of EHR systems can be expensive. Smaller healthcare practices may struggle to afford the upfront costs, especially if they lack the resources to implement and maintain the systems effectively.
- Training and Support: Healthcare providers and staff need extensive training to learn how to use EHR systems effectively. Ongoing support is also essential to address technical issues and ensure that users are up-to-date on system updates and features.
- Data Security and Privacy: EHRs contain sensitive patient data, so it’s crucial to implement robust security measures to protect this information from unauthorized access. Data breaches can have serious consequences for patients and healthcare organizations.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that different EHR systems can communicate with each other is essential for seamless data exchange and patient care coordination. However, interoperability challenges remain a significant hurdle, particularly in fragmented healthcare systems.
Data Security and Privacy in Health Information Management

In today’s digital age, where healthcare data is increasingly stored and transmitted electronically, ensuring data security and privacy is paramount. Protecting patient health information is not only a legal requirement but also a moral obligation, fostering trust between patients and healthcare providers.
Importance of Data Security and Privacy in Healthcare
Data security and privacy in healthcare are crucial for several reasons.
- Patient Trust and Confidentiality:Patients entrust healthcare providers with sensitive personal information, expecting it to be kept confidential. Breaches of data security can erode this trust, leading to reluctance to seek care.
- Legal Compliance:Numerous laws and regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, govern the handling and protection of patient health information. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions.
- Financial Security:Data breaches can expose patients to identity theft and financial fraud. This can lead to significant financial losses for both individuals and healthcare organizations.
- Reputational Damage:Data breaches can severely damage the reputation of healthcare organizations, impacting patient trust and potentially leading to decreased revenue.
Legal and Ethical Considerations Related to Health Information Management
Healthcare organizations and professionals are bound by legal and ethical principles that dictate how they handle patient health information.
- HIPAA:The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient health information (PHI) in the United States. It defines the rules for collecting, using, disclosing, and securing PHI.
- Privacy and Confidentiality:Ethical guidelines emphasize the importance of maintaining patient privacy and confidentiality. Healthcare professionals have a moral obligation to protect patient information and ensure it is not disclosed without consent.
- Informed Consent:Patients have the right to be informed about how their health information is being used and to provide consent for its use and disclosure.
- Data Security and Breach Notification:Healthcare organizations are required to implement robust data security measures to protect PHI from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. In the event of a data breach, they must notify affected individuals and regulatory bodies.
Role of Health Information Management Professionals in Ensuring Patient Data Confidentiality
Health information management (HIM) professionals play a vital role in safeguarding patient data confidentiality.
- Data Security Policies and Procedures:HIM professionals are responsible for developing and implementing data security policies and procedures that comply with legal and ethical standards.
- Data Access Control:HIM professionals manage access to patient health information, ensuring that only authorized individuals can view or modify it. This involves implementing user authentication, access controls, and data encryption.
- Data Integrity and Accuracy:HIM professionals are responsible for ensuring the accuracy and completeness of patient health information. This involves data validation, error detection, and correction processes.
- Data Breach Response:In the event of a data breach, HIM professionals play a crucial role in coordinating the response, including notifying affected individuals, reporting the breach to regulatory authorities, and conducting investigations.
- Training and Education:HIM professionals provide training and education to healthcare staff on data security and privacy best practices.
Health Information Management in Different Healthcare Settings: Why Health Information Management
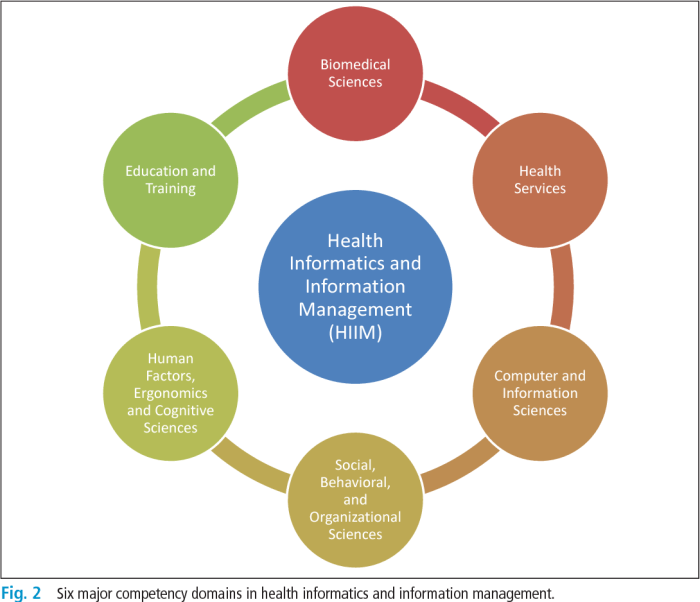
Health information management (HIM) plays a crucial role in various healthcare settings, adapting its practices and responsibilities to meet the specific needs of each environment. From hospitals to clinics and other healthcare facilities, HIM professionals ensure the accuracy, completeness, and security of patient health information, contributing significantly to the quality and efficiency of care delivery.
The Role of HIM in Different Healthcare Settings
The role of HIM professionals varies across different healthcare settings, reflecting the unique characteristics and demands of each environment.
- Hospitals: HIM professionals in hospitals are responsible for managing a vast amount of patient data, including medical records, billing information, and clinical data. They play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and completeness of patient records, facilitating patient care, and supporting research and quality improvement initiatives.
Health information management is a vital field that ensures the accuracy and accessibility of medical records, playing a crucial role in patient care and research. Staying active is a key component of overall health, and Planet Fitness offers a convenient and affordable option for achieving fitness goals.
Check out planet fitness coupons code to save on your membership and prioritize your well-being. With a robust health information management system in place, healthcare professionals can easily access patient data, including fitness information, to provide comprehensive and personalized care.
They also manage the hospital’s electronic health record (EHR) system, ensuring its functionality and security.
- Clinics: HIM professionals in clinics manage patient records, handle billing and coding, and ensure compliance with privacy regulations. They often work closely with physicians and other healthcare providers to ensure accurate documentation and efficient patient care. Due to the smaller size of clinics, HIM professionals may have a broader range of responsibilities, including data entry, record retrieval, and patient education.
- Other Healthcare Settings: HIM professionals also work in various other healthcare settings, such as long-term care facilities, home health agencies, and mental health clinics. Their responsibilities may include managing patient records, coding and billing, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. They may also be involved in data analysis and reporting, contributing to the overall improvement of patient care and operational efficiency.
Challenges and Opportunities in Different Healthcare Settings
HIM professionals face unique challenges and opportunities in different healthcare environments.
- Hospitals: HIM professionals in hospitals often face the challenge of managing large volumes of data and ensuring its accuracy and completeness. They also need to keep up with evolving regulations and technological advancements, such as the implementation of new EHR systems.
Health information management plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of healthcare systems, especially in a state like Texas. The Texas Health and Human Services Commissioner relies heavily on accurate and readily available health data to make informed decisions about public health programs and policies.
Ultimately, the efficiency and effectiveness of health information management directly impact the health and well-being of Texans.
However, hospitals offer HIM professionals opportunities to work in a complex and dynamic environment, contributing to the delivery of high-quality patient care and advancing the field of health information management.
- Clinics: HIM professionals in clinics may face challenges related to limited resources and staff, requiring them to be highly adaptable and efficient. They may also encounter challenges in maintaining patient confidentiality, especially in smaller clinics with limited privacy measures. However, clinics offer HIM professionals opportunities to build close relationships with patients and providers, playing a vital role in the patient care process.
- Other Healthcare Settings: HIM professionals in other healthcare settings may face challenges related to specialized patient populations and specific regulatory requirements. They may also need to adapt their practices to the unique needs of different facilities, such as long-term care facilities or home health agencies.
However, these settings offer HIM professionals opportunities to work in diverse and challenging environments, contributing to the improvement of patient care and the advancement of the healthcare field.
Variations in HIM Practices Across Different Healthcare Settings
HIM practices vary across different healthcare settings, reflecting the unique needs and characteristics of each environment.
- Recordkeeping Practices: Hospitals often have more complex recordkeeping systems due to the volume and complexity of patient data. Clinics may have simpler recordkeeping systems, while other healthcare settings may have specialized recordkeeping practices tailored to their specific patient population or services.
- Coding and Billing Practices: Hospitals and clinics typically have dedicated coding and billing departments, while other healthcare settings may have smaller teams or rely on external billing services. Coding and billing practices may also vary depending on the type of services provided and the patient population served.
- Technology Adoption: Hospitals are more likely to adopt advanced health information systems, such as EHRs and data analytics tools, compared to clinics and other healthcare settings. The adoption of technology varies depending on the size and resources of the healthcare setting.
The Future of Health Information Management

The field of health information management (HIM) is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing healthcare needs, and a growing emphasis on data security and privacy. As healthcare becomes increasingly complex and data-driven, HIM professionals play a critical role in ensuring the accuracy, accessibility, and security of patient information.
Health information management is a vital field, ensuring the accuracy and security of medical data. This crucial role extends beyond hospitals, as we see in the rise of online health and beauty platforms, like beauty store ulta , which collect and manage customer information for personalized recommendations and services.
The importance of health information management is evident in such diverse sectors, highlighting its impact on our daily lives.
Emerging Trends and Technologies, Why health information management
The future of HIM is shaped by several emerging trends and technologies that are transforming the way healthcare data is managed and utilized.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):AI and ML are revolutionizing healthcare by automating tasks, improving diagnostic accuracy, and personalizing treatment plans. HIM professionals will need to understand how these technologies are impacting data management and analysis. For example, AI-powered tools can be used to automate tasks such as coding and abstracting, freeing up HIM professionals to focus on more complex activities.
- Big Data Analytics:The volume of healthcare data is growing exponentially, creating opportunities for insights that can improve patient care and population health. HIM professionals will need to be skilled in data analytics to identify trends, patterns, and actionable insights from large datasets.
For example, analyzing data on patient demographics, diagnoses, and treatment outcomes can help healthcare organizations identify areas for improvement in care delivery.
- Cloud Computing:Cloud computing enables healthcare organizations to store and access patient data securely and efficiently from anywhere. HIM professionals will need to be familiar with cloud-based platforms and their implications for data management and security. For example, cloud-based electronic health record (EHR) systems can provide greater flexibility and scalability, allowing healthcare organizations to access patient data from multiple locations.
- Interoperability:The ability to share patient data seamlessly across different healthcare systems is essential for improving patient care and reducing healthcare costs. HIM professionals will need to understand interoperability standards and best practices to ensure that patient information can be exchanged securely and effectively.
For example, the adoption of FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) standards is facilitating data exchange between different healthcare systems.
- Blockchain Technology:Blockchain technology is emerging as a secure and transparent way to manage healthcare data. HIM professionals will need to understand how blockchain can be used to improve data integrity, security, and privacy. For example, blockchain can be used to track the movement of patient records, ensuring that they are not tampered with or accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Skills and Knowledge
To thrive in the future of HIM, professionals will need to develop a range of skills and knowledge.
- Data Analytics and Interpretation:HIM professionals will need to be able to analyze large datasets, identify trends, and draw meaningful conclusions. This requires proficiency in data mining, statistical analysis, and data visualization tools.
- Technology Proficiency:HIM professionals will need to be comfortable working with a variety of technologies, including EHR systems, data management platforms, and cloud-based applications. This requires a strong understanding of technology concepts and the ability to adapt to new technologies.
- Cybersecurity and Privacy:With the increasing volume and sensitivity of healthcare data, cybersecurity and privacy are paramount. HIM professionals will need to understand data security principles, best practices, and relevant regulations, such as HIPAA. This includes being able to identify and mitigate security risks, implement appropriate safeguards, and respond to data breaches.
- Communication and Collaboration:HIM professionals will need to effectively communicate with a variety of stakeholders, including patients, physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. This requires strong written and verbal communication skills, as well as the ability to work collaboratively in a team environment.
- Leadership and Project Management:HIM professionals will play a critical role in implementing new technologies and processes. They will need to be able to lead and manage projects, ensuring that they are completed on time and within budget.
Evolving Role of HIM Professionals
HIM professionals are evolving to meet the changing needs of healthcare.
- Data Stewards:HIM professionals are increasingly taking on the role of data stewards, ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and integrity of patient data. This involves developing and implementing data governance policies, ensuring compliance with regulations, and managing data quality initiatives.
- Data Analysts and Researchers:HIM professionals are using their data management skills to conduct data analysis and research, contributing to clinical decision-making, population health initiatives, and healthcare quality improvement efforts.
- Healthcare Informatics Specialists:HIM professionals are becoming more involved in healthcare informatics, working with clinical and administrative staff to design and implement data-driven solutions to improve patient care and operational efficiency.
- Patient Engagement Advocates:HIM professionals are playing a greater role in patient engagement, helping patients understand their health information and participate in their care. This includes educating patients about their rights and responsibilities regarding their health information.
Final Summary
As healthcare continues to evolve, the importance of health information management will only grow. The demand for skilled professionals in this field is high, and those who choose this career path will be at the forefront of innovation and change.
With the rise of technology, data analytics, and new regulations, health information management professionals will be critical in shaping the future of healthcare.
FAQ Compilation
What are the different types of health information management professionals?
There are various specializations within health information management, including Registered Health Information Technicians (RHIT), Registered Health Information Administrators (RHIA), and Certified Health Data Analysts (CHDA). Each role focuses on different aspects of managing health information.
What are the career prospects in health information management?
The job market for health information management professionals is strong, with a projected growth rate exceeding the average for all occupations. This field offers diverse career opportunities in hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and government agencies.
How can I become a health information management professional?
To become a health information management professional, you typically need a bachelor’s degree in health information management or a related field. You may also need to pass a certification exam to demonstrate your expertise.